|
Deep Focus
Deep focus is a photographic and cinematographic technique using a large depth of field. Depth of field is the front-to-back range of focus in an image, or how much of it appears sharp and clear. In deep focus, the foreground, middle ground, and background are all in focus. Deep focus is normally achieved by choosing a small aperture. Since the aperture of a camera determines how much light enters through the lens, achieving deep focus requires a bright scene or long exposure. A wide-angle lens also makes a larger portion of the image appear sharp. It is also possible to achieve the illusion of deep focus with optical tricks (split-focus diopter) or by compositing two or more images together. The opposite of deep focus is shallow focus, in which the plane of the image that is in focus is very shallow. For example, the foreground might be in focus while the middle-ground and background are out-of-focus. When avoiding deep focus is used specifically for aesthetic effect—espe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aperture Diagram
In optics, an aperture is a hole or an opening through which light travels. More specifically, the aperture and focal length of an optical system determine the cone angle of a bundle of rays that come to a focus in the image plane. An optical system typically has many openings or structures that limit the ray bundles (ray bundles are also known as ''pencils'' of light). These structures may be the edge of a lens or mirror, or a ring or other fixture that holds an optical element in place, or may be a special element such as a diaphragm placed in the optical path to limit the light admitted by the system. In general, these structures are called stops, and the aperture stop is the stop that primarily determines the ray cone angle and brightness at the image point. In some contexts, especially in photography and astronomy, ''aperture'' refers to the diameter of the aperture stop rather than the physical stop or the opening itself. For example, in a telescope, the aperture s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akio Jissoji
(March 29, 1937 – November 29, 2006) was a Japanese television and film director best known outside Japan for the 1960s TV series ''Ultraman'' and '' Ultraseven'', as well as for his auteur erotic ATG-produced Buddhist trilogy , , and . He was also known for his film adaptations of Japanese horror author Edogawa Rampo. Jissoji possessed a very distinctive visual style that was notable even in Japanese cinema which is known internationally for its visual style. Every project he directed, from children's action shows to disturbing adult films had an uncompromising approach to cinematic story telling. His episodes of the ''Ultraman'' TV shows are unique and quite unusual for children's television. His career is also unusual in that he went back and forth from children's television to film projects that were sexually provocative in some way or another. It is perhaps this aspect of his work that has prevented wider distribution of his films. Sadomasochistic and non-consensua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Mann (director)
Michael Kenneth Mann (born February 5, 1943) is an American director, screenwriter, and producer of film and television who is best known for his distinctive style of crime drama. His most acclaimed works include the films ''Thief'' (1981), '' Manhunter'' (1986), ''The Last of the Mohicans'' (1992), ''Heat'' (1995), '' The Insider'' (1999), ''Collateral'' (2004), and '' Public Enemies'' (2009). He is also known for his role as executive producer on the popular TV series ''Miami Vice'' (1984–89), which he adapted into a 2006 feature film. For his work, he has received nominations from international organizations and juries, including the British Academy of Film and Television Arts, Cannes, and the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences. As a producer, Mann has twice received nominations for the Academy Award for Best Picture, first for ''The Insider'' and then '' The Aviator'' (2004), which Mann had been hired to direct before the project was transferred to Martin Scors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miami Vice
''Miami Vice'' is an American crime drama television series created by Anthony Yerkovich and produced by Michael Mann for NBC. The series stars Don Johnson as James "Sonny" Crockett and Philip Michael Thomas as Ricardo "Rico" Tubbs, two Metro-Dade Police Department detectives working undercover in Miami. The series ran for five seasons on NBC from 1984 to 1989. The USA Network began airing reruns in 1988 and broadcast an originally unaired episode during its syndication run of the series on January 25, 1990. Unlike standard police procedurals, the show drew heavily upon 1980s New Wave culture and is noted for its integration of contemporary pop and rock music and stylish or stylized visuals. ''People'' magazine states that ''Miami Vice'' was the "first show to look really new and different since color TV was invented". Michael Mann directed a film adaptation of the series, which was released July 28, 2006. Conception The conception of the show is unclear. One version o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Focal Length
The focal length of an optical system is a measure of how strongly the system converges or diverges light; it is the inverse of the system's optical power. A positive focal length indicates that a system converges light, while a negative focal length indicates that the system diverges light. A system with a shorter focal length bends the rays more sharply, bringing them to a focus in a shorter distance or diverging them more quickly. For the special case of a thin lens in air, a positive focal length is the distance over which initially collimated (parallel) rays are brought to a focus, or alternatively a negative focal length indicates how far in front of the lens a point source must be located to form a collimated beam. For more general optical systems, the focal length has no intuitive meaning; it is simply the inverse of the system's optical power. In most photography and all telescopy, where the subject is essentially infinitely far away, longer focal length (lower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lens (optics)
A lens is a transmissive optical device which focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements''), usually arranged along a common axis. Lenses are made from materials such as glass or plastic, and are ground and polished or molded to a desired shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly focus or disperse waves and radiation other than visible light are also called lenses, such as microwave lenses, electron lenses, acoustic lenses, or explosive lenses. Lenses are used in various imaging devices like telescopes, binoculars and cameras. They are also used as visual aids in glasses to correct defects of vision such as myopia and hypermetropia. History The word '' lens'' comes from '' lēns'', the Latin name of the lentil (a seed of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Film Gauge
Film gauge is a physical property of photographic or motion picture film stock which defines its width. Traditionally, the major movie film gauges are 8 mm, 16 mm, 35 mm, and 65/70 mm (in this case 65 mm for the negative and 70 mm for the release print; the extra five millimeters are reserved for the magnetic soundtrack). There have been other historic gauges in the past, especially in the silent era, most notably 9.5 mm film, as well as a panoply of others ranging from 3 mm to 75 mm. Larger film gauge is generally associated with higher image quality, higher image detail, greater materials expense, heavier camera equipment, larger and most costly projection equipment, as well as greater bulk and weight for distribution and storage (both interim and archival). See also *Film format A film format is a technical definition of a set of standard characteristics regarding image capture on photographic film for still images or film stock for filmmaking. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
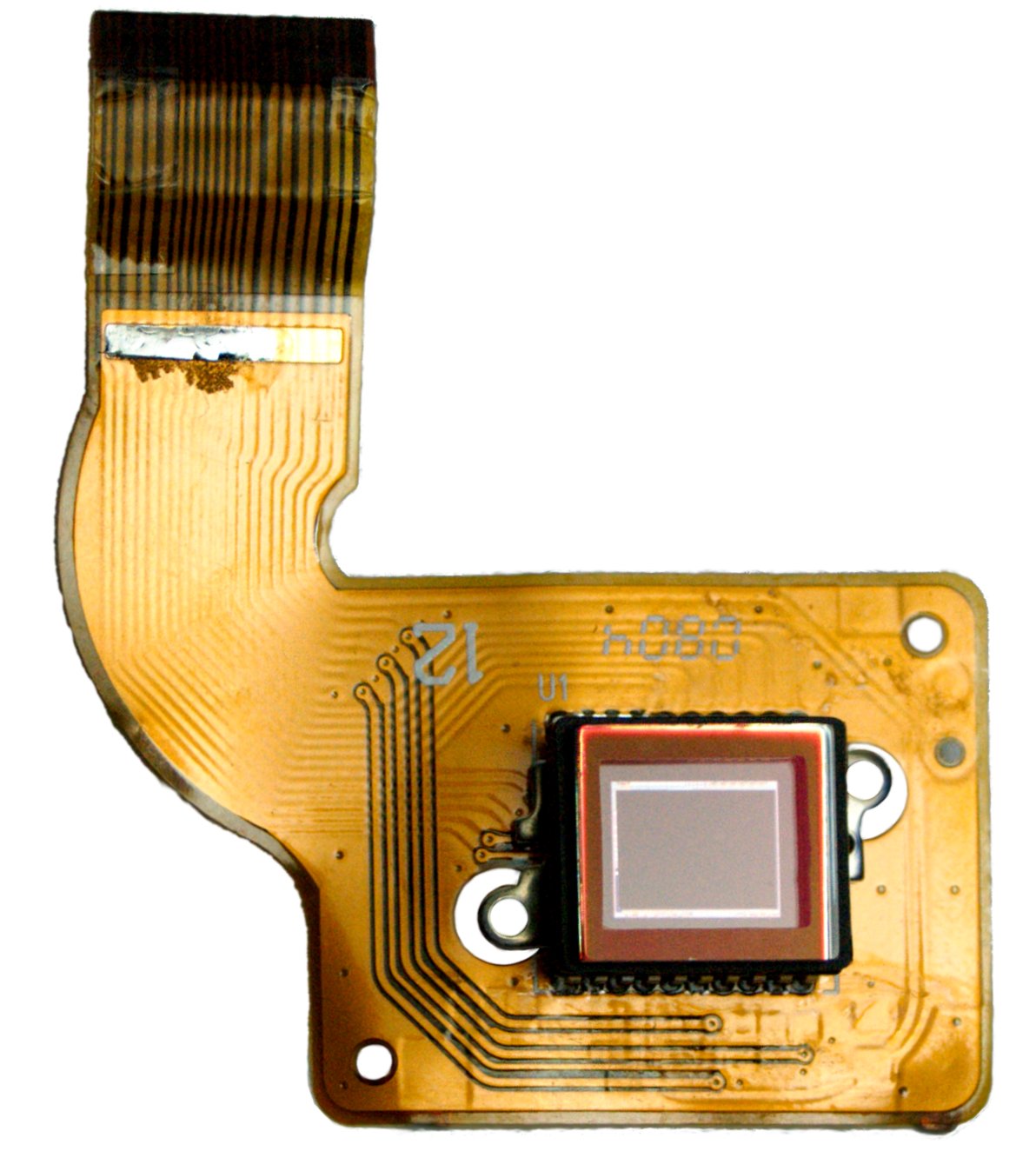
Image Sensor
An image sensor or imager is a sensor that detects and conveys information used to make an image. It does so by converting the variable attenuation of light waves (as they pass through or reflect off objects) into signals, small bursts of current that convey the information. The waves can be light or other electromagnetic radiation. Image sensors are used in electronic imaging devices of both analog and digital types, which include digital cameras, camera modules, camera phones, optical mouse devices, medical imaging equipment, night vision equipment such as thermal imaging devices, radar, sonar, and others. As technology changes, electronic and digital imaging tends to replace chemical and analog imaging. The two main types of electronic image sensors are the charge-coupled device (CCD) and the active-pixel sensor ( CMOS sensor). Both CCD and CMOS sensors are based on metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) technology, with CCDs based on MOS capacitors and CMOS sensors ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Best Years Of Our Lives
''The Best Years of Our Lives'' (also known as ''Glory for Me'' and ''Home Again'') is a 1946 American epic drama film directed by William Wyler, and starring Myrna Loy, Fredric March, Dana Andrews, Teresa Wright, Virginia Mayo and Harold Russell. The film is about three United States servicemen re-adjusting to societal changes and civilian life after coming home from World War II. The three men come from different services with different ranks that do not correspond with their civilian social class backgrounds. The film was a critical and commercial success. It won seven Academy Awards: Best Picture, Best Director (William Wyler), Best Actor (Fredric March), Best Supporting Actor (Harold Russell), Best Film Editing (Daniel Mandell), Best Adapted Screenplay (Robert E. Sherwood), and Best Original Score (Hugo Friedhofer). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
André Bazin
André Bazin (; 18 April 1918 – 11 November 1958) was a renowned and influential French film critic and film theorist. Bazin started to write about film in 1943 and was a co-founder of the renowned film magazine ''Cahiers du cinéma'' in 1951, with Jacques Doniol-Valcroze and Joseph-Marie Lo Duca. He is notable for arguing that realism is the most important function of cinema. His call for objective reality, deep focus, and lack of montage are linked to his belief that the interpretation of a film or scene should be left to the spectator. This placed him in opposition to film theory of the 1920s and 1930s, which emphasized how the cinema could manipulate reality. Life Bazin was born in Angers, France in 1918. He met future film and television producer Janine Kirsch while working at Labour and Culture, a militant organization associated with the French Communist party during World War II and eventually they married in 1949 and had a son named Florent. He died in 1958, age ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gregg Toland
Gregg Wesley Toland, A.S.C. (May 29, 1904 – September 28, 1948) was an American cinematographer known for his innovative use of techniques such as deep focus, examples of which can be found in his work on Orson Welles' ''Citizen Kane'' (1941), William Wyler's ''The Best Years of Our Lives'' (1946), and John Ford's ''The Grapes of Wrath'', and '' The Long Voyage Home'' (both, 1940). He is also known for his work as a director of photography for ''Wuthering Heights'' (1939), '' The Westerner'' (1940), ''Ball of Fire'' (1941), '' The Outlaw'' (1943), ''Song of the South'' (1946) and '' The Bishop's Wife'' (1947). Toland earned six Academy Award nominations for Best Cinematography, and won for his work on ''Wuthering Heights''. He was voted one of the top 10 most influential cinematographers in the history of film by the International Cinematographers Guild in 2003. Career Toland was born in Charleston, Illinois on May 29, 1904 to Jennie, a housekeeper, and Frank Toland. His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Wong Howe
Wong Tung Jim, A.S.C. (; August 28, 1899 – July 12, 1976), known professionally as James Wong Howe (Houghto), was a Chinese-born American cinematographer who worked on over 130 films. During the 1930s and 1940s, he was one of the most sought after cinematographers in Hollywood due to his innovative filming techniques. Howe was known as a master of the use of shadow and one of the first to use deep-focus cinematography, in which both foreground and distant planes remain in focus. Born in Canton (Guangzhou), China, Howe immigrated to the United States at age five and grew up in Washington. He was a professional boxer during his teenage years, and later began his career in the film industry as an assistant to Cecil B. DeMille. Howe pioneered the use of wide-angle lenses and low-key lighting, as well as the use of the crab dolly. Despite the success of his professional life, Howe faced significant racial discrimination in his private life. He became an American citizen only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_1.jpg)