|
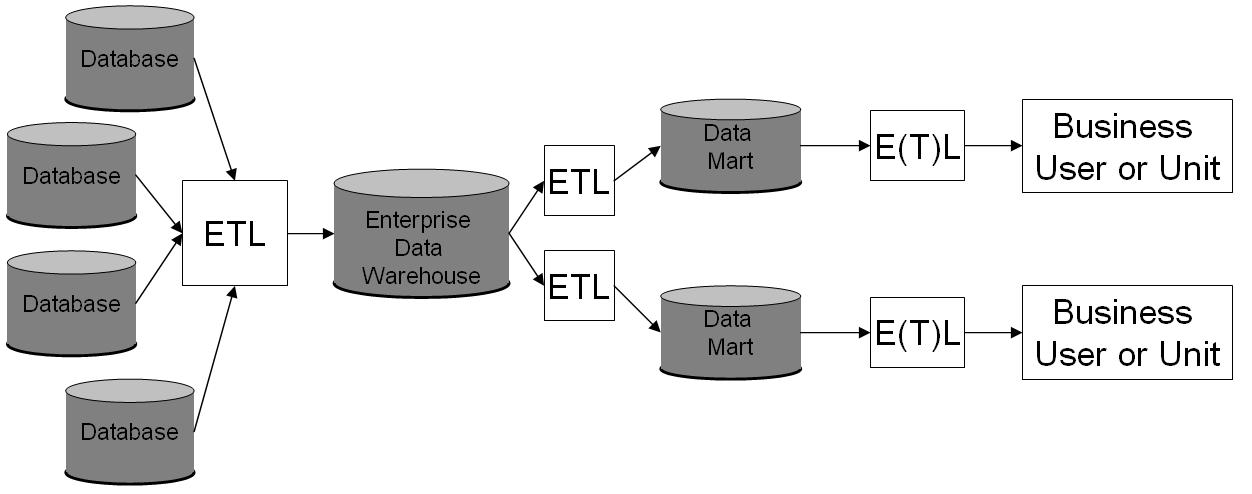
Data Warehouse
In computing, a data warehouse (DW or DWH), also known as an enterprise data warehouse (EDW), is a system used for reporting and data analysis and is considered a core component of business intelligence. Data warehouses are central repositories of integrated data from one or more disparate sources. They store current and historical data in one single place that are used for creating analytical reports for workers throughout the enterprise. This is beneficial for companies as it enables them to interrogate and draw insights from their data and make decisions. The data stored in the warehouse is uploaded from the operational systems (such as marketing or sales). The data may pass through an operational data store and may require data cleansing for additional operations to ensure data quality before it is used in the data warehouse for reporting. Extract, transform, load (ETL) and extract, load, transform (ELT) are the two main approaches used to build a data warehouse sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Warehouse Feeding Data Mart
In the pursuit of knowledge, data (; ) is a collection of discrete values that convey information, describing quantity, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of symbols that may be further interpreted. A datum is an individual value in a collection of data. Data is usually organized into structures such as tables that provide additional context and meaning, and which may themselves be used as data in larger structures. Data may be used as variables in a computational process. Data may represent abstract ideas or concrete measurements. Data is commonly used in scientific research, economics, and in virtually every other form of human organizational activity. Examples of data sets include price indices (such as consumer price index), unemployment rates, literacy rates, and census data. In this context, data represents the raw facts and figures which can be used in such a manner in order to capture the useful information out of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Facts
A flexible alternating current transmission system (FACTS) is a system composed of static equipment used for the alternating current (AC) transmission of electrical energy. It is meant to enhance controllability and increase power transfer capability of the network. It is generally a power electronics-based system. FACTS is defined by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) as "a power electronic based system and other static equipment that provide control of one or more AC transmission system parameters to enhance controllability and increase power transfer capability". According to Siemens, "FACTS Increase the reliability of AC grids and reduce power delivery costs. They improve transmission quality and efficiency of power transmission by supplying inductive or reactive power to grid. Technology Shunt compensation In shunt compensation, power system is connected in shunt (parallel) with the FACTS. It works as a controllable current source. Shunt comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Data Model
A common data model (CDM) can refer to any standardised data model which allows for data and information exchange between different applications and data sources. Common data models aim to standardise logical infrastructure so that related applications can "operate on and share the same data", and can be seen as a way to "organize data from many sources that are in different formats into a standard structure". A common data model has been described as one of the components of a " strong information system". A standardised common data model has also been described as a typical component of a well designed agile application besides a common communication protocol. Providing a single common data model within an organisation is one of the typical tasks of a data warehouse. Examples of common data models Border crossings X-trans.eu was a cross-border pilot project between the Free State of Bavaria (Germany) and Upper Austria with the aim of developing a faster procedure for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provenance
Provenance (from the French ''provenir'', 'to come from/forth') is the chronology of the ownership, custody or location of a historical object. The term was originally mostly used in relation to works of art but is now used in similar senses in a wide range of fields, including archaeology, paleontology, archives, manuscripts, printed books, the circular economy, and science and computing. The primary purpose of tracing the provenance of an object or entity is normally to provide contextual and circumstantial evidence for its original production or discovery, by establishing, as far as practicable, its later history, especially the sequences of its formal ownership, custody and places of storage. The practice has a particular value in helping authenticate objects. Comparative techniques, expert opinions and the results of scientific tests may also be used to these ends, but establishing provenance is essentially a matter of documentation. The term dates to the 1780s in Englis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transaction Processing
Transaction processing is information processing in computer science that is divided into individual, indivisible operations called ''transactions''. Each transaction must succeed or fail as a complete unit; it can never be only partially complete. For example, when you purchase a book from an online bookstore, you exchange money (in the form of credit) for a book. If your credit is good, a series of related operations ensures that you get the book and the bookstore gets your money. However, if a single operation in the series fails during the exchange, the entire exchange fails. You do not get the book and the bookstore does not get your money. The technology responsible for making the exchange balanced and predictable is called transaction processing. Transactions ensure that data-oriented resources are not permanently updated unless all operations within the transactional unit complete successfully. By combining a set of related operations into a unit that either completely s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extract, Load, Transform
Extract, load, transform (ELT) is an alternative to extract, transform, load (ETL) used with data lake implementations. In contrast to ETL, in ELT models the data is not transformed on entry to the data lake, but stored in its original raw format. This enables faster loading times. However, ELT requires sufficient processing power within the data processing engine to carry out the transformation on demand, to return the results in a timely manner. Since the data is not processed on entry to the data lake, the query and schema do not need to be defined a priori (although often the schema will be available during load since many data sources are extracts from databases or similar structured data systems and hence have an associated schema). ELT is a data pipeline model. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ELT Diagram
ELT may refer to: Education * English language teaching * Expanded learning time, an American education strategy * Kolb's experiential learning theory Mathematics and science * Ending lamination theorem * Extremely large telescope, a type of telescope * Extremely Large Telescope, an astronomical observatory under construction in Chile * Effective lifetime temperature, used in rehydroxylation dating Medicine * Endovenous laser treatment * Euglobulin lysis time * Excimer laser trabeculostomy Music * Every Little Thing (band), a Japanese J-Pop band * "ELT", a song by the band Wilco from their 1999 album ''Summerteeth'' Technology * Emergency locator transmitter * Extract, load, transform, a data processing concept * End-of-life tyre Transport * East London Transit, a British public transport system * El Tor Airport, in Egypt * Elizabethtown station, Pennsylvania Other uses * Electrical lighting technician, a stage-lighting technician * Electronic lien and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metadata
Metadata is "data that provides information about other data", but not the content of the data, such as the text of a message or the image itself. There are many distinct types of metadata, including: * Descriptive metadata – the descriptive information about a resource. It is used for discovery and identification. It includes elements such as title, abstract, author, and keywords. * Structural metadata – metadata about containers of data and indicates how compound objects are put together, for example, how pages are ordered to form chapters. It describes the types, versions, relationships, and other characteristics of digital materials. * Administrative metadata – the information to help manage a resource, like resource type, permissions, and when and how it was created. * Reference metadata – the information about the contents and quality of Statistical data type, statistical data. * Statistical metadata – also called process data, may describe processes that collect, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Business Intelligence Tools
Business intelligence software is a type of application software designed to retrieve, analyze, transform and report data for business intelligence. The applications generally read data that has been previously stored, often - though not necessarily - in a data warehouse or data mart. History Development of business intelligence software The first comprehensive business intelligence systems were developed by IBM and Siebel (currently acquired by Oracle) in the period between 1970 and 1990. At the same time, small developer teams were emerging with attractive ideas, and pushing out some of the products companies still use nowadays. In 1988, specialists and vendors organized a Multiway Data Analysis Consortium in Rome, where they considered making data management and analytics more efficient, and foremost available to smaller and financially restricted businesses. By 2000, there were many professional reporting systems and analytic programs, some owned by top performing software pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Dictionary
A data dictionary, or metadata repository, as defined in the ''IBM Dictionary of Computing'', is a "centralized repository of information about data such as meaning, relationships to other data, origin, usage, and format". ''Oracle'' defines it as a collection of tables with metadata. The term can have one of several closely related meanings pertaining to databases and database management systems (DBMS): * A document describing a database or collection of databases * An integral component of a DBMS that is required to determine its structure * A piece of middleware that extends or supplants the native data dictionary of a DBMS Documentation The terms ''data dictionary'' and ''data repository'' indicate a more general software utility than a catalogue. A ''catalogue'' is closely coupled with the DBMS software. It provides the information stored in it to the user and the DBA, but it is mainly accessed by the various software modules of the DBMS itself, such as DDL and DML com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decision Support
A decision support system (DSS) is an information system that supports business or organizational decision-making activities. DSSs serve the management, operations and planning levels of an organization (usually mid and higher management) and help people make decisions about problems that may be rapidly changing and not easily specified in advance—i.e. unstructured and semi-structured decision problems. Decision support systems can be either fully computerized or human-powered, or a combination of both. While academics have perceived DSS as a tool to support decision making processes, DSS users see DSS as a tool to facilitate organizational processes. Some authors have extended the definition of DSS to include any system that might support decision making and some DSS include a decision-making software component; Sprague (1980)Sprague, R;(1980).A Framework for the Development of Decision Support Systems" MIS Quarterly. Vol. 4, No. 4, pp.1-25. defines a properly termed DSS a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Market Research
Market research is an organized effort to gather information about target markets and customers: know about them, starting with who they are. It is an important component of business strategy and a major factor in maintaining competitiveness. Market research helps to identify and analyze the needs of the market, the market size and the competition. Its techniques encompass both qualitative techniques such as focus groups, in-depth interviews, and ethnography, as well as quantitative techniques such as customer surveys, and analysis of secondary data. It includes social and opinion research, and is the systematic gathering and interpretation of information about individuals or organizations using statistical and analytical methods and techniques of the applied social sciences to gain insight or support decision making. Market research, marketing research, and marketing are a sequence of business activities; sometimes these are handled informally. The field of ''marketing resea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |