|
Dacryocystitis
Dacryocystitis is an infection of the lacrimal sac, secondary to obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct at the junction of lacrimal sac. The term derives from the Greek ''dákryon'' ( tear), ''cysta'' (sac), and ''-itis'' (inflammation). It causes pain, redness, and swelling over the inner aspect of the lower eyelid and epiphora. When nasolacrimal duct obstruction is secondary to a congenital barrier it is referred to as dacryocystocele. It is most commonly caused by '' Staphylococcus aureus'' and ''Streptococcus pneumoniae''. The most common complication is corneal ulceration, frequently in association with ''S. pneumoniae''. The mainstays of treatment are oral antibiotics, warm compresses, and relief of nasolacrimal duct obstruction by dacryocystorhinostomy. Signs and symptoms *Pain, swelling, redness over the lacrimal sac at medial canthus *Tearing, crusting, fever *Digital pressure over the lacrimal sac may extrude pus through the punctum *In chronic cases, tearing may be th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dacryocystocele
Dacryocystocele (Dacryocystitis) or timo cyst is a benign, bluish-gray mass in the inferomedial canthus that develops within a few days or weeks after birth. The uncommon condition forms as a result as a consequence of narrowing or obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct, usually during prenatal development. Nasolacrimal duct obstruction disrupts the lacrimal drainage system, eventually creating a swelling cyst in the lacrimal sac area by the nasal cavity. The location of the cyst can cause respiratory dysfunction, compromising the airway. The obstruction ultimately leads to epiphora, an abundance of tear production. Signs and symptoms Dacryocystocele is a condition that can occur to all, at any age. However, the population most affected by this rare condition are infants. The intensity of the symptoms may vary depending on the type of dacryocystocele. There are three types of dacrycystocele: acute, congenital and chronic. Acute dacryocystocele is a bacterial infection, that includes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dacryocystocele
Dacryocystocele (Dacryocystitis) or timo cyst is a benign, bluish-gray mass in the inferomedial canthus that develops within a few days or weeks after birth. The uncommon condition forms as a result as a consequence of narrowing or obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct, usually during prenatal development. Nasolacrimal duct obstruction disrupts the lacrimal drainage system, eventually creating a swelling cyst in the lacrimal sac area by the nasal cavity. The location of the cyst can cause respiratory dysfunction, compromising the airway. The obstruction ultimately leads to epiphora, an abundance of tear production. Signs and symptoms Dacryocystocele is a condition that can occur to all, at any age. However, the population most affected by this rare condition are infants. The intensity of the symptoms may vary depending on the type of dacryocystocele. There are three types of dacrycystocele: acute, congenital and chronic. Acute dacryocystocele is a bacterial infection, that includes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lacrimal Sac
The lacrimal sac or lachrymal sac is the upper dilated end of the nasolacrimal duct, and is lodged in a deep groove formed by the lacrimal bone and frontal process of the maxilla. It connects the lacrimal canaliculi, which drain tears from the eye's surface, and the nasolacrimal duct, which conveys this fluid into the nasal cavity. Lacrimal sac occlusion leads to dacryocystitis. Structure It is oval in form and measures from 12 to 15 mm. in length; its upper end is closed and rounded; its lower is continued into the nasolacrimal duct. Its superficial surface is covered by a fibrous expansion derived from the medial palpebral ligament, and its deep surface is crossed by the lacrimal part of the orbicularis oculi, which is attached to the crest on the lacrimal bone. Histology Like the nasolacrimal duct, the sac is lined by stratified columnar epithelium with mucus-secreting goblet cells, with surrounding connective tissue. The Lacrimal Sac also drains the eye of debris and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dacryocystorhinostomy
Dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR) is a surgical procedure to restore the flow of tears into the nose from the lacrimal sac when the nasolacrimal duct does not function. Process Traditional A small incision is made on the side of the nose and some bone is removed to make a connection to the nose. Drains are left behind to prevent the gap from becoming closed and are removed after a few months. A Jones or Crawford tube is placed to facilitate the flow of tears from the eye to the nose. The lacrimal sacs must be avoided during this surgical procedure. Endoscopic The operation can also be performed endoscopically through the nose where an opening is fashioned in the lacrimal sac from within the nose. The advantages include lesser peri-operative morbidity, and no scar. Data suggests a slightly lower success rate than the "traditional" technique. With the advent of nasal endoscopes, endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy is becoming popular. In this procedure, a nasal endoscope is used to visuali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epiphora (medicine)
Epiphora is an overflow of tears onto the face, other than caused by normal crying. It is a clinical sign or condition that constitutes insufficient tear film drainage from the eyes, in that tears will drain down the face rather than through the nasolacrimal system. Cause Causes of epiphora are any that cause either overproduction of tears or decreased drainage of tears, resulting in tearing onto the cheek. This can be due to ocular irritation and inflammation (including trichiasis and entropion) or an obstructed tear outflow tract which is divided according to its anatomical location (i.e. ectropion, punctal, canalicular or nasolacrimal duct obstruction). The latter is often due to aging (a spontaneous process), conjunctivochalasis, infection (i.e. dacryocystitis), rhinitis, and in neonates or infants, failure of the nasolacrimal duct to open. Another cause could be poor reconstruction of the nasolacrimal duct system after trauma to the area. Cause of trauma could be facial f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of such infections. They may either kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the common cold or influenza; drugs which inhibit viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals rather than antibiotics. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against microbes, but in the usual medical usage, antibiotics (such as penicillin) are those produced naturally (by one microorganism fighting another), whereas non-antibiotic antibacterials (such as sulfonamides and antiseptics) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blindness
Visual impairment, also known as vision impairment, is a medical definition primarily measured based on an individual's better eye visual acuity; in the absence of treatment such as correctable eyewear, assistive devices, and medical treatment– visual impairment may cause the individual difficulties with normal daily tasks including reading and walking. Low vision is a functional definition of visual impairment that is chronic, uncorrectable with treatment or correctable lenses, and impacts daily living. As such low vision can be used as a disability metric and varies based on an individual's experience, environmental demands, accommodations, and access to services. The American Academy of Ophthalmology defines visual impairment as the best-corrected visual acuity of less than 20/40 in the better eye, and the World Health Organization defines it as a presenting acuity of less than 6/12 in the better eye. The term blindness is used for complete or nearly complete vision loss. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proptosis
Exophthalmos (also called exophthalmus, exophthalmia, proptosis, or exorbitism) is a bulging of the eye anteriorly out of the orbit. Exophthalmos can be either bilateral (as is often seen in Graves' disease) or unilateral (as is often seen in an orbital tumor). Complete or partial dislocation from the orbit is also possible from trauma or swelling of surrounding tissue resulting from trauma. In the case of Graves' disease, the displacement of the eye results from abnormal connective tissue deposition in the orbit and extraocular muscles, which can be visualized by CT or MRI. If left untreated, exophthalmos can cause the eyelids to fail to close during sleep, leading to corneal dryness and damage. Another possible complication is a form of redness or irritation called superior limbic keratoconjunctivitis, in which the area above the cornea becomes inflamed as a result of increased friction when blinking. The process that is causing the displacement of the eye may also compre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
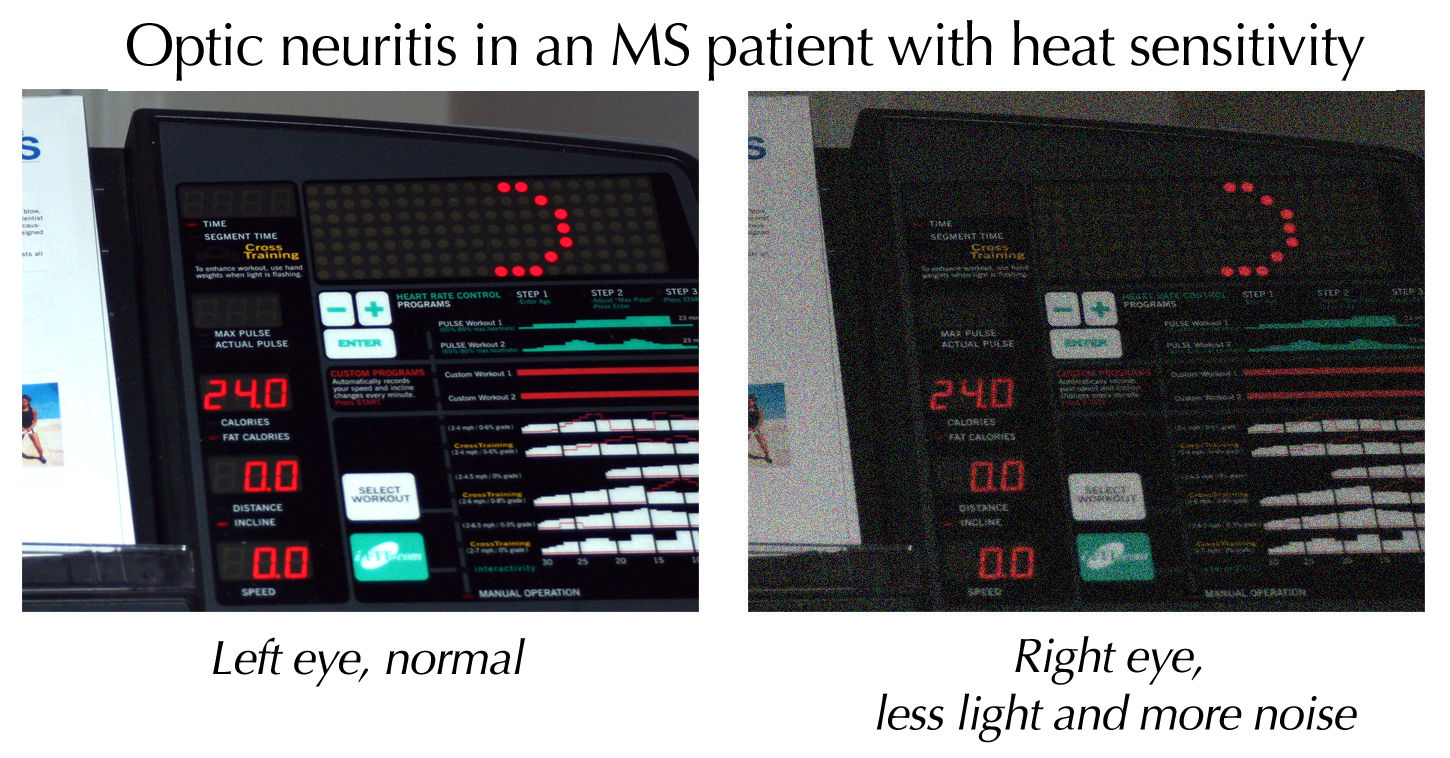
Optic Neuritis
Optic neuritis describes any condition that causes inflammation of the optic nerve; it may be associated with demyelinating diseases, or infectious or inflammatory processes. It is also known as optic papillitis (when the head of the optic nerve is involved), neuroretinitis (when there is a combined involvement of the optic disc and surrounding retina in the macular area) and retrobulbar neuritis (when the posterior part of the nerve is involved). Prelaminar optic neuritis describes involvement of the non-myelinated axons in the retina. It is most often associated with multiple sclerosis, and it may lead to complete or partial loss of vision in one or both eyes. Other causes include: # Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy # Parainfectious optic neuritis (associated with viral infections such as measles, mumps, chickenpox, whooping cough and glandular fever) # Infectious optic neuritis (sinus related or associated with cat-scratch fever, tuberculosis, Lyme disease and crypt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Cellulitis
Orbital cellulitis is inflammation of eye tissues behind the orbital septum. It is most commonly caused by an acute spread of infection into the eye socket from either the adjacent sinuses or through the blood. It may also occur after trauma. When it affects the rear of the eye, it is known as retro-orbital cellulitis. It should not be confused with periorbital cellulitis, which refers to cellulitis anterior to the septum. Without proper treatment, orbital cellulitis may lead to serious consequences, including permanent loss of vision or even death. Signs and symptoms Orbital cellulitis commonly presents with painful eye movement, sudden vision loss, chemosis, bulging of the infected eye, and limited eye movement. Along with these symptoms, patients typically have redness and swelling of the eyelid, pain, discharge, inability to open the eye, occasional fever and lethargy. Complications Complications include hearing loss, blood infection, meningitis, cavernous sinus thromb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warm Compresses
A warm compress is a method of applying heat to the body. Heating sources can include warm water, microwaveable pads, wheat packs and electrical or chemical pads. Some unorthodox methods can include warmed potatoes, uncooked rice, and hard-boiled eggs. The most common warm compress is a warm, wet washcloth. Uses Warm compresses are a common non-pharmacological therapy used in the treatment of things such as sports injuries, dental pain, post-operative wound healing, and ophthalmic conditions. They are believed to improve blood flow, increase oxygenation in tissues and help manage inflammation. For eye problems Warm compresses are commonly used for the treatment of certain ocular conditions such as: * dry eyes * pinkeye (conjunctivitis) * stye or chalazion * swollen eyelids ( blepharitis) * meibomian gland dysfunction * muscle spasms A spasm is a sudden involuntary contraction of a muscle, a group of muscles, or a hollow organ such as the bladder. A spasmodic muscle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |