 |
Dihedral (aeronautics)
In aeronautics, dihedral is the angle between the left and right wings (or tail surfaces) of an aircraft. "Dihedral" is also used to describe the effect of sideslip on the rolling of the aircraft. Dihedral angle is the upward angle from horizontal of the wings or tailplane of a fixed-wing aircraft. "Anhedral angle" is the name given to negative dihedral angle, that is, when there is a ''downward'' angle from horizontal of the wings or tailplane of a fixed-wing aircraft. Dihedral angle has a strong influence on dihedral effect, which is named after it. Dihedral effect is the amount of roll moment produced in proportion to the amount of sideslip. Dihedral effect is a critical factor in the stability of an aircraft about the roll axis (the spiral mode). It is also pertinent to the nature of an aircraft's Dutch roll oscillation and to maneuverability about the roll axis. Longitudinal dihedral is a comparatively obscure term related to the pitch axis of an airplane. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Dihedral On A TUI Boeing 737-800 (G-TAWJ) Taxying For Take Off At Bristol Airport, England 14May2019 , a geometric shape
{{d ...
Dihedral or polyhedral may refer to: * Dihedral angle, the angle between two mathematical planes * Dihedral (aeronautics), the upward angle of a fixed-wing aircraft's wings where they meet at the fuselage, dihedral ''effect'' of an aircraft, longitudinal dihedral angle of a fixed-wing aircraft * Dihedral group, the group of symmetries of the ''n''-sided polygon in abstract algebra ** Also Dihedral symmetry in three dimensions * Dihedral kite, also known as a bowed kite * Dihedral doors, also known as butterfly doors * Dihedral prime, also known as a dihedral calculator prime * In rock climbing, an inside corner of rock See also * Anhedral (other) * Euhedral, a crystal structure * Polyhedron In geometry, a polyhedron (plural polyhedra or polyhedrons; ) is a three-dimensional shape with flat polygonal faces, straight edges and sharp corners or vertices. A convex polyhedron is the convex hull of finitely many points, not all on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Sideslip
A slip is an aerodynamic state where an aircraft is moving ''somewhat'' sideways as well as forward relative to the oncoming airflow or relative wind. In other words, for a conventional aircraft, the nose will be pointing in the opposite direction to the bank of the wing(s). The aircraft is not in coordinated flight and therefore is flying inefficiently. Background Flying in a slip is aerodynamically inefficient, since the lift-to-drag ratio is reduced. More drag is at play consuming energy but not producing lift. Inexperienced or inattentive pilots will often enter slips unintentionally during turns by failing to coordinate the aircraft with the rudder. Airplanes can readily enter into a slip climbing out from take-off on a windy day. If left unchecked, climb performance will suffer. This is especially dangerous if there are nearby obstructions under the climb path and the aircraft is underpowered or heavily loaded. A slip can also be a ''piloting maneuver'' where the pilot d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Yaw Rate
A yaw rotation is a movement around the yaw axis of a rigid body that changes the direction it is pointing, to the left or right of its direction of motion. The yaw rate or yaw velocity of a car, aircraft, projectile or other rigid body is the angular velocity of this rotation, or rate of change of the heading angle when the aircraft is horizontal. It is commonly measured in degrees per second or radians per second. Another important concept is the yaw moment, or yawing moment, which is the component of a torque about the yaw axis. Measurement Yaw velocity can be measured by measuring the ground velocity at two geometrically separated points on the body, or by a gyroscope, or it can be synthesized from accelerometers and the like. It is the primary measure of how drivers sense a car's turning visually. It is important in electronic stabilized vehicles. The yaw rate is directly related to the lateral acceleration of the vehicle turning at constant speed around a constant radiu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Drop Tank
In aviation, a drop tank (external tank, wing tank or belly tank) is used to describe auxiliary fuel tanks externally carried by aircraft. A drop tank is expendable and often capable of being jettisoned. External tanks are commonplace on modern military aircraft A military aircraft is any fixed-wing or rotary-wing aircraft that is operated by a legal or insurrectionary armed service of any type. Military aircraft can be either combat or non-combat: * Combat aircraft are designed to destroy enemy equi ... and occasionally found in civilian ones, although the latter are less likely to be discarded except in an emergency. Overview The primary disadvantage with drop tanks is that they impose a drag penalty on the aircraft. External fuel tanks will also increase the moment of inertia, thereby reducing Flight dynamics, roll rates for Air combat manoeuvring, air maneuvers. Some of the drop tank's fuel is used to overcome the added drag and weight of the tank. Drag in this sen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Materiel
Materiel (; ) refers to supplies, equipment, and weapons in military supply-chain management, and typically supplies and equipment in a commercial supply chain context. In a military context, the term ''materiel'' refers either to the specific needs (excluding manpower) of a force to complete a specific mission, or the general sense of the needs (excluding manpower) of a functioning army. An important category of materiel is commonly referred to as ordnance, especially concerning mounted guns (artillery) and the shells it consumes. Along with fuel, and munitions in general, the steady supply of ordnance is an ongoing logistic challenge in active combat zones. Materiel management consists of continuing actions relating to planning, organizing, directing, coordinating, controlling, and evaluating the application of resources to ensure the effective and economical support of military forces. It includes provisioning, cataloging, requirements determination, acquisition, di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Swept-wing
A swept wing is a wing that angles either backward or occasionally Forward-swept wing, forward from its root rather than in a straight sideways direction. Swept wings have been flown since the pioneer days of aviation. Wing sweep at high speeds was first investigated in Germany as early as 1935 by Albert Betz and Adolph Busemann, finding application just before the end of the Second World War. It has the effect of delaying the shock waves and accompanying aerodynamic drag rise caused by fluid compressibility near the speed of sound, improving performance. Swept wings are therefore almost always used on jet aircraft designed to fly at these speeds. The term "swept wing" is normally used to mean "swept back", but variants include forward-swept wing, forward sweep, Variable-sweep wing, variable sweep wings and oblique wings in which one side sweeps forward and the other back. The delta wing is also aerodynamically a form of swept wing. Reasons for sweep There are three main reasons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
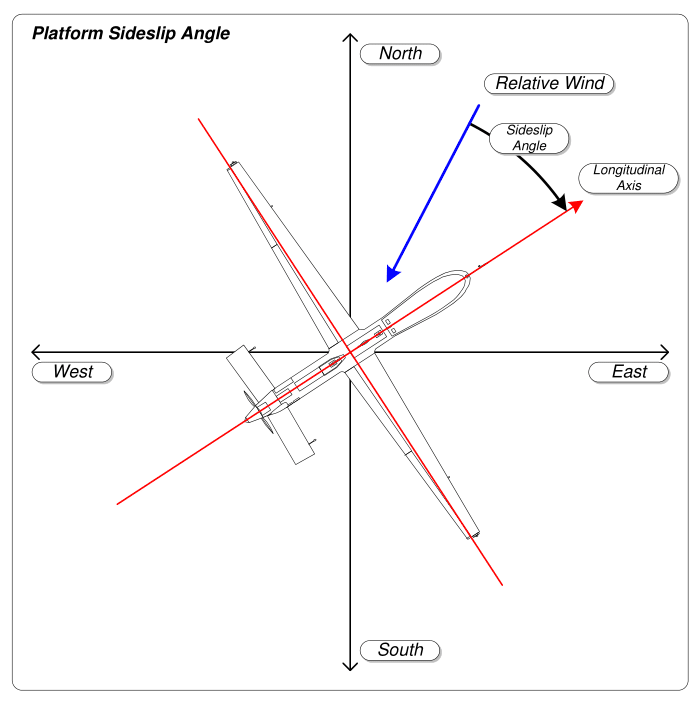
Sideslip Angle
A slip is an aerodynamic state where an aircraft is moving ''somewhat'' sideways as well as forward relative to the oncoming airflow or relative wind. In other words, for a conventional aircraft, the nose will be pointing in the opposite direction to the bank of the wing(s). The aircraft is not in coordinated flight and therefore is flying inefficiently. Background Flying in a slip is aerodynamically inefficient, since the lift-to-drag ratio is reduced. More drag is at play consuming energy but not producing lift. Inexperienced or inattentive pilots will often enter slips unintentionally during turns by failing to coordinate the aircraft with the rudder. Airplanes can readily enter into a slip climbing out from take-off on a windy day. If left unchecked, climb performance will suffer. This is especially dangerous if there are nearby obstructions under the climb path and the aircraft is underpowered or heavily loaded. A slip can also be a ''piloting maneuver'' where the pilot de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Dynamic Pressure
In fluid dynamics, dynamic pressure (denoted by or and sometimes called velocity pressure) is the quantity defined by:Clancy, L.J., ''Aerodynamics'', Section 3.5 :q = \frac\rho\, u^2 where (in SI units): * is the dynamic pressure in pascals (i.e., kg/ m⋅ s2), * is the fluid mass density (e.g. in kg/m3), and * is the flow speed in m/s. It can be thought of as the fluid's kinetic energy per unit volume. For incompressible flow, the dynamic pressure of a fluid is the difference between its total pressure and static pressure. From Bernoulli's law, dynamic pressure is given by : p_0 - p_\text = \frac\rho\, u^2 where and are the total and static pressures, respectively. Physical meaning Dynamic pressure is the kinetic energy per unit volume of a fluid. Dynamic pressure is one of the terms of Bernoulli's equation, which can be derived from the conservation of energy for a fluid in motion. It can also appear as a term in the incompressible Navier-Stokes equation whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Stability Derivatives
Stability derivatives, and also control derivatives, are measures of how particular forces and moments on an aircraft change as other parameters related to stability change (parameters such as airspeed, altitude, angle of attack, etc.). For a defined "trim" flight condition, changes and oscillations occur in these parameters. ''Equations of motion'' are used to analyze these changes and oscillations. Stability and control derivatives are used to linearize (simplify) these equations of motion so the stability of the vehicle can be more readily analyzed. Stability and control derivatives change as flight conditions change. The collection of stability and control derivatives as they change over a range of flight conditions is called an aero model. Aero models are used in engineering flight simulators to analyze stability, and in real-time flight simulators for training and entertainment. ''Stability'' derivative vs. ''control'' derivative ''Stability'' derivatives and ''control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Her Majesty's Stationery Office
The Office of Public Sector Information (OPSI) is the body responsible for the operation of His Majesty's Stationery Office (HMSO) and of other public information services of the United Kingdom. The OPSI is part of the National Archives of the United Kingdom and is responsible for Crown copyright. The OPSI announced on 21 June 2006 that it was merging with the National Archives. The merger took place in October 2006. The OPSI continues to discharge its roles and responsibilities from within the structure of the National Archives. Controller of HMSO and Director of OPSI The Controller of HMSO is also the Director of OPSI. HMSO continues to operate from within the expanded remit of OPSI. The Controller of HMSO also holds the offices of Kings's Printer of Acts of Parliament, King's Printer for Scotland and Government Printer for Northern Ireland. By virtue of holding these offices OPSI publishes, through HMSO, the '' London Gazette'', '' Edinburgh Gazette'', '' Belfast Gazette' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Charles Harvard Gibbs-Smith
Charles Harvard Gibbs-Smith (22 March 1909 – 3 December 1981)Charles Gibbs-Smith, famous people from Teddington at Information Britain web site was a British polymath historian of aeronautics and aviation. His obituary in '' The Times'' described him as "the recognised authority on the early development of flying in Europe and America" called him "The greatest of all historians of early aviation". Biography [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Sir George Cayley
Sir George Cayley, 6th Baronet (27 December 1773 – 15 December 1857) was an English engineer, inventor, and aviator. He is one of the most important people in the history of aeronautics. Many consider him to be the first true scientific aerial investigator and the first person to understand the underlying principles and forces of flight and the first man to create the wire wheel. * * * In 1799, he set forth the concept of the modern aeroplane as a fixed-wing flying machine with separate systems for lift, propulsion, and control. He was a pioneer of aeronautical engineering and is sometimes referred to as "the father of aviation." He identified the four forces which act on a heavier-than-air flying vehicle: weight, lift, drag and thrust. Modern aeroplane design is based on those discoveries and on the importance of cambered wings, also proposed by Cayley. He constructed the first flying model aeroplane and also diagrammed the elements of vertical flight. He also designe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |