|
Digital Broadcasting
Digital broadcasting is the practice of using digital signals rather than analogue signals for broadcasting over radio frequency bands. Digital television broadcasting (especially satellite television) is widespread. Digital audio broadcasting is being adopted more slowly for radio broadcasting where it is mainly used in Satellite radio. Digital links, thanks to the use of data compression, generally have greater spectral efficiency than analog links. Content providers can provide more services or a higher-quality signal than was previously available. It is estimated that the share of digital broadcasting increased from 7% of the total amount of broadcast information in 2000, to 25% in 2007. Some countries have completed a Digital television transition. See also *Digital radio *Digital television *ATSC Standards * ATSC tuner *Digital Audio Broadcasting *Digital Radio Mondiale *Digital Video Broadcasting *HD Radio *Satellite radio *Satellite television Satellite television i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Television
Digital television (DTV) is the transmission of television signals using digital encoding, in contrast to the earlier analog television technology which used analog signals. At the time of its development it was considered an innovative advancement and represented the first significant evolution in television technology since color television in the 1950s. Modern digital television is transmitted in high-definition television (HDTV) with greater resolution than analog TV. It typically uses a widescreen aspect ratio (commonly 16:9) in contrast to the narrower format of analog TV. It makes more economical use of scarce radio spectrum space; it can transmit up to seven channels in the same bandwidth as a single analog channel, and provides many new features that analog television cannot. A transition from analog to digital broadcasting began around 2000. Different digital television broadcasting standards have been adopted in different parts of the world; below are the more wid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
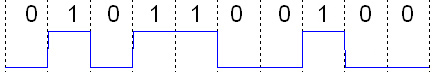
Digital Signal
A digital signal is a signal that represents data as a sequence of discrete values; at any given time it can only take on, at most, one of a finite number of values. This contrasts with an analog signal, which represents continuous values; at any given time it represents a real number within a continuous range of values. Simple digital signals represent information in discrete bands of analog levels. All levels within a band of values represent the same information state. In most digital circuits, the signal can have two possible valid values; this is called a binary signal or logic signal. They are represented by two voltage bands: one near a reference value (typically termed as ''ground'' or zero volts), and the other a value near the supply voltage. These correspond to the two values "zero" and "one" (or "false" and "true") of the Boolean domain, so at any given time a binary signal represents one binary digit (bit). Because of this discretization, relatively small c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Television Transition
The digital television transition, also called the digital switchover (DSO), the analogue switch/sign-off (ASO), the digital migration, or the analogue shutdown, is the process in which older analogue television broadcasting technology is converted to and replaced by digital television. Conducted by individual nations on different schedules, this primarily involves the conversion of analogue terrestrial television broadcasting infrastructure to digital terrestrial (DTT), a major benefit being extra frequencies on the radio spectrum and lower broadcasting costs, as well as improved viewing qualities for consumers. The transition may also involve analogue cable conversion to digital cable or Internet Protocol television, as well as analog to digital satellite television. Transition of land based broadcasting was begun by some countries around 2000. By contrast, transition of satellite television systems was well underway or completed in many countries by this time. It is an i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite Television
Satellite television is a service that delivers television programming to viewers by relaying it from a communications satellite orbiting the Earth directly to the viewer's location. The signals are received via an outdoor parabolic antenna commonly referred to as a satellite dish and a low-noise block downconverter. A satellite receiver then decodes the desired television program for viewing on a television set. Receivers can be external set-top boxes, or a built-in television tuner. Satellite television provides a wide range of channels and services. It is usually the only television available in many remote geographic areas without terrestrial television or cable television service. Modern systems signals are relayed from a communications satellite on the X band (8–12 GHz) or Ku band (12–18 GHz) frequencies requiring only a small dish less than a meter in diameter. The first satellite TV systems were an obsolete type now known as television receive-only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HD Radio
HD Radio (HDR) is a trademark for an in-band on-channel (IBOC) digital radio broadcast technology. It generally simulcasts an existing analog radio station in digital format with less noise and with additional text information. HD Radio is used primarily by AM and FM radio stations in the United States, Canada, and Mexico, with a few implementations outside North America. The term "on channel" is a misnomer because the system actually broadcasts on the ordinarily unused channels adjacent to an existing radio station's allocation. This leaves the original analog signal intact, allowing enabled receivers to switch between digital and analog as required. In most FM implementations, from 96 to 128 kbps of capacity is available. High-fidelity audio requires only 48 kbps so there is ample capacity for additional channels, which HD Radio refers to as "multicasting". HD Radio is licensed so that the simulcast of the main channel is royalty-free. The company makes its money ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Video Broadcasting
Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB) is a set of international open standards for digital television. DVB standards are maintained by the DVB Project, an international industry consortium, and are published by a Joint Technical Committee (JTC) of the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI), European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization (CENELEC) and European Broadcasting Union (EBU). Transmission DVB systems distribute data using a variety of approaches, including: * Satellite: DVB-S, DVB-S2, and DVB-SH ** DVB-SMATV for distribution via SMATV * Cable: DVB-C, DVB-C2 * Terrestrial television: DVB-T, DVB-T2 ** Digital terrestrial television for handhelds: DVB-H, DVB-SH * Microwave: using DTT ( DVB-MT), the MMDS ( DVB-MC), and/or MVDS standards ( DVB-MS) These standards define the physical layer and data link layer of the distribution system. Devices interact with the physical layer via a synchronous parallel interface (SPI), synchronous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Radio Mondiale
Digital Radio Mondiale (DRM; ''mondiale'' being Italian and French for "worldwide") is a set of digital audio broadcasting technologies designed to work over the bands currently used for analogue radio broadcasting including AM broadcasting—particularly shortwave—and FM broadcasting. DRM is more spectrally efficient than AM and FM, allowing more stations, at higher quality, into a given amount of bandwidth, using xHE-AAC audio coding format. Various other MPEG-4 and Opus codecs are also compatible, but the standard now specifies xHE-AAC. Digital Radio Mondiale is also the name of the international non-profit consortium that has designed the platform and is now promoting its introduction. Radio France Internationale, TéléDiffusion de France, BBC World Service, Deutsche Welle, Voice of America, Telefunken (now Transradio) and Thomcast (now Ampegon) took part at the formation of the DRM consortium. The principle of DRM is that bandwidth is the limiting factor, and com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Audio Broadcasting
Digital radio is the use of digital technology to transmit or receive across the radio spectrum. Digital transmission by radio waves includes digital broadcasting, and especially digital audio radio services. Types In digital broadcasting systems, the analog audio signal is digitized, compressed using an audio coding format such as AAC+ (MDCT) or MP2, and transmitted using a digital modulation scheme. The aim is to increase the number of radio programs in a given spectrum, to improve the audio quality, to eliminate fading problems in mobile environments, to allow additional datacasting services, and to decrease the transmission power or the number of transmitters required to cover a region. However, analog radio (AM and FM) is still more popular and listening to radio over IP (Internet Protocol) is growing in popularity. In 2012 four digital wireless radio systems are recognized by the International Telecommunication Union: the two European systems Digital Audio Broadc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ATSC Tuner
An ATSC (Advanced Television Systems Committee) tuner, often called an ATSC receiver or HDTV tuner, is a type of television tuner that allows reception of digital television (DTV) television channels that use ATSC standards, as transmitted by television stations in North America, parts of Central America, and South Korea. Such tuners are usually integrated into a television set, VCR, digital video recorder (DVR), or set-top box which provides audio/video output connectors of various types. Another type of television tuner is a digital television adapter (DTA) with an analog passthrough. Technical overview The terms "tuner" and "receiver" are used loosely, and it is perhaps more appropriately called an ATSC receiver, with the tuner being part of the receiver (see Metonymy). The receiver generates the audio and video (AV) signals needed for television, and performs the following tasks: demodulation; error correction; MPEG transport stream demultiplexing; decompression; AV synch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ATSC Standards
Advanced Television Systems Committee (ATSC) standards are an American set of standards for digital television transmission over terrestrial, cable and satellite networks. It is largely a replacement for the analog NTSC standard and, like that standard, is used mostly in the United States, Mexico, Canada, and South Korea. Several former NTSC users, such as Japan, have not used ATSC during their digital television transition, because they adopted other systems such as ISDB developed by Japan, and DVB developed in Europe, for example. The ATSC standards were developed in the early 1990s by the Grand Alliance, a consortium of electronics and telecommunications companies that assembled to develop a specification for what is now known as HDTV. The standard is now administered by the Advanced Television Systems Committee. It includes a number of patented elements, and licensing is required for devices that use these parts of the standard. Key among these is the 8VSB modula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Radio
Digital radio is the use of digital technology to transmit or receive across the radio spectrum. Digital transmission by radio waves includes digital broadcasting, and especially digital audio radio services. Types In digital broadcasting systems, the analog audio signal is digitized, compressed using an audio coding format such as AAC+ ( MDCT) or MP2, and transmitted using a digital modulation scheme. The aim is to increase the number of radio programs in a given spectrum, to improve the audio quality, to eliminate fading problems in mobile environments, to allow additional datacasting services, and to decrease the transmission power or the number of transmitters required to cover a region. However, analog radio (AM and FM) is still more popular and listening to radio over IP (Internet Protocol) is growing in popularity. In 2012 four digital wireless radio systems are recognized by the International Telecommunication Union: the two European systems Digital Audio Broadca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science (journal)
''Science'', also widely referred to as ''Science Magazine'', is the peer-reviewed academic journal of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) and one of the world's top academic journals. It was first published in 1880, is currently circulated weekly and has a subscriber base of around 130,000. Because institutional subscriptions and online access serve a larger audience, its estimated readership is over 400,000 people. ''Science'' is based in Washington, D.C., United States, with a second office in Cambridge, UK. Contents The major focus of the journal is publishing important original scientific research and research reviews, but ''Science'' also publishes science-related news, opinions on science policy and other matters of interest to scientists and others who are concerned with the wide implications of science and technology. Unlike most scientific journals, which focus on a specific field, ''Science'' and its rival ''Nature'' cover the full r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |