|
Diphenyl Diselenide
Diphenyl diselenide is the chemical compound with the formula (C6H5)2Se2, abbreviated Ph2Se2. This orange-coloured solid is the oxidized derivative of benzeneselenol. It is used as a source of the PhSe unit in organic synthesis. Preparation and properties Ph2Se2 is prepared by the oxidation of benzeneselenoate, the conjugate base of benzeneselenol which is generated via the Grignard reagent: : PhMgBr + Se → PhSeMgBr :2 PhSeMgBr + Br2 → Ph2Se2 + 2 MgBr2 The molecule has idealized C2-symmetry, like hydrogen peroxide and related molecules. The Se-Se bond length of 2.29 Å the C-Se-Se-C dihedral angle is 82° and the C-Se-Se angles are near 110°. Antioxidant action "Dietary supplementation with Ph2Se2 prevented CH3HgCl-induced locomotor impairment. This effect appeared to be mediated by antioxidant action. Ph2Se2 may be a viable approach to prevention or reduction CH3HgCl-mediated neurotoxic effects." The protective effects of diphenyl diselenide against methy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dichloromethane
Dichloromethane (DCM or methylene chloride, methylene bichloride) is an organochlorine compound with the formula . This colorless, volatile liquid with a chloroform-like, sweet odour is widely used as a solvent. Although it is not miscible with water, it is slightly polar, and miscible with many organic solvents.Rossberg, M. ''et al.'' (2006) "Chlorinated Hydrocarbons" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. . Occurrence Natural sources of dichloromethane include oceanic sources, macroalgae, wetlands, and volcanoes. However, the majority of dichloromethane in the environment is the result of industrial emissions. Production DCM is produced by treating either chloromethane or methane with chlorine gas at 400–500 °C. At these temperatures, both methane and chloromethane undergo a series of reactions producing progressively more chlorinated products. In this way, an estimated 400,000 tons were produced in the US, Europe, and Japan in 1993. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epoxide
In organic chemistry, an epoxide is a cyclic ether () with a three-atom ring. This ring approximates an equilateral triangle, which makes it strained, and hence highly reactive, more so than other ethers. They are produced on a large scale for many applications. In general, low molecular weight epoxides are colourless and nonpolar, and often volatile. Nomenclature A compound containing the epoxide functional group can be called an epoxy, epoxide, oxirane, and ethoxyline. Simple epoxides are often referred to as oxides. Thus, the epoxide of ethylene (C2H4) is ethylene oxide (C2H4O). Many compounds have trivial names; for instance, ethylene oxide is called "oxirane". Some names emphasize the presence of the epoxide functional group, as in the compound ''1,2-epoxyheptane'', which can also be called ''1,2-heptene oxide''. A polymer formed from epoxide precursors is called an ''epoxy'', but such materials do not contain epoxide groups (or contain only a few residual epoxy grou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahedron (journal)
''Tetrahedron'' is a weekly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering the field of organic chemistry. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', ''Tetrahedron'' has a 2020 impact factor of 2.457. ''Tetrahedron'' and Elsevier, its publisher, support an annual symposium. In 2010, complaints were raised over its high subscription cost. Notable papers , the Web of Science lists ten papers from ''Tetrahedron'' that have more than 1000 citations. The four articles that have been cited more than 2000 times are: * – cited 2228 times * – cited 2162 times * – cited 2124 times * – cited 2107 times See also * ''Tetrahedron Letters'' * ''Tetrahedron Computer Methodology'' * ''Polyhedron In geometry, a polyhedron (plural polyhedra or polyhedrons; ) is a three-dimensional shape with flat polygonal faces, straight edges and sharp corners or vertices. A convex polyhedron is the convex hull of finitely many points, not all on th ...'' (journal) Refere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Reactions
Organic reactions are chemical reactions involving organic compounds. The basic organic chemistry reaction types are addition reactions, elimination reactions, substitution reactions, pericyclic reactions, rearrangement reactions, photochemical reactions and redox reactions. In organic synthesis, organic reactions are used in the construction of new organic molecules. The production of many man-made chemicals such as drugs, plastics, food additives, fabrics depend on organic reactions. The oldest organic reactions are combustion of organic fuels and saponification of fats to make soap. Modern organic chemistry starts with the Wöhler synthesis in 1828. In the history of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry awards have been given for the invention of specific organic reactions such as the Grignard reaction in 1912, the Diels-Alder reaction in 1950, the Wittig reaction in 1979 and olefin metathesis in 2005. Classifications Organic chemistry has a strong tradition of naming a specific reac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbonyl Compound
In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group is a functional group composed of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom: C=O. It is common to several classes of organic compounds, as part of many larger functional groups. A compound containing a carbonyl group is often referred to as a carbonyl compound. The term carbonyl can also refer to carbon monoxide as a ligand in an inorganic or organometallic complex (a metal carbonyl, e.g. nickel carbonyl). The remainder of this article concerns itself with the organic chemistry definition of carbonyl, where carbon and oxygen share a double bond. Carbonyl compounds In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group characterizes the following types of compounds: Other organic carbonyls are urea and the carbamates, the derivatives of acyl chlorides chloroformates and phosgene, carbonate esters, thioesters, lactones, lactams, hydroxamates, and isocyanates. Examples of inorganic carbonyl compounds are carbon dioxide and carbonyl sulfide. A sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of The American Chemical Society
The ''Journal of the American Chemical Society'' is a weekly peer-reviewed scientific journal that was established in 1879 by the American Chemical Society. The journal has absorbed two other publications in its history, the ''Journal of Analytical and Applied Chemistry'' (July 1893) and the ''American Chemical Journal'' (January 1914). It covers all fields of chemistry. Since 2021, the editor-in-chief is Erick M. Carreira (ETH Zurich). In 2014, the journal moved to a hybrid open access publishing model. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in Chemical Abstracts Service, Scopus, EBSCO databases, ProQuest databases, Index Medicus/MEDLINE/PubMed, and the Science Citation Index Expanded. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor of 16.383. Editors-in-chief The following people are or have been editor-in-chief: * 1879–1880 – Hermann Endemann * 1880–1881 – Gideon E. Moore * 1881–1882 – Hermann Endemann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactam
A lactam is a cyclic amide, formally derived from an amino alkanoic acid. The term is a portmanteau of the words ''lactone'' + ''amide''. Nomenclature Greek prefixes in alphabetical order indicate ring size: * α-Lactam (3-atom rings) * β-Lactam (4-atom rings) * γ-Lactam (5-atom rings) * δ-Lactam (6-atom rings) * ε-Lactam (7-atom rings) This ring-size nomenclature stems from the fact that a hydrolyzed α-Lactam leads to an α-amino acid and a β-Lactam to a β-amino acid, ''etc''. Synthesis General synthetic methods exist for the organic synthesis of lactams. Beckmann rearrangement Lactams form by the acid-catalyzed rearrangement of oximes in the Beckmann rearrangement. Schmidt reaction Lactams form from cyclic ketones and hydrazoic acid in the Schmidt reaction. Cyclization of amino acids Lactams can be formed from cyclisation of amino acids via the coupling between an amine and a carboxylic acid within the same molecule. Lactamization is most efficient in this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group (these may respectively be called alkylamines and arylamines; amines in which both types of substituent are attached to one nitrogen atom may be called alkylarylamines). Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines, trimethylamine, and aniline; Inorganic derivatives of ammonia are also called amines, such as monochloramine (). The substituent is called an amino group. Compounds with a nitrogen atom attached to a carbonyl group, thus having the structure , are called amides and have different chemical properties from amines. Classification of amines Amines can be classified according to the nature and number of substituents on nitrogen. Aliphatic amines contain only H and alkyl substituents. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene is often used as synonym of olefin, that is, any hydrocarbon containing one or more double bonds.H. Stephen Stoker (2015): General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry'. 1232 pages. Two general types of monoalkenes are distinguished: terminal and internal. Also called α-olefins, terminal alkenes are more useful. However, the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) recommends using the name "alkene" only for acyclic hydrocarbons with just one double bond; alkadiene, alkatriene, etc., or polyene for acyclic hydrocarbons with two or more double bonds; cycloalkene, cycloalkadiene, etc. for cyclic ones; and "olefin" for the general class – cyclic or acyclic, with one or more double bonds. Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups (also known as mono-enes) form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula with '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organolithium Reagent
In organometallic chemistry, organolithium reagents are chemical compounds that contain carbon–lithium (C–Li) bonds. These reagents are important in organic synthesis, and are frequently used to transfer the organic group or the lithium atom to the substrates in synthetic steps, through nucleophilic addition or simple deprotonation. Organolithium reagents are used in industry as an initiator for anionic polymerization, which leads to the production of various elastomers. They have also been applied in asymmetric synthesis in the pharmaceutical industry. Due to the large difference in electronegativity between the carbon atom and the lithium atom, the C−Li bond is highly ionic. Owing to the polar nature of the C−Li bond, organolithium reagents are good nucleophiles and strong bases. For laboratory organic synthesis, many organolithium reagents are commercially available in solution form. These reagents are highly reactive, and are sometimes pyrophoric. History and dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
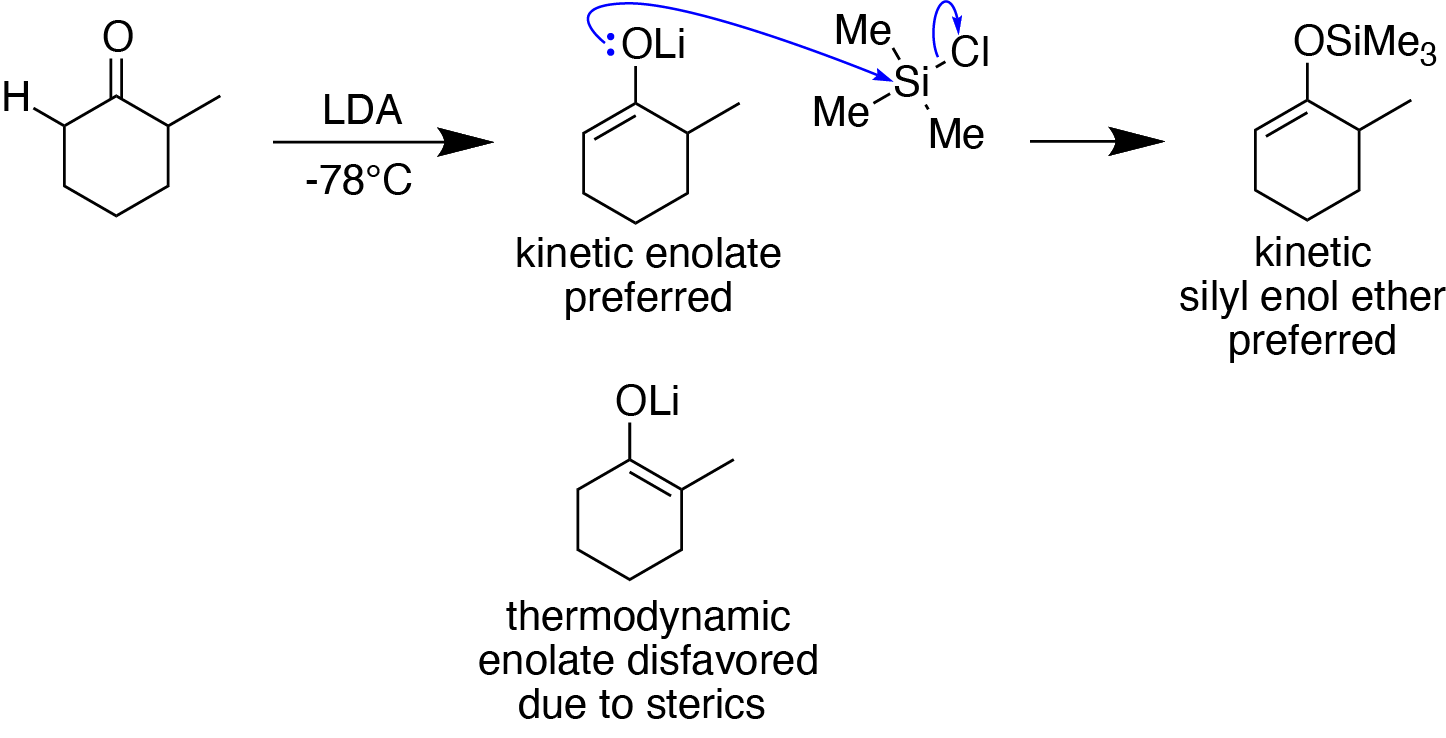
Enol Silyl Ethers
Silyl enol ethers in organic chemistry are a class of organic compounds that share a common functional group composed of an enolate bonded through its oxygen end to an organosilicon group. They are important intermediates in organic synthesis. Synthesis Silyl enol ethers are generally prepared by reacting an enolizable carbonyl compound with a silyl electrophile and a base, or just reacting an enolate with a silyl electrophile.Clayden, J., Greeves, N., & Warren, S. (2012). Silyl enol ethers. In ''Organic chemistry'' (Second ed., pp. 466-467). Oxford University Press. Since silyl electrophiles are hard and silicon-oxygen bonds are very strong, the oxygen (of the carbonyl compound or enolate) acts as the nucleophile to form a Si-O single bond. The most commonly used silyl electrophile is trimethylsilyl chloride. To increase the rate of reaction, trimethylsilyl triflate may also be used in the place of trimethylsilyl chloride as a more electrophilic substrate. When using an uns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |