|
Darcs
Darcs is a distributed version control system created by David Roundy. Key features include the ability to choose which changes to accept from other repositories, interaction with either other local (on-disk) repositories or remote repositories via SSH, HTTP, or email, and an unusually interactive interface. The developers also emphasize the use of advanced software tools for verifying correctness: the expressive type system of the functional programming language Haskell enforces some properties, and randomized testing via QuickCheck verifies many others. The name is a recursive acronym for Darcs Advanced Revision Control System. Model Darcs treats patches as first-class citizens. For the user, a repository can be seen as a set of patches, where each patch is not necessarily ordered with respect to other patches, i.e. the set of patches is only a partially ordered set. In many cases patches can be independently transmitted between various repositories. Many branching, mergin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comparison Of Version Control Software
The following tables describe attributes of notable version control and software configuration management (SCM) systems that can be used to compare and contrast the various systems. For SCM software not suitable for source code, see Comparison of open-source configuration management software. General information The following table contains relatively general attributes of version-control software systems, including: *Repository model, the relationship between copies of the source code repository ** Client–server, users access a master repository via a client; typically, their local machines hold only a working copy of a project tree. Changes in one working copy must be committed to the master repository before they are propagated to other users. ** Distributed, repositories act as peers, and users typically have a local repository with version history available, in addition to their working copies. *Concurrency model, how changes to the working copy are managed to pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merge (version Control)
In version control, merging (also called integration) is a fundamental operation that reconciles changes made to a version-controlled collection of files. Most often, it is necessary when a file is modified on two independent branching (software), branches and subsequently merged. The result is a single collection of files that contains both sets of changes. In some cases, the merge can be performed automatically, because there is sufficient history information to reconstruct the changes, and the changes do not conflict (version control), conflict. In other cases, a person must decide exactly what the resulting files should contain. Many revision control software tools include merge capabilities. Types of merges There are two types of merges: unstructured and structured. Unstructured merge Unstructured merge operates on raw text, typically using lines of text as atomic units. This is what Unix tools (diff/patch) and CVS tools (SVN, Git) use. This is limited, as a line of text ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Roundy
David Roundy is a physicist, known also as the author of the Darcs version control system. He obtained a B.A. in Physics and Chemistry in 1995 and a Ph.D. in physics from Berkeley in 2001. Between 2001 and 2006 he did postdoctoral work at MIT The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Established in 1861, MIT has played a significant role in the development of many areas of modern technology and sc ... and Cornell. He was an assistant professor in Physics at Oregon State University from 2006 to 2014, and an associate professor from 2014 to 2022. Notable publications * 2002 - The origin of the anomalous superconducting properties of MgB2 * 2010 - Meep: A flexible free-software package for electromagnetic simulations by the FDTD method * 2004 - A tunable carbon nanotube electromechanical oscillator References External links 1973 births Living people Oregon State University fac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QuickCheck
QuickCheck is a software library, a combinator library, originally written in the programming language Haskell, designed to assist in software testing by generating test cases for test suites – an approach known as property testing. Software It is compatible with the compiler, Glasgow Haskell Compiler (GHC) and the interpreter, Haskell User's Gofer System ( Hugs). It is free and open-source software released under a BSD-style license. In QuickCheck, assertions are written about logical properties that a function should fulfill. Then QuickCheck attempts to generate a test case that falsifies such assertions. Once such a test case is found, QuickCheck tries to reduce it to a minimal failing subset by removing or simplifying input data that are unneeded to make the test fail. The project began in 1999. Besides being used to test regular programs, QuickCheck is also useful for building up a functional specification, for documenting what functions should be doing, and for tes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributed Version Control Systems
Distribution may refer to: Mathematics *Distribution (mathematics), generalized functions used to formulate solutions of partial differential equations *Probability distribution, the probability of a particular value or value range of a variable **Cumulative distribution function, in which the probability of being no greater than a particular value is a function of that value *Frequency distribution, a list of the values recorded in a sample * Inner distribution, and outer distribution, in coding theory *Distribution (differential geometry), a subset of the tangent bundle of a manifold * Distributed parameter system, systems that have an infinite-dimensional state-space *Distribution of terms, a situation in which all members of a category are accounted for *Distributivity, a property of binary operations that generalises the distributive law from elementary algebra *Distribution (number theory) *Distribution problems, a common type of problems in combinatorics where the goal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-platform Free Software
Within computing, cross-platform software (also called multi-platform software, platform-agnostic software, or platform-independent software) is computer software that is designed to work in several computing platforms. Some cross-platform software requires a separate build for each platform, but some can be directly run on any platform without special preparation, being written in an interpreted language or compiled to portable bytecode for which the interpreters or run-time packages are common or standard components of all supported platforms. For example, a cross-platform application may run on Linux, macOS and Microsoft Windows. Cross-platform software may run on many platforms, or as few as two. Some frameworks for cross-platform development are Codename One, ArkUI-X, Kivy, Qt, GTK, Flutter, NativeScript, Xamarin, Apache Cordova, Ionic, and React Native. Platforms ''Platform'' can refer to the type of processor (CPU) or other hardware on which an operating syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edit Conflict
An edit conflict is a computer problem that may occur when multiple editors edit the same file and cannot merge without losing part or all of their edit. The conflict occurs when an editor gets a copy of a shared document file, changes the copy and attempts to save the changes to the original file, which has been altered by another editor after the copy was obtained. Resolution The simplest way to resolve an edit conflict is to ignore intervening edits and overwrite the current file. This may lead to a substantial loss of information, and alternative methods are often employed to resolve or prevent conflicts: * Manual resolution, where the editor determines which version to retain and may manually incorporate edits into the current version of the file. * Store backups or file comparisons of each edit, so there are the previous versions of the file can still be accessed once the original is overwritten. * File locking, which limits the file to one editor at a time to prevent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNU Arch
GNU arch software is a distributed revision control system that is part of the GNU Project and licensed under the GNU General Public License. It is used to keep track of the changes made to a source tree and to help programmers combine and otherwise manipulate changes made by multiple people or at different times. As of 2009, GNU arch's official status is deprecation, and only security fixes are applied. Bazaar (or 'bzr') has since also been made an official GNU project and can thus be considered the replacement for GNU arch. It is not a fork of arch. Features Being a distributed, decentralized versioning system, each revision stored using arch is uniquely globally identifiable; such identifier can be used in a distributed setting to easily merge or "cherry-pick" changes from completely disparate sources. Being decentralized means that there is no need for a central server for which developers have to be authorized in order to contribute. As with other systems, a full re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
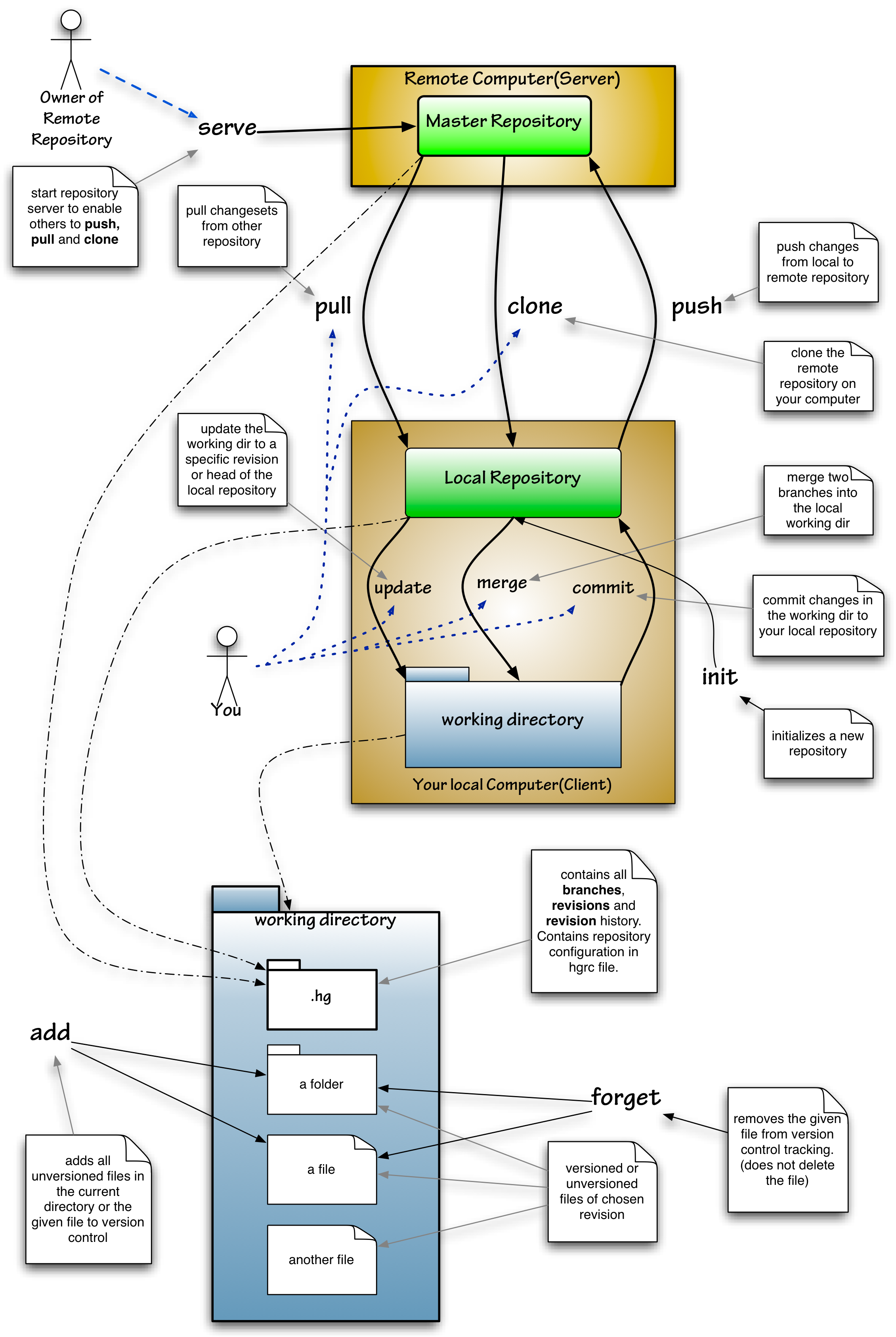
Mercurial
Mercurial is a distributed revision control tool for software developers. It is supported on Microsoft Windows, Linux, and other Unix-like systems, such as FreeBSD and macOS. Mercurial's major design goals include high performance and scalability, decentralization, fully distributed collaborative development, robust handling of both plain text and binary files, and advanced branching and merging capabilities, while remaining conceptually simple. It includes an integrated web-interface. Mercurial has also taken steps to ease the transition for users of other version control systems, particularly Subversion. Mercurial is primarily a command-line driven program, but graphical user interface extensions are available, e.g. TortoiseHg, and several IDEs offer support for version control with Mercurial. All of Mercurial's operations are invoked as arguments to its driver program hg (a reference to Hg – the chemical symbol of the element mercury). Olivia Mackall originated Mercu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Git (software)
Git () is a distributed version control software system, system that tracks versions of computer file, files. It is often used to control source code by Programmer, programmers who are software development, developing software collaboratively. Design goals of Git include speed, data integrity, and support for Distributed computing, distributed, non-linear workflows — thousands of parallel Branching (version control), branches running on different computers. "So I'm writing some scripts to try to track things a whole lot faster." As with most other distributed version control systems, and unlike most client–server systems, Git maintains a local copy of the entire Repository (version control), repository, also known as "repo", with history and version-tracking abilities, independent of Computer network, network access or a central Server (computing), server. A repository is stored on each computer in a standard directory (computing), directory with additional, Hidden f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partially Ordered Set
In mathematics, especially order theory, a partial order on a Set (mathematics), set is an arrangement such that, for certain pairs of elements, one precedes the other. The word ''partial'' is used to indicate that not every pair of elements needs to be comparable; that is, there may be pairs for which neither element precedes the other. Partial orders thus generalize total orders, in which every pair is comparable. Formally, a partial order is a homogeneous binary relation that is Reflexive relation, reflexive, antisymmetric relation, antisymmetric, and Transitive relation, transitive. A partially ordered set (poset for short) is an ordered pair P=(X,\leq) consisting of a set X (called the ''ground set'' of P) and a partial order \leq on X. When the meaning is clear from context and there is no ambiguity about the partial order, the set X itself is sometimes called a poset. Partial order relations The term ''partial order'' usually refers to the reflexive partial order relatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First-class Citizen
In a given programming language design, a first-class citizen is an entity which supports all the operations generally available to other entities. These operations typically include being passed as an argument, returned from a function, and assigned to a variable. History The concept of first- and second-class objects was introduced by Christopher Strachey in the 1960s. He did not actually define the term strictly, but contrasted real numbers and procedures in ALGOL: First and second class objects. In ALGOL, a real number may appear in an expression or be assigned to a variable, and either of them may appear as an actual parameter in a procedure call. A procedure, on the other hand, may only appear in another procedure call either as the operator (the most common case) or as one of the actual parameters. There are no other expressions involving procedures or whose results are procedures. Thus in a sense procedures in ALGOL are second class citizens—they always have to appear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |