|
Diethylene Glycol Dinitrate
Diethylene glycol dinitrate (DEGDN) is an explosive nitrated alcohol ester with the formula C4H8N2O7. While chemically similar to numerous other high explosives, pure diethylene glycol dinitrate is difficult to ignite or detonate. Ignition typically requires localized heating to the decomposition point unless the DEGDN is first atomized. Preparation and uses Diethylene glycol dinitrate can be made by nitration of diethylene glycol with nitric acid in presence of a dehydrating agent like concentrated sulfuric acid. DEGDN can be mixed with nitrocellulose or nitroglycol to form a colloid, which is used in smokeless powder for artillery and rocket propellant. During World War II, the Kriegsmarine frequently used this mixture in their artillery. It has also found use as desensitizing plasticizer because it contributes to the power of the mixture while stabilizing the explosives. Toxicity If ingested, like nitroglycerine, it rapidly causes vasodilation through the releas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of UN Numbers 0001 To 0100
UN numbers from UN 0001 to UN 0100 as assigned by the United Nations Committee of Experts on the Transport of Dangerous Goods are as follows: __NOTOC__ UN 0001 to UN 0100 See also *Lists of UN numbers The UN numbers range from UN0001 to about UN3600 and are assigned by the United Nations Committee of Experts on the Transport of Dangerous Goods. UN 0001 to 0600 * List of UN numbers 0001 to 0100 * List of UN numbers 0101 to 0200 * List of UN nu ... References {{UN number list navbox Lists of UN numbers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kriegsmarine
The (, ) was the navy of Germany from 1935 to 1945. It superseded the Imperial German Navy of the German Empire (1871–1918) and the inter-war (1919–1935) of the Weimar Republic. The was one of three official branches, along with the and the , of the , the German armed forces from 1935 to 1945. In violation of the Treaty of Versailles, the grew rapidly during German naval rearmament in the 1930s. The 1919 treaty had limited the size of the German navy and prohibited the building of submarines. ships were deployed to the waters around Spain during the Spanish Civil War (1936–1939) under the guise of enforcing non-intervention, but in reality supported the Nationalists against the Spanish Republicans. In January 1939, Plan Z, a massive shipbuilding program, was ordered, calling for surface naval parity with the British Royal Navy by 1944. When World War II broke out in September 1939, Plan Z was shelved in favour of a crash building program for submarines (U-boat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TNT Equivalent
TNT equivalent is a convention for expressing energy, typically used to describe the energy released in an explosion. The is a unit of energy defined by that convention to be , which is the approximate energy released in the detonation of a metric ton (1,000 kilograms) of TNT. In other words, for each gram of TNT exploded, (or 4184 joules) of energy is released. This convention intends to compare the destructiveness of an event with that of conventional explosive materials, of which TNT is a typical example, although other conventional explosives such as dynamite contain more energy. Kiloton and megaton The "kiloton (of TNT)" is a unit of energy equal to 4.184 terajoules (). The "megaton (of TNT)" is a unit of energy equal to 4.184 petajoules (). The kiloton and megaton of TNT have traditionally been used to describe the energy output, and hence the destructive power, of a nuclear weapon. The TNT equivalent appears in various nuclear weapon control treaties, and has b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimethylolethane Trinitrate
Trimethylolethane trinitrate (TMETN), also known as metriol trinitrate (METN, MTN, METRTN) or nitropentaglycerin, is a nitrate ester. It is a high explosive similar to nitroglycerin. It is a transparent oily liquid, colorless to light brown. It is odorless. It is used in some solid propellants and smokeless powders as a plasticizer. Its chemical formula is . TMETN was first prepared and patented in Italy under name Metriolo. Germans began producing it before World War II, when it was demonstrated to be an erosion and flash-reducing agent in smokeless powders. It is a liquid explosive with properties similar to nitroglycerin, but more stable to heat. It is prepared by nitration of trimethylolethane (metriol). It does not induce headaches. TMETN can be initiated by friction, impact, and electrostatic discharge. It can be used as a high-viscosity plasticizer-binder together with nitrocellulose, but its poor colloidal properties has made such use rare. Long-term milling can however as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triethylene Glycol Dinitrate
Triethylene glycol dinitrate (TEGDN) is a nitrated alcohol ester of triethylene glycol. It is used as an energetic plasticizer in explosives and propellants. Its chemical formula is O2N-O-CH2CH2-O-CH2CH2-O-CH2CH2-O-NO2. It is a pale yellow oily liquid. It is somewhat similar to nitroglycerin. TEGDN is often used together with trimethylolethane trinitrate (TMETN). Triethylene glycol dinitrate, diethylene glycol dinitrate Diethylene glycol dinitrate (DEGDN) is an explosive nitration, nitrated Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol ester with the formula C4H8N2O7. While chemically similar to numerous other high explosives, pure diethylene glycol dinitrate is difficult to ig ..., and trimethylolethane trinitrate are being considered as replacements for nitroglycerin in propellants. at stormingmedia.us References [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palliative
Palliative care (derived from the Latin root , or 'to cloak') is an interdisciplinary medical caregiving approach aimed at optimizing quality of life and mitigating suffering among people with serious, complex, and often terminal illnesses. Within the published literature, many definitions of palliative care exist. The World Health Organization (WHO) describes palliative care as "an approach that improves the quality of life of patients and their families facing the problems associated with life-threatening illness, through the prevention and relief of suffering by means of early identification and impeccable assessment and treatment of pain and other problems, physical, psychosocial, and spiritual." In the past, palliative care was a disease specific approach, but today the WHO takes a more broad approach, that the principles of palliative care should be applied as early as possible to any chronic and ultimately fatal illness. Palliative care is appropriate for individuals with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perchlorate
A perchlorate is a chemical compound containing the perchlorate ion, . The majority of perchlorates are commercially produced salts. They are mainly used as oxidizers for pyrotechnic devices and to control static electricity in food packaging. Perchlorate contamination in food, water, and other parts of the environment has been studied in the U.S. because of harmful effects on human health. Perchlorate ions are somewhat toxic to the thyroid gland. Most perchlorates are colorless solids that are soluble in water. Four perchlorates are of primary commercial interest: ammonium perchlorate , perchloric acid , potassium perchlorate and sodium perchlorate . Perchlorate is the anion resulting from the dissociation of perchloric acid and its salts upon their dissolution in water. Many perchlorate salts are soluble in non-aqueous solutions. Production Perchlorate salts are produced industrially by the oxidation of aqueous solutions of sodium chlorate by electrolysis. This method is used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitro Compound
In organic chemistry, nitro compounds are organic compounds that contain one or more nitro functional groups (). The nitro group is one of the most common explosophores (functional group that makes a compound explosive) used globally. The nitro group is also strongly electron-withdrawing. Because of this property, bonds alpha (adjacent) to the nitro group can be acidic. For similar reasons, the presence of nitro groups in aromatic compounds retards electrophilic aromatic substitution but facilitates nucleophilic aromatic substitution. Nitro groups are rarely found in nature. They are almost invariably produced by nitration reactions starting with nitric acid. Synthesis Preparation of aromatic nitro compounds Aromatic nitro compounds are typically synthesized by nitration. Nitration is achieved using a mixture of nitric acid and sulfuric acid, which produce the nitronium ion (), which is the electrophile: + The nitration product produced on the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
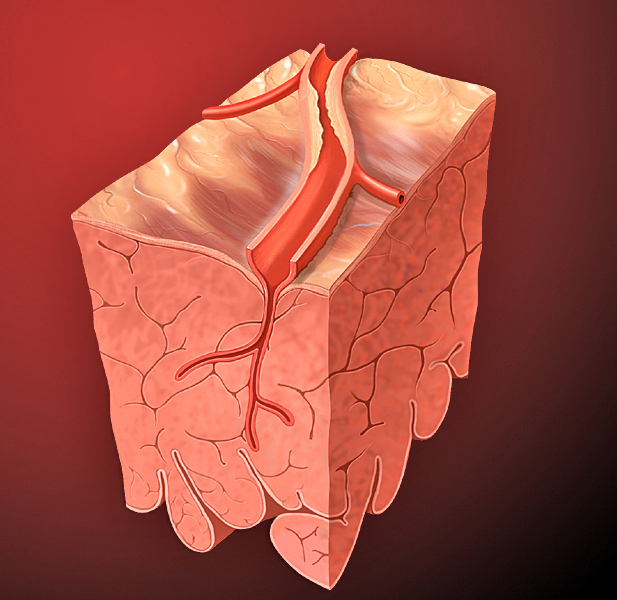
Cardiac
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to the lungs. In humans, the heart is approximately the size of a closed fist and is located between the lungs, in the middle compartment of the chest. In humans, other mammals, and birds, the heart is divided into four chambers: upper left and right atria and lower left and right ventricles. Commonly the right atrium and ventricle are referred together as the right heart and their left counterparts as the left heart. Fish, in contrast, have two chambers, an atrium and a ventricle, while most reptiles have three chambers. In a healthy heart blood flows one way through the heart due to heart valves, which prevent backflow. The heart is enclosed in a protective sac, the pericardium, which also contains a small amount of fluid. The wall o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chest Pain
Chest pain is pain or discomfort in the chest, typically the front of the chest. It may be described as sharp, dull, pressure, heaviness or squeezing. Associated symptoms may include pain in the shoulder, arm, upper abdomen, or jaw, along with nausea, sweating, or shortness of breath. It can be divided into heart-related and non-heart-related pain. Pain due to insufficient blood flow to the heart is also called angina pectoris. Those with diabetes or the elderly may have less clear symptoms. Serious and relatively common causes include acute coronary syndrome such as a heart attack (31%), pulmonary embolism (2%), pneumothorax, pericarditis (4%), aortic dissection (1%) and esophageal rupture. Other common causes include gastroesophageal reflux disease (30%), muscle or skeletal pain (28%), pneumonia (2%), shingles (0.5%), pleuritis, traumatic and anxiety disorders. Determining the cause of chest pain is based on a person's medical history, a physical exam and other medical te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angina Pectoris
Angina, also known as angina pectoris, is chest pain or pressure, usually caused by insufficient blood flow to the heart muscle (myocardium). It is most commonly a symptom of coronary artery disease. Angina is typically the result of obstruction or spasm of the arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle. The main mechanism of coronary artery obstruction is atherosclerosis as part of coronary artery disease. Other causes of angina include abnormal heart rhythms, heart failure and, less commonly, anemia. The term derives from the Latin ''angere'' ("to strangle") and ''pectus'' ("chest"), and can therefore be translated as "a strangling feeling in the chest". There is a weak relationship between severity of angina and degree of oxygen deprivation in the heart muscle, however, the severity of angina does not always match the degree of oxygen deprivation to the heart or the risk of a myocardial infarction (heart attack). Some people may experience severe pain even though the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitric Oxide
Nitric oxide (nitrogen oxide or nitrogen monoxide) is a colorless gas with the formula . It is one of the principal oxides of nitrogen. Nitric oxide is a free radical: it has an unpaired electron, which is sometimes denoted by a dot in its chemical formula In chemistry, a chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, ... (•N=O or •NO). Nitric oxide is also a heteronuclear diatomic molecule, a class of molecules whose study spawned early modern molecular orbital theory, theories of chemical bonding. An important Reaction intermediate, intermediate in chemical industry, industrial chemistry, nitric oxide forms in combustion systems and can be generated by lightning in thunderstorms. In mammals, including humans, nitric oxide is a signaling molecule in many physiological and pathological pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |