|
Desecularisation
In sociology, desecularization (also spelled desecularisation) is a resurgence or growth of religion after a period of secularization. The theory of desecularization is a reaction to the theory known as the ''secularization thesis,'' which posits a gradual decline in the importance of religion and in religious belief itself, as a universal feature of modern society. The term ''desecularization'' was coined by Peter L. Berger, a former proponent of the secularization thesis, in his 1999 book ''The Desecularization of the World''. Proponents of the theory of desecularization point to examples such as the Islamic revival since the 1970s, in particular the Iranian Revolution, the resurgence of religion in Russia and China, where governments have practiced state atheism, and the growing Christian population in the Global south, Global South. Berger also cited the rise of Evangelicalism, evangelical Christianity in the United States and elsewhere, rising religiosity in Hinduism, Sikhism a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
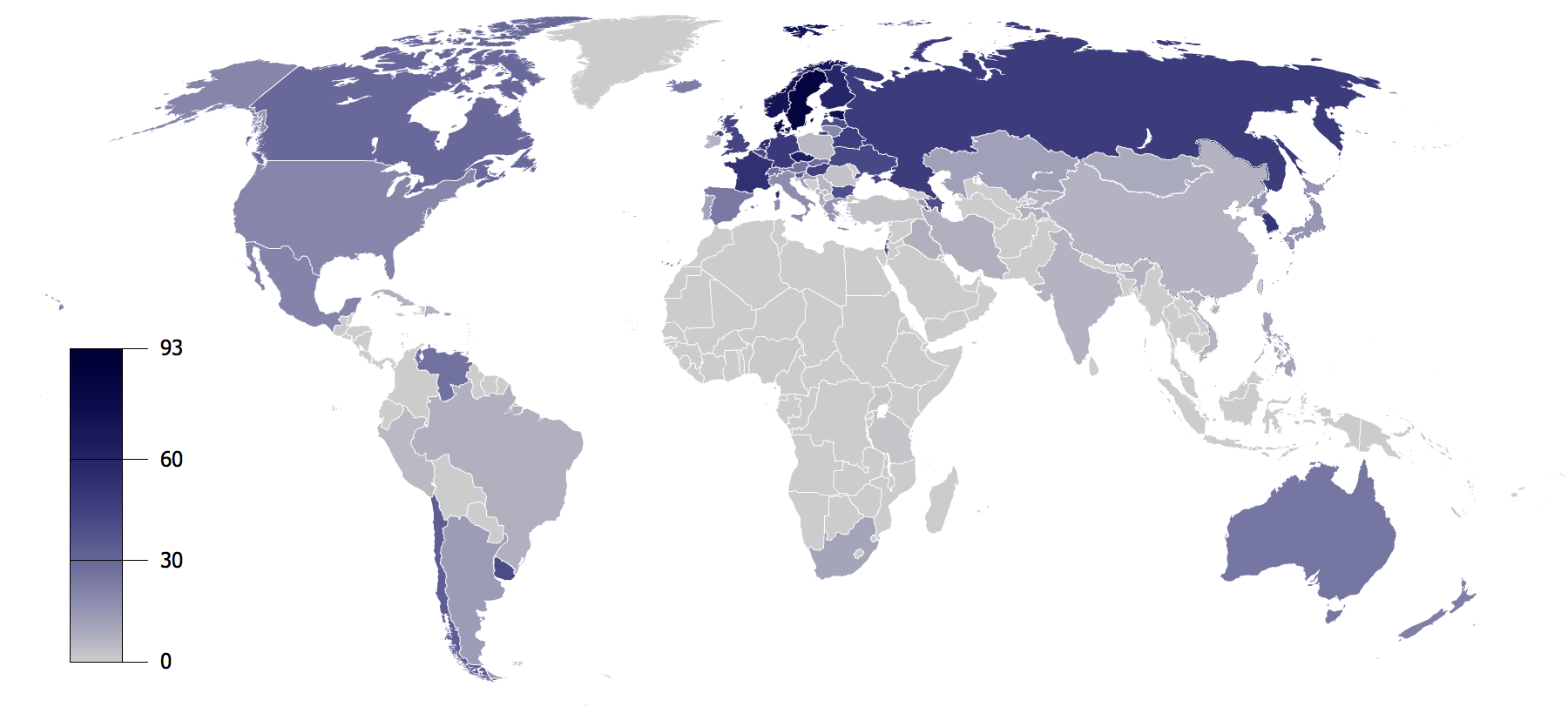
Countries By Importance Of Religion
A country is a distinct part of the Earth, world, such as a state (polity), state, nation, or other polity, political entity. When referring to a specific polity, the term "country" may refer to a sovereign state, List of states with limited recognition, state with limited recognition, Country (other)#Administrative divisions, constituent country, or dependent territory. Most sovereign states, but not all countries, are members of the United Nations. There is no universal agreement on List of sovereign states, the number of "countries" in the world, since several states have disputed sovereignty status or limited recognition, and a number of non-sovereign entities are commonly considered countries. The definition and usage of the word "country" are flexible and have changed over time. ''The Economist'' wrote in 2010 that "any attempt to find a clear definition of a country soon runs into a thicket of exceptions and anomalies." Areas much smaller than a political entit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emile Durkheim
Emile or Émile may refer to: * Émile (novel) (1827), autobiographical novel based on Émile de Girardin's early life * Emile, Canadian film made in 2003 by Carl Bessai * '' Emile: or, On Education'' (1762) by Jean-Jacques Rousseau, a treatise on education; full title ''Émile ou de l'education'' People * Emile (producer), American hip hop producer Emile Haynie * Emil (given name), includes people and characters with given name Emile or Émile * Barbara Emile, British television producer * Chris Emile, American dancer * Jonathan Emile, stage name of Jamaican-Canadian singer, rapper and record producer Jonathan Whyte Potter-Mäl (born 1986) * Yonan Emile Yonan Emile was an Iraqi basketball player. He competed in the men's tournament at the 1948 Summer Olympics The 1948 Summer Olympics, officially the Games of the XIV Olympiad and officially branded as London 1948, were an international mul ..., Iraqi Olympic basketball player * Emile Witbooi. South African soccer pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin America And The Caribbean
The term Latin America and the Caribbean (LAC) is an English language, English-language acronym referring to the Latin American and the Caribbean region. The term LAC covers an extensive region, extending from The Bahamas and Mexico to Argentina and Chile. The region has over 670,230,000 people , and spanned for . List of countries and territories by subregion Various countries within the Latin American and the Caribbean region do not use either Spanish language in the Americas, Spanish, Portuguese language in the Americas, Portuguese or American French, French as official languages, but rather Caribbean English, English or Surinamese Dutch, Dutch. Caribbean Scattered island in the Caribbean Sea * Federal Dependencies of Venezuela (Venezuela) West Indies = Antilles = Greater Antilles * (United Kingdom) * * * * * * * (United States) * List of territorial disputes, Disputed territory administered by the United States, land claim, claimed by Haiti. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asia–Pacific
The Asia–Pacific (APAC) also Known as Indo-Pacific is the region of the world adjoining the western Pacific Ocean. The region's precise boundaries vary depending on context, but countries and territories in Australasia, East Asia, and Southeast Asia are often included. In a wider context, Central Asia, North Asia, the list of islands in the Pacific Ocean, Pacific Islands, South Asia, West Asia (including the Arabian Peninsula and the Levant), and even Pacific Rim, Pacific-adjoining countries in the Americas can be included. For example, the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) includes five economies (Canada, Chile, Mexico, Peru, and the United States) in the New World (more standardly referred to as the Western Hemisphere). The term has become popular since the late 1980s in commerce, finance, and politics. Despite the heterogeneity of the regions' economies, most individual nations within the zone are emerging markets experiencing significant growth. Sometimes, the notion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latinobarómetro
Latinobarómetro Corporation is a private non-profit organization, based in Providencia, Chile. It is responsible for carrying out barómetro, an annual public opinion survey that involves some 20,000 interviews in 18 Latin America Latin America is the cultural region of the Americas where Romance languages are predominantly spoken, primarily Spanish language, Spanish and Portuguese language, Portuguese. Latin America is defined according to cultural identity, not geogr ...n countries, representing more than 600 million people. It observes the development of democracies, economies and societies, using indicators of attitude, opinion and behavior. References External links WebsiteLatinobarómetro Survey 1996-2000 Public opinion research companies Non-profit organisations based in Chile Latin American studies Statistical data sets Companies of Chile {{area-studies-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phil Zuckerman
Philip Joseph Zuckerman is a sociologist and professor of sociology and secular studies at Pitzer College in Claremont, California. He specializes in the sociology of substantial secularity and is the author of eight books, including ''Beyond Doubt: The Secularization of Society'' (2023) ''What It Means to Be Moral: Why Religion Is Not Necessary for Living an Ethical Life'' (2019). Early life and education Born June 26, 1969, to secular Ashkenazi Jewish parents in Los Angeles, California, Zuckerman grew up in Pacific Palisades and studied at Santa Monica College. He transferred to the University of Oregon in Eugene, and there earned a Bachelor of Arts (1992), Master of Arts (1995), and Doctor of Philosophy (1998), all in sociology. Career Zuckerman is a professor of sociology and secular studies at Pitzer College in Claremont, California. He is also an affiliated adjunct professor at Claremont Graduate University. He was a guest professor at Aarhus University in Denmark in 200 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gordon–Conwell Theological Seminary
Gordon–Conwell Theological Seminary (GCTS) is an evangelical seminary with its main campus in Hamilton, Massachusetts, and three other campuses in Boston, Massachusetts; Charlotte, North Carolina; and Jacksonville, Florida. According to the Association of Theological Schools, Gordon-Conwell ranks as one of the largest evangelical seminaries in North America in terms of total number of full-time students enrolled. History Gordon-Conwell arose primarily from the merging and refounding of two separate schools, Gordon Divinity School, formerly of Gordon College (1889) in Wenham, Massachusetts, and the Conwell School of Theology (1888), formerly of Temple University in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Both schools were founded in the Baptist theological heritage. Both Adoniram Judson Gordon and Russell Conwell, the namesakes of Gordon-Conwell, were Baptist ministers; Gordon's divinity school was first established as Gordon Bible Institute in 1889, while Conwell's theological school w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Ludwig Berger
Peter Ludwig Berger (17 March 1929 – 27 June 2017) was an Austrian-born American sociologist and Protestant theologian. Berger became known for his work in the sociology of knowledge, the sociology of religion, study of modernization, and contributions to sociological theory. Berger is arguably best known for his book, co-authored with Thomas Luckmann, '' The Social Construction of Reality: A Treatise in the Sociology of Knowledge'' (New York, 1966), which is considered one of the most influential texts in the sociology of knowledge and played a central role in the development of social constructionism. In 1998 the International Sociological Association named this book as the fifth most-influential book written in the field of sociology during the 20th century. In addition to this book, some of the other books that Berger has written include: '' Invitation to Sociology: A Humanistic Perspective'' (1963); '' A Rumor of Angels: Modern Society and the Rediscovery of the Supernatura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center (also simply known as Pew) is a nonpartisan American think tank based in Washington, D.C. It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the world. It also conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, random sample survey research, and panel based surveys, media content analysis, and other empirical social science research. The Pew Research Center states it does not take policy stances. It is a subsidiary of the Pew Charitable Trusts and a charter member of the American Association of Public Opinion Research's Transparency Initiative. History In 1990, the Times Mirror Company founded the Times Mirror Center for the People & the Press as a research project, tasked with conducting polls on politics and policy. Andrew Kohut became its director in 1993, and the Pew Charitable Trusts became its primary sponsor in 1996, when it was renamed the Pew Research Center for the Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Age Of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment (also the Age of Reason and the Enlightenment) was a Europe, European Intellect, intellectual and Philosophy, philosophical movement active from the late 17th to early 19th century. Chiefly valuing knowledge gained through rationalism and empiricism, the Enlightenment was concerned with a wide range of social and Politics, political ideals such as natural law, liberty, and progress, toleration and fraternity (philosophy), fraternity, constitutional government, and the formal separation of church and state. The Enlightenment was preceded by and overlapped the Scientific Revolution, which included the work of Johannes Kepler, Galileo Galilei, Francis Bacon, Pierre Gassendi, Christiaan Huygens and Isaac Newton, among others, as well as the philosophy of Descartes, Hobbes, Spinoza, Leibniz, and John Locke. The dating of the period of the beginning of the Enlightenment can be attributed to the publication of René Descartes' ''Discourse on the Method'' in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rationalism
In philosophy, rationalism is the Epistemology, epistemological view that "regards reason as the chief source and test of knowledge" or "the position that reason has precedence over other ways of acquiring knowledge", often in contrast to other possible sources of knowledge such as religious faith, faith, tradition, or sensory experience. More formally, rationalism is defined as a methodology or a theory "in which the criterion of truth is not sensory but intellectual and Deductive reasoning, deductive".Bourke, Vernon J., "Rationalism", p. 263 in Runes (1962). In a major philosophical debate during the Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment,John Locke (1690), An Essay Concerning Human Understanding rationalism (sometimes here equated with innatism) was opposed to empiricism. On the one hand, rationalists like René Descartes emphasized that knowledge is primarily innate and the intellect, the inner Faculty (other)#Biology, faculty of the human mind, can therefore direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |