|
Dapifer
A steward is an official who is appointed by the legal ruling monarch to represent them in a country and who may have a mandate to govern it in their name; in the latter case, it is synonymous with the position of regent, vicegerent, viceroy, king's lieutenant (for Romance languages), governor, or deputy (the Roman '' rector'', '' praefectus'', or ''vicarius''). Etymology From Old English ''stíweard, stiȝweard'', from ''stiȝ'' "hall, household" + ''weard'' "warden, keeper"; corresponding to Dutch: ''stadhouder'', German ''Statthalter'' "place holder", a Germanic parallel to French ''lieutenant''. The Old English term ''stíweard'' is attested from the 11th century. Its first element is most probably ''stiȝ-'' "house, hall" (attested only in composition; its cognate ''stiȝu'' is the ancestor of Modern English ''sty''). Old French and Old Norse ''stívarðr'' are adopted from the Old English. The German and Dutch term (Middle High German ''stat-halter'') is a parallel but ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Official
An official is someone who holds an office (function or mandate, regardless whether it carries an actual working space with it) in an organization or government and participates in the exercise of authority, (either their own or that of their superior and/or employer, public or legally private). An elected official is a person who is an official by virtue of an election. Officials may also be appointed '' ex officio'' (by virtue of another office, often in a specified capacity, such as presiding, advisory, secretary). Some official positions may be inherited. A person who currently holds an office is referred to as an incumbent. Something "official" refers to something endowed with governmental or other authoritative recognition or mandate, as in official language, official gazette, or official scorer. Etymology The word ''official'' as a noun has been recorded since the Middle English period, first seen in 1314. It comes from the Old French ''official'' (12th century), from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estate (land)
An estate is a large parcel of land under single ownership, which would historically generate income for its owner. British context In the UK, historically an estate comprises the houses, outbuildings, supporting farmland, and woods that surround the gardens and grounds of a very large property, such as a country house, mansion, palace or castle. It is the modern term for a manor, but lacks a manor's now-abolished jurisdiction. The "estate" formed an economic system where the profits from its produce and rents (of housing or agricultural land) sustained the main household, formerly known as the manor house. Thus, "the estate" may refer to all other cottages and villages in the same ownership as the mansion itself, covering more than one former manor. Examples of such great estates are Woburn Abbey in Bedfordshire, England, and Blenheim Palace, in Oxfordshire, England, built to replace the former manor house of Woodstock. In a more urban context are the "Great Estates" i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
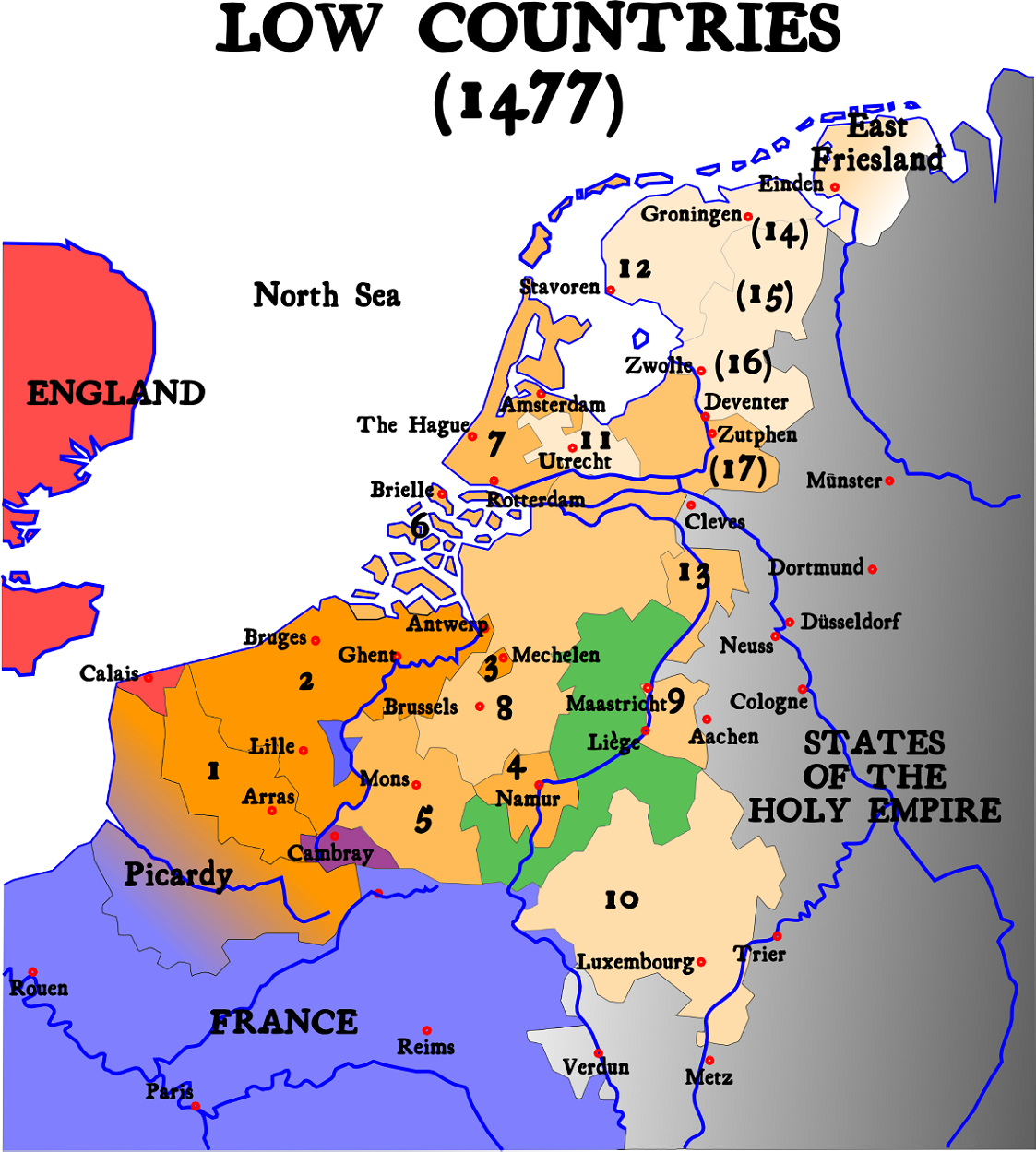
Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in Northwestern Europe forming the lower basin of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta and consisting of three countries: Belgium, the Netherlands and Luxembourg. Geographically and historically, the area also includes parts of France and Germany such as the French Flanders and the German regions of East Frisia and Cleves. During the Middle Ages, the Low Countries were divided into numerous semi-independent principalities. Historically, the regions without access to the sea linked themselves politically and economically to those with access to form various unions of ports and hinterland, stretching inland as far as parts of the German Rhineland. Because of this, nowadays not only physically low-altitude areas, but also some hilly or elevat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seventeen Provinces
The Seventeen Provinces were the Imperial states of the Habsburg Netherlands in the 16th century. They roughly covered the Low Countries, i.e., what is now the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, and most of the French departments of Nord (French Flanders and French Hainaut) and Pas-de-Calais (Artois). Also within this area were semi-independent fiefdoms, mainly ecclesiastical ones, such as Liège, Cambrai and Stavelot-Malmedy. The Seventeen Provinces arose from the Burgundian Netherlands, a number of fiefs held by the House of Valois-Burgundy and inherited by the Habsburg dynasty in 1482, and held by Habsburg Spain from 1556. Starting in 1512, the Provinces formed the major part of the Burgundian Circle. In 1581, the Seven United Provinces seceded to form the Dutch Republic. Composition After the Habsburg emperor Charles V had re-acquired the Duchy of Guelders from Duke William of Jülich-Cleves-Berg by the 1543 Treaty of Venlo, the Seventeen Provinces comprised: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feudal
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, cultural and political customs that flourished in medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structuring society around relationships that were derived from the holding of land in exchange for service or labour. Although it is derived from the Latin word ''feodum'' or ''feudum'' (fief), which was used during the Medieval period, the term ''feudalism'' and the system which it describes were not conceived of as a formal political system by the people who lived during the Middle Ages. The classic definition, by François Louis Ganshof (1944), François Louis Ganshof (1944). ''Qu'est-ce que la féodalité''. Translated into English by Philip Grierson as ''Feudalism'', with a foreword by F. M. Stenton, 1st ed.: New York and London, 1952; 2nd ed: 1961; 3rd ed.: 1976. describes a set of reciprocal legal and military obligations which existed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands (Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiography as the Dutch Republic, was a federal republic that existed from 1579, during the Dutch Revolt, to 1795 (the Batavian Revolution). It was a predecessor state of the Netherlands and the first fully independent Dutch nation state. The republic was established after seven Dutch provinces in the Spanish Netherlands revolted against rule by Spain. The provinces formed a mutual alliance against Spain in 1579 (the Union of Utrecht) and declared their independence in 1581 (the Act of Abjuration). It comprised Groningen, Frisia, Overijssel, Guelders, Utrecht, Holland and Zeeland. Although the state was small and contained only around 1.5 million inhabitants, it controlled a worldwide network of seafaring trade routes. Through its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Head Of State
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international persona." in its unity and legitimacy. Depending on the country's form of government and separation of powers, the head of state may be a ceremonial figurehead or concurrently the head of government and more (such as the president of the United States, who is also commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces). In a parliamentary system, such as the United Kingdom or India, the head of state usually has mostly ceremonial powers, with a separate head of government. However, in some parliamentary systems, like South Africa, there is an executive president that is both head of state and head of government. Likewise, in some parliamentary systems the head of state is not the head of government, but still has significant powers, for example Morocco. In contrast, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord High Steward Of Ireland
The Lord High Steward of Ireland is a hereditary Great Officer of State in the United Kingdom, sometimes known as the Hereditary Great Seneschal. The Earls of Shrewsbury (Earls of Waterford in the Peerage of Ireland) have held the office since the 15th century. Although the Irish Free State, later the Republic of Ireland, became independent in 1922, the title remained the same, rather than reflecting the region of Northern Ireland, which remains within the United Kingdom. The 1st Earl of Shrewsbury was created Earl of Waterford and Lord High Steward of Ireland on 17 July 1446 by letters patent of King Henry VI, to hold in tail male. The current Lord High Steward is his heir, the 22nd Earl of Shrewsbury. It was the Lord High Steward of Ireland, the Earl of Shrewsbury, who performed the responsibility of the curtana, and carrying the Sword of State at the Coronation of Queen Elizabeth II in June 1953. Four Swords of State are used, and the Lord High Steward of Ireland carries o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Steward Of Scotland
The title of High Steward or Great Steward is that of an officer who controls the domestic affairs of a royal household. In the 12th century King David I of Scotland gave the title to Walter fitz Alan, a nobleman from Brittany, whose descendants adopted the surname "Steward", later "Stewart" and later founded the royal House of Stewart. A junior branch of the Stewart family descended from the younger son of Alexander Stewart, 4th High Steward of Scotland (d.1283), namely " Stewart of Darnley", paternal ancestors of King James I & VI, lived for several generations in France, when the name became spelt in the French manner "Stuart" and "Dernelé". In 1371 Robert Stewart, 7th High Steward of Scotland inherited the throne of Scotland via his mother and became King Robert II of Scotland, when the title or office of High Steward of Scotland merged into the crown. However it was re-granted by the monarch to his elder son and heir apparent, together with the titles Duke of Rothesay ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clan Stewart
Clan Stewart ( Gaelic: ''Stiùbhart'') is a Scottish Highland and Lowland clan. The clan is recognised by Court of the Lord Lyon; however, it does not have a Clan Chief recognised by the Lord Lyon King of Arms. Because the clan has no chief it can be considered an armigerous clan; however, the Earls of Galloway are now considered to be the principal branch of this clan, and the crest and motto of The Earls of Galloway's arms are used in the Clan Stewart crest badge. The Court of the Lord Lyon recognises two other Stewart/Stuart clans, Clan Stuart of Bute and Clan Stewart of Appin. Clan Stuart of Bute is the only one of the three clans at present which has a recognised chief. History Origins of the Clan The Stewarts who became monarchs of Scotland were descended from a family who were seneschals (stewards) of Dol in Brittany, France. After the Norman conquest of England, the Stewarts acquired estates in England as the FitzAlan family, also Earls of Arundel. Walter Flaad or Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Steward
The Lord Steward or Lord Steward of the Household is an official of the Royal Household in England. He is always a peer. Until 1924, he was always a member of the Government. Until 1782, the office was one of considerable political importance and carried Cabinet rank. The Lord Steward receives his appointment from the Sovereign in person and bears a white staff as the emblem and warrant of his authority. He is the first dignitary of the court. In the House of Lords Precedence Act 1539, an Act of Parliament for placing of the lords, he is described as the grand master or lord steward of the king's most honourable household. He presided at the Board of Green Cloth, until the Board of Green Cloth disappeared in the reform of local government licensing in 2004, brought about by the Licensing Act 2003 (section 195). In his department are the Treasurer of the Household and Comptroller of the Household, who rank next to him. These officials were usually peers or the sons of peers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord High Steward
The Lord High Steward is the first of the Great Officers of State in England, nominally ranking above the Lord Chancellor. The office has generally remained vacant since 1421, and is now an ''ad hoc'' office that is primarily ceremonial and is filled only for a coronation. At coronations of the British monarch, the Lord High Steward bears St Edward's Crown. The Lord High Steward has the sole legal power to preside over impeachment trials of peers (which last happened in 1806). The trial of peers by their peers (a law which applied for felonies) was abolished in 1948. In general, but not invariably, the Lord Chancellor was deputised (to act as Lord High Steward) in the felony trials. There was a "Court of the Lord High Steward" which served this purpose when Parliament was not in session.William Blackstone (1769)''Commentaries on the Laws of England''vol. 4, chapter 19 Initially the position was largely an honorary one. It grew in importance until its holder became one of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)