|
Cymenshore
Cymenshore is a place in Southern England where, according to the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'', Ælle of Sussex landed in AD 477 and battled the Britons with his three sons Cymen, Wlencing and Cissa, after the first of whom Cymenshore was held to have been named. Its location is unclear but was probably near Selsey. Historical context Foundation myths The account of Ælle and his three sons landing at Cymenshore appears in the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'', a collection of seven vernacular manuscripts, commissioned in the 9th century, some 400 years or more after the events at ''Cymenshore''. The legendary foundation of Saxon Sussex, by Ælle, is likely to have originated in an oral tradition before being recorded in the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle''. According to the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' ''Cymenshore'' is named after ''Cymen'', one of Ælle's sons. From 491 until the arrival of Christianity in the 7th century, there was a dearth of contemporary written material.Because of the lac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cissa Of Sussex
Cissa () was part of an Anglo-Saxon invasion force that landed in three ships at a place called Cymensora in AD 477. The invasion was led by Cissa's father Ælle and included his two brothers. They are said to have fought against the local Britons. Their conquest of what became Sussex, England continued when they fought a battle on the margins of Mecredesburne in 485 and Pevensey in 491 where they are said to have slaughtered their opponents to the last man. The main source for this story is the '' Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'', a series of annals written in the vernacular Old English. The ''Anglo Saxon Chronicle'' was commissioned in the reign of Alfred the Great some 400 years after the landing at Cymenshore. One of the purposes of the chronicle was to provide genealogies of the West Saxon kings. Although a lot of the ''facts'' provided by the chronicle can be verified, the foundation story of Sussex involving Ælle and his three sons can not. It is known that Anglo-Saxons did se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
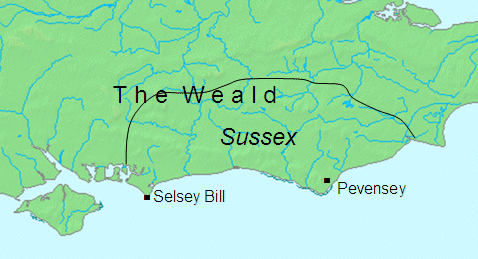
Kingdom Of Sussex
la, Regnum Sussaxonum , conventional_long_name = Kingdom of the South Saxons , capital = , era = Heptarchy , status = Vassal of Wessex (686–726, 827–860)Vassal of Mercia (771–796) , government_type = Monarchy , title_leader = Monarchs (see full list) , leader1 = Ælle , year_leader1 = 477–491 or later , leader2 = Æðelwealh , year_leader2 = ''fl.'' , p1 = Sub-Roman Britain , flag_p1 = Vexilloid of the Roman Empire.svg , border_p1 = no , p2 = Kingdom of Haestingas , flag_p2 = , s1 = Kingdom of England , flag_s1 = Flag of Wessex.svg , image_flag = , image_coat = , flag = , flag_type = , coat_type = , image_map = British kingdoms c 800.svg , image_map_c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ælle Of Sussex
Ælle (also Aelle or Ella) is recorded in early sources as the first king of the South Saxons, reigning in what is now called Sussex, England, from 477 to perhaps as late as 514. According to the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'', Ælle and three of his sons are said to have landed at a place called Cymensora and fought against the local Britons. The chronicle goes on to report a victory in 491, at present day Pevensey, where the battle ended with the Saxons slaughtering their opponents to the last man. Ælle was the first king recorded by the 8th century chronicler Bede to have held "''imperium''", or overlordship, over other Anglo-Saxon kingdoms.Bede, ''Ecclesiastical History'', II 5. In the late 9th-century ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' (around four hundred years after his time) Ælle is recorded as being the first bretwalda, or "Britain-ruler", though there is no evidence that this was a contemporary title. Ælle's death is not recorded and although he may have been the founder of a S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AD 477
__NOTOC__ Year 477 ( CDLXXVII) was a common year starting on Saturday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year after the Consulship of Basiliscus and Armatus (or, less frequently, year 1230 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 477 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Africa * January 25 – Genseric, ruler of the Vandal Kingdom, dies a natural death at Carthage, and is succeeded by his eldest son Huneric. He maintains control over the islands in the western Mediterranean Sea with his Vandal fleet, and rescinds his father's policy of persecuting the Roman Catholics in Africa. * The independent Mauro-Roman Kingdom (Kingdom of the Moors and Romans) is formed by Christian Berbers in the Roman province of Mauretania Caesariensis (present-day northern Algeria), bordering the Vandal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern England
Southern England, or the South of England, also known as the South, is an area of England consisting of its southernmost part, with cultural, economic and political differences from the Midlands and the North. Officially, the area includes Greater London, the South East, the West Country (or the South West), and the East (sometimes referred to as East Anglia). The distinction between the south and rest of England and Great Britain is sometimes referred to as the north–south divide. With a population of nearly 28 million; and an area of , the south accounts for roughly 40% of the population of the United Kingdom and approximately 25% of its area. Definitions For official purposes, the UK government does not refer to the Southern England as a single entity, but the Office for National Statistics divides UK into twelve regions. In England, the North West, North East and Yorkshire and the Humber make up the North ("centre-north"); the West Midlands and East Midlands (as wel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jetty Remains, Pagham Harbour - Geograph
A jetty is a structure that projects from land out into water. A jetty may serve as a breakwater, as a walkway, or both; or, in pairs, as a means of constricting a channel. The term derives from the French word ', "thrown", signifying something thrown out. For regulating rivers Another form of jetties, wing dams are extended out, opposite one another, ''from each bank of a river'', at intervals, to contract a wide channel, and by concentration of the current to produce a deepening. At the outlet of tideless rivers Jetties have been constructed on each side of the outlet river of some of the rivers flowing into the Baltic, with the objective of prolonging the scour of the river and protecting the channel from being shoaled by the littoral drift along the shore. Another application of parallel jetties is in lowering the bar in front of one of the mouths of a deltaic river flowing into a tide — a virtual prolongation of its less sea, by extending the scour of the rive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th century, and the first Old English literature, Old English literary works date from the mid-7th century. After the Norman conquest of 1066, English was replaced, for a time, by Anglo-Norman language, Anglo-Norman (a langues d'oïl, relative of French) as the language of the upper classes. This is regarded as marking the end of the Old English era, since during this period the English language was heavily influenced by Anglo-Norman, developing into a phase known now as Middle English in England and Early Scots in Scotland. Old English developed from a set of Anglo-Frisian languages, Anglo-Frisian or Ingvaeonic dialects originally spoken by Germanic peoples, Germanic tribes traditionally known as the Angles, Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Highdown Hill
Highdown Hill is a hill in the South Downs, with a height of . The summit of the hill and its western slopes lie in the parish of Ferring in the Arun district, while its eastern slopes lie in the borough of Worthing. It is a popular spot for picnickers, dog-walkers and local riders. It overlooks Littlehampton, Angmering, Ferring and Worthing with views, when the weather is good, east as far as the Seven Sisters and west to the Isle of Wight. It is the property of the National Trust. To the north the ancient hill forts of Cissbury Ring and Chanctonbury Ring can be seen, and the remains of an ancient hill fort exist on the summit of Highdown Hill. Highdown Hill is the traditional burial-place of the kings of Sussex.Alec Hamilton-Barr. In Saxon Sussex. The Arundel Press, Bognor Regis. p 21 At the base of the hill there is a car park, toilets, gardens, cafe, hotel and restaurant. The gardens are currently undergoing refurbishment. Early history Human occupation of the hill is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Ouse, Sussex
The Ouse ( ) is a 35 mile (56 kilometre) long river in the English county, counties of West Sussex, West and East Sussex. It rises near Lower Beeding in West Sussex, and flows eastwards and then southwards to reach the sea at Newhaven, East Sussex, Newhaven. It skirts Haywards Heath and passes through Lewes. It forms the main spine of an extensive network of smaller streams, of which the River Uck is the main tributary. As it nears the coast it passes through the Lewes and Laughton Levels, an area of flat, low-lying land that borders the river and another tributary, the Glynde Reach. It was a large tidal inlet at the time of the Domesday book in 1086, but over the following centuries, some attempts were made to reclaim some of the valley floor for agriculture, by building embankments, but the drainage was hampered by the buildup of a large shingle bar which formed across the mouth of the river by longshore drift. In 1539, a new channel for the entrance to the river was cut thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Cuckmere
The River Cuckmere rises near Heathfield in East Sussex, England on the southern slopes of the Weald. The name of the river probably comes from an Old English word meaning "fast-flowing", since it descends over 100 m (328 ft) in its initial four miles (6.4 km). It flows into the English Channel, and has the only undeveloped river mouth on the Sussex coast. Description The river has many tributaries at its upper end, the principal one being the River Bull; and its main channel begins at Hellingly. After crossing the Low Weald area of farmland, the Cuckmere cuts through the South Downs in its own valley. It reaches the English Channel at Cuckmere Haven, between Seaford and the Seven Sisters cliff face. The lower part of its course in the floodplain is marked by meandering. The Cuckmere Valley Nature Reserve is located in the lower estuary portion of the river. The valley is very important for nature conservation. It has been designated a Site of Special Scient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilfrid
Wilfrid ( – 709 or 710) was an English bishop and saint. Born a Northumbrian noble, he entered religious life as a teenager and studied at Lindisfarne, at Canterbury, in Francia, and at Rome; he returned to Northumbria in about 660, and became the abbot of a newly founded monastery at Ripon. In 664 Wilfrid acted as spokesman for the Roman position at the Synod of Whitby, and became famous for his speech advocating that the Roman method for calculating the date of Easter should be adopted. His success prompted the king's son, Alhfrith, to appoint him Bishop of Northumbria. Wilfrid chose to be consecrated in Gaul because of the lack of what he considered to be validly consecrated bishops in England at that time. During Wilfrid's absence Alhfrith seems to have led an unsuccessful revolt against his father, Oswiu of Northumbria, Oswiu, leaving a question mark over Wilfrid's appointment as bishop. Before Wilfrid's return Oswiu had appointed Saint Chad, Ceadda in his place, res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

.jpg)


