|
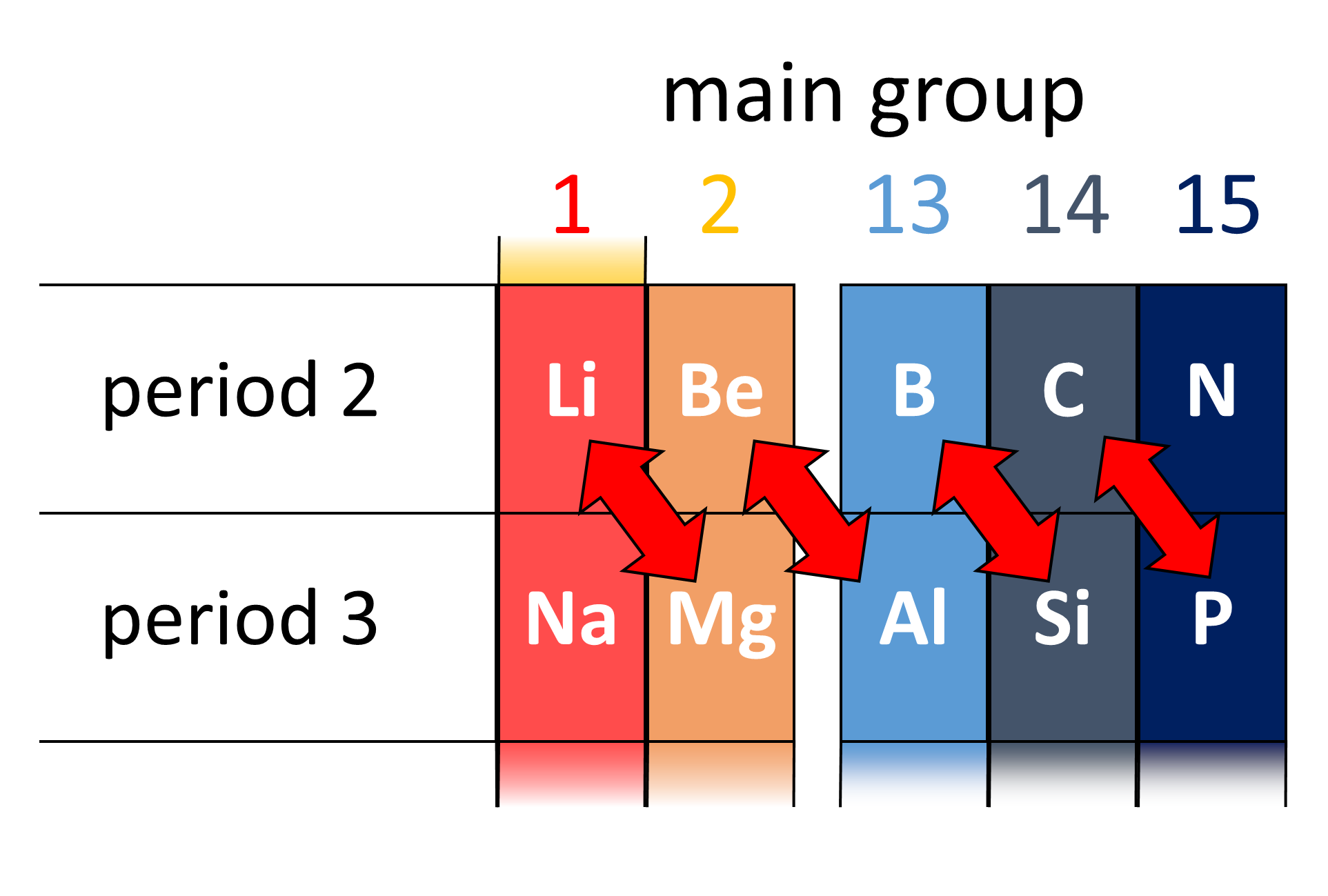
Diagonal Relationship
A diagonal relationship is said to exist between certain pairs of diagonally adjacent elements in the second and third periods (first 20 elements) of the periodic table. These pairs (lithium (Li) and magnesium (Mg), beryllium (Be) and aluminium (Al), boron (B) and silicon (Si), etc.) exhibit similar properties; for example, boron and silicon are both semiconductors, forming halides that are hydrolysed in water and have acidic oxides. The organization of elements on the periodic table into horizontal rows and vertical columns makes certain relationships more apparent (periodic law). Moving rightward and descending the periodic table have opposite effects on atomic radii of isolated atoms. Moving rightward across the period decreases the atomic radii of atoms, while moving down the group will increase the atomic radii. Similarly, on moving rightward a period, the elements become progressively more covalent, less basic and more electronegative, whereas on moving down a group th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charge Density
In electromagnetism, charge density is the amount of electric charge per unit length, surface area, or volume. Volume charge density (symbolized by the Greek letter ρ) is the quantity of charge per unit volume, measured in the SI system in coulombs per cubic meter (C⋅m−3), at any point in a volume. Surface charge density (σ) is the quantity of charge per unit area, measured in coulombs per square meter (C⋅m−2), at any point on a surface charge distribution on a two dimensional surface. Linear charge density (λ) is the quantity of charge per unit length, measured in coulombs per meter (C⋅m−1), at any point on a line charge distribution. Charge density can be either positive or negative, since electric charge can be either positive or negative. Like mass density, charge density can vary with position. In classical electromagnetic theory charge density is idealized as a '' continuous'' scalar function of position \boldsymbol, like a fluid, and \rho(\bol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnesium Chloride
Magnesium chloride is the family of inorganic compounds with the formula , where x can range from 0 to 12. These salts are colorless or white solids that are highly soluble in water. These compounds and their solutions, both of which occur in nature, have a variety of practical uses. Anhydrous magnesium chloride is the principal precursor to magnesium metal, which is produced on a large scale. Hydrated magnesium chloride is the form most readily available. Production Magnesium chloride can be extracted from brine or sea water. In North America, it is produced primarily from Great Salt Lake brine. In the Jordan Valley, it is obtained from the Dead Sea. The mineral bischofite () is extracted (by solution mining) out of ancient seabeds, for example, the Zechstein seabed in northwest Europe. Some deposits result from high content of magnesium chloride in the primordial ocean. Some magnesium chloride is made from evaporation of seawater. In the Dow process, magnesium chloride is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
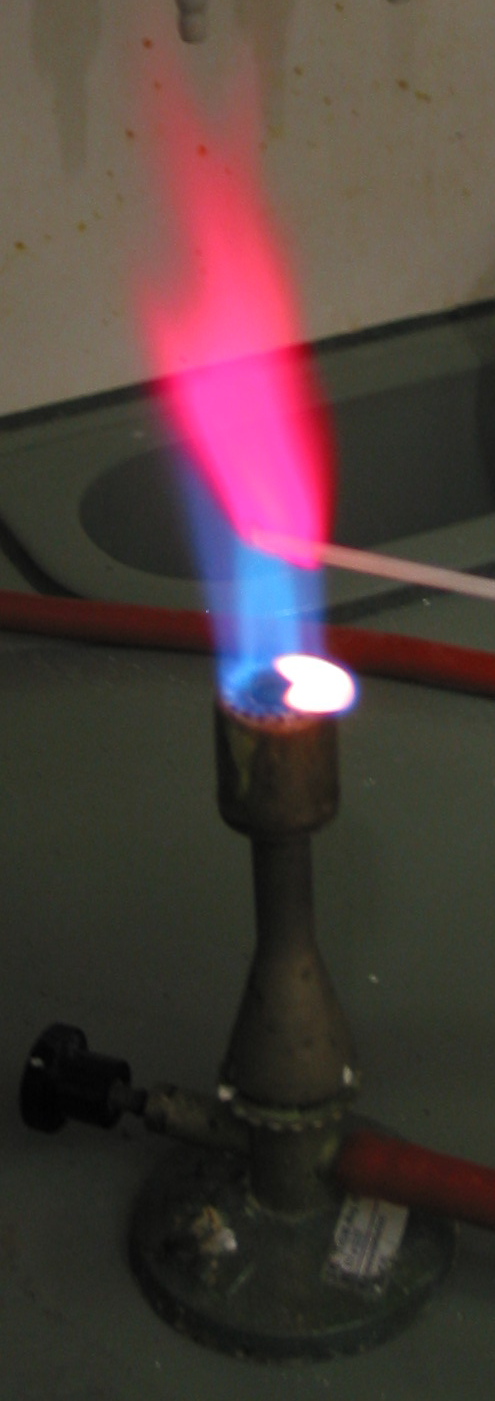
Lithium Chloride
Lithium chloride is a chemical compound with the formula Li Cl. The salt is a typical ionic compound (with certain covalent characteristics), although the small size of the Li+ ion gives rise to properties not seen for other alkali metal chlorides, such as extraordinary solubility in polar solvents (83.05 g/100 mL of water at 20 °C) and its hygroscopic properties. Chemical properties The salt forms crystalline hydrates, unlike the other alkali metal chlorides. Mono-, tri-, and pentahydrates are known. The anhydrous salt can be regenerated by heating the hydrates. LiCl also absorbs up to four equivalents of ammonia/mol. As with any other ionic chloride, solutions of lithium chloride can serve as a source of chloride ion, e.g., forming a precipitate upon treatment with silver nitrate: : LiCl + AgNO3 → AgCl + LiNO3 Preparation Lithium chloride is produced by treatment of lithium carbonate with hydrochloric acid. Anhydrous LiCl is prepared from the hydrate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyridine
Pyridine is a basic (chemistry), basic heterocyclic compound, heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula . It is structurally related to benzene, with one methine group replaced by a nitrogen atom. It is a highly flammable, weakly alkaline, water-miscible liquid with a distinctive, unpleasant fish-like smell. Pyridine is colorless, but older or impure samples can appear yellow, due to the formation of extended, unsaturated polymeric chains, which show significant electrical conductivity. The pyridine ring occurs in many important compounds, including agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and vitamins. Historically, pyridine was produced from coal tar. As of 2016, it is synthesized on the scale of about 20,000 tons per year worldwide. Properties Physical properties The molecular electric dipole moment is 2.2 debyes. Pyridine is diamagnetism, diamagnetic and has a Magnetic susceptibility, diamagnetic susceptibility of −48.7 × 10−6 cm3·mol−1. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohol (chemistry)
In chemistry, an alcohol is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term ''alcohol'' originally referred to the primary alcohol ethanol (ethyl alcohol), which is used as a drug and is the main alcohol present in alcoholic drinks. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest examples, includes all compounds which conform to the general formula . Simple monoalcohols that are the subject of this article include primary (), secondary () and tertiary () alcohols. The suffix ''-ol'' appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority. When a higher priority group is present in the compound, the prefix ''hydroxy-'' is used in its IUPAC name. The suffix ''-ol'' in non-IUPAC names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance is an alcohol. However, some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deliquescent
Hygroscopy is the phenomenon of attracting and holding water molecules via either absorption or adsorption from the surrounding environment, which is usually at normal or room temperature. If water molecules become suspended among the substance's molecules, adsorbing substances can become physically changed, e.g., changing in volume, boiling point, viscosity or some other physical characteristic or property of the substance. For example, a finely dispersed hygroscopic powder, such as a salt, may become clumpy over time due to collection of moisture from the surrounding environment. ''Deliquescent'' materials are sufficiently hygroscopic that they absorb so much water that they become liquid and form an aqueous solution. Etymology and pronunciation The word ''hygroscopy'' () uses combining forms of '' hygro-'' and '' -scopy''. Unlike any other ''-scopy'' word, it no longer refers to a viewing or imaging mode. It did begin that way, with the word ''hygroscope'' referring in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grignard Reagents
A Grignard reagent or Grignard compound is a chemical compound with the general formula , where X is a halogen and R is an organic group, normally an alkyl or aryl. Two typical examples are methylmagnesium chloride and phenylmagnesium bromide . They are a subclass of the organomagnesium compounds. Grignard compounds are popular reagents in organic synthesis for creating new carbon-carbon bonds. For example, when reacted with another halogenated compound in the presence of a suitable catalyst, they typically yield and the magnesium halide as a byproduct; and the latter is insoluble in the solvents normally used. In this aspect, they are similar to organolithium reagents. Pure Grignard reagents are extremely reactive solids. They are normally handled as solutions in solvents such as diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran; which are relatively stable as long as water is excluded. In such a medium, a Grignard reagent is invariably present as a complex with the magnesium atom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organometallic
Organometallic chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds, chemical compounds containing at least one chemical bond between a carbon atom of an organic molecule and a metal, including alkali, alkaline earth, and transition metals, and sometimes broadened to include metalloids like boron, silicon, and selenium, as well. Aside from bonds to organyl fragments or molecules, bonds to 'inorganic' carbon, like carbon monoxide (metal carbonyls), cyanide, or carbide, are generally considered to be organometallic as well. Some related compounds such as transition metal hydrides and metal phosphine complexes are often included in discussions of organometallic compounds, though strictly speaking, they are not necessarily organometallic. The related but distinct term " metalorganic compound" refers to metal-containing compounds lacking direct metal-carbon bonds but which contain organic ligands. Metal β-diketonates, alkoxides, dialkylamides, and metal phosphine complexes are r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group 2 Element
A group is a number of persons or things that are located, gathered, or classed together. Groups of people * Cultural group, a group whose members share the same cultural identity * Ethnic group, a group whose members share the same ethnic identity * Religious group (other), a group whose members share the same religious identity * Social group, a group whose members share the same social identity * Tribal group, a group whose members share the same tribal identity * Organization, an entity that has a collective goal and is linked to an external environment * Peer group, an entity of three or more people with similar age, ability, experience, and interest Social science * In-group and out-group * Primary, secondary, and reference groups * Social group * Collectives Science and technology Mathematics * Group (mathematics), a set together with a binary operation satisfying certain algebraic conditions Chemistry * Functional group, a group of atoms whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium Nitride
Lithium nitride is a compound with the formula Li3N. It is the only stable alkali metal nitride. The solid has a reddish-pink color and high melting point. Preparation and handling Lithium nitride is prepared by direct combination of elemental lithium with nitrogen gas: :6 Li + N2 → 2 Li3N Instead of burning lithium metal in an atmosphere of nitrogen, a solution of lithium in liquid sodium metal can be treated with N2. Lithium nitride reacts violently with water to produce ammonia: :Li3N + 3 H2O → 3 LiOH + NH3 Structure and properties ''alpha''-Li3N (stable at room temperature and pressure) has an unusual crystal structure that consists of two types of layers, one sheet has the composition Li2N− contains 6-coordinate N centers and the other sheet consists only of lithium cations. Two other forms are known: ''beta''-Lithium nitride, formed from the alpha phase at has the sodium arsenide (Na3As) structure; ''gamma''-Lithium nitride (same structure as Li3Bi) forms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitride
In chemistry, a nitride is an inorganic compound of nitrogen. The "nitride" anion, N3- ion, is very elusive but compounds of nitride are numerous, although rarely naturally occuring. Some nitrides have a find applications, such as wear-resistant coatings (e.g., titanium nitride, TiN), hard ceramic materials (e.g., silicon nitride, Si3N4), and semiconductors (e.g., gallium nitride, GaN). The development of GaN-based light emitting diodes was recognized by the 2014 Nobel Prize in Physics. Metal nitrido complexes are also common. Synthesis of inorganic metal nitrides is challenging because nitrogen gas (N2) is not very reactive at low temperatures, but it becomes more reactive at higher temperatures. Therefore, a balance must be achieved between the low reactivity of nitrogen gas at low temperatures and the entropy driven formation of N2 at high temperatures. However, synthetic methods for nitrides are growing more sophisticated and the materials are of increasing technolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |