|
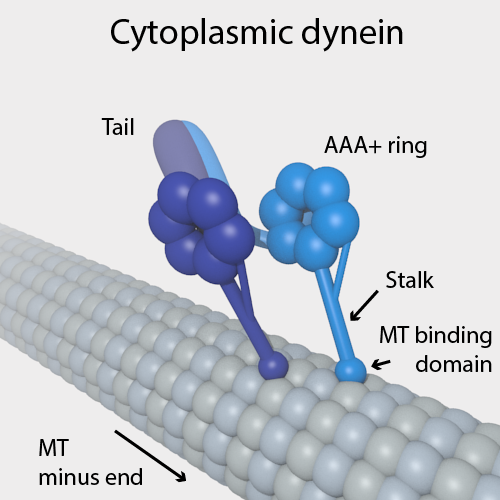
Cytoplasmic Dynein
Dyneins are a family of cytoskeletal motor proteins that move along microtubules in cells. They convert the chemical energy stored in ATP to mechanical work. Dynein transports various cellular cargos, provides forces and displacements important in mitosis, and drives the beat of eukaryotic cilia and flagella. All of these functions rely on dynein's ability to move towards the minus-end of the microtubules, known as retrograde transport; thus, they are called "minus-end directed motors". In contrast, most kinesin motor proteins move toward the microtubules' plus-end, in what is called anterograde transport. Classification Dyneins can be divided into two groups: cytoplasmic dyneins and axonemal dyneins, which are also called ciliary or flagellar dyneins. * cytoplasmic ** heavy chain: DYNC1H1, DYNC2H1 ** intermediate chain: DYNC1I1, DYNC1I2 ** light intermediate chain: DYNC1LI1, DYNC1LI2, DYNC2LI1 ** light chain: DYNLL1, DYNLL2, DYNLRB1, DYNLRB2, DYNLT1, DYNLT3 * axonemal * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DYNC1I1
Cytoplasmic dynein 1 intermediate chain 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''DYNC1I1'' gene. In melanocytic cells DYNC1I1 gene expression may be regulated by MITF. Interactions DYNC1I1 has been shown to interact with DYNLL1 Dynein light chain 1, cytoplasmic is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''DYNLL1'' gene. Function Cytoplasmic dyneins are large enzyme complexes with a molecular mass of about 1,200 kD. They contain two force-producing heads formed prim .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-7-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNAH1
Dynein axonemal heavy chain 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DNAH1 gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba .... Function This gene encodes an inner dynein arm heavy chain that provides structural support between the radial spokes and the outer doublet of the sperm tail. Naturally occurring mutations in this gene are associated with primary ciliary dyskinesia and multiple morphological anomalies of the flagella that result in asthenozoospermia and male infertility. Mice with a homozygous knockout of the orthologous gene are viable but have reduced sperm motility and are infertile. rovided by RefSeq, Feb 2017 References Further reading * * * * * * {{NLM content ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DYNLT3
Dynein, light chain, Tctex-type 3, also known as DYNLT3, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''DYNLT3'' gene. Function DYNLT3 is a member of the dynein motor protein family. DYNLT3 binds to BUB3, a spindle checkpoint protein is present on kinetochores at prometaphase. DYNLT3 can also function as a transcription regulator of Bcl-2 gene through binding to SATB1 in a dynein-independent manner. Interactions DYNLT3 has been shown to interact with VDAC1 Voltage-dependent anion-selective channel 1 (VDAC-1) is a beta barrel protein that in humans is encoded by the ''VDAC1'' gene located on chromosome 5. It forms an ion channel in the outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM) and also the outer cell membra .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-X-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DYNLT1
Dynein light chain Tctex-type 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DYNLT1 gene. Cytoplasmic dynein is the major motor protein complex responsible for minus-end, microtubule-based motile processes. Each dynein complex consists of 2 heavy chains that have ATPase and motor activities, plus a group of accessory polypeptides Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides. A p .... TCTEX1 is a dynein light chain involved in cargo binding (Chuang et al., 2005). upplied by OMIMref name="entrez" /> References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-6-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DYNLRB1
Dynein light chain roadblock-type 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''DYNLRB1'' gene. This gene is a member of the roadblock dynein light chain family and encodes a cytoplasmic protein that is capable of binding intermediate chain proteins. Upregulation of this gene has been associated with hepatocellular carcinomas Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of primary liver cancer in adults and is currently the most common cause of death in people with cirrhosis. HCC is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. It occurs in t ..., suggesting that this gene may be involved in tumor progression. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * {{gene-20-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DYNLL2
Dynein light chain 2, cytoplasmic is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''DYNLL2'' gene. Interactions DYNLL2 has been shown to interact with DLG4, C12orf40, DLGAP1, MYO5A Unconventional myosin-Va is a motor protein in charge of the intracellular transport of vesicles, organelles and protein complexes along the actin filaments. In humans it is coded for by the ''MYO5A'' gene. Structure In the presence of cargo ada ... and BMF. References Further reading * * * * * * * * External links * * {{gene-17-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DYNLL1
Dynein light chain 1, cytoplasmic is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''DYNLL1'' gene. Function Cytoplasmic dyneins are large enzyme complexes with a molecular mass of about 1,200 kD. They contain two force-producing heads formed primarily from dynein heavy chains, and stalks linking the heads to a basal domain, which contains a varying number of accessory intermediate chains. The complex is involved in intracellular transport and motility. The protein described in this record is a light chain and exists as part of this complex but also physically interacts with and inhibits the activity of neuronal nitric oxide synthase. Binding of this protein destabilizes the neuronal nitric oxide synthase dimer, a conformation necessary for activity, and it may regulate numerous biologic processes through its effects on nitric oxide synthase activity. Alternate transcriptional splice variants have been characterized. Interactions DYNLL1 has been shown to interact with: * BCL2L1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DYNC2LI1
DYFM (101.9 FM), broadcasting as Radyo5 101.9 News FM, is a radio station owned by the Nation Broadcasting Corporation and operated by TV5 Network Inc. The station's studio and transmitter are located at TV5 Complex, Capitol Road, Camp Marina, Brgy. Kalunasan, Cebu City. This station operates daily from 4:00 AM to 12:00 MN, concurrent with its flagship station in Manila. It is considered to be the first stereo FM station in Cebu City. History 1975-1998: MRS DYNC was Cebu's first FM station established on February 1, 1975, as MRS 101.9 Most Requested Song. It carried an adult contemporary format. It was located along Juana Osmeña, Ext. and later moved to Krizia Bldg. along Gorordo Ave. 1998-2008: Charlie On September 1, 1998, after NBC was acquired by PLDT Beneficial Trust Fund's broadcasting division MediaQuest Holdings, Inc from the consortium of the Yabut family and then House Speaker Manny Villar, the station was reformatted as ''Charlie @ Rhythms 101.9'', with a Top ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |