|
Cyclopropenium
The cyclopropenium ion is the cation with the formula . It has attracted attention as the smallest example of an aromatic cation. Its salts have been isolated, and many derivatives have been characterized by X-ray crystallography. The cation and some simple derivatives have been identified in the atmosphere of the Saturnian moon Titan. Bonding With two π electrons, the cyclopropenium cation class obeys Hückel’s rules of aromaticity for electrons since, in this case, ''n'' = 0. Consistent with this prediction, the C3H3 core is planar and the C–C bonds are equivalent. In the case of the cation in 3(SiMe3)3sup>+, the ring C–C distances range from 1.374(2) to 1.392(2) Å. Syntheses Salts of many cyclopropenyl cations have been characterized. Their stability varies according to the steric and inductive effects of the substituents. Salts of triphenylcyclopropenium were first reported by Ronald Breslow in 1957. The salt was prepared in two steps starting with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclopropenium Synthesis3
The cyclopropenium ion is the cation with the formula . It has attracted attention as the smallest example of an aromatic cation. Its salts have been isolated, and many derivatives have been characterized by X-ray crystallography. The cation and some simple derivatives have been identified in the atmosphere of the Saturnian moon Titan. Bonding With two π electrons, the cyclopropenium cation class obeys Hückel’s rules of aromaticity for electrons since, in this case, ''n'' = 0. Consistent with this prediction, the C3H3 core is planar and the C–C bonds are equivalent. In the case of the cation in 3(SiMe3)3sup>+, the ring C–C distances range from 1.374(2) to 1.392(2) Å. Syntheses Salts of many cyclopropenyl cations have been characterized. Their stability varies according to the steric and inductive effects of the substituents. Salts of triphenylcyclopropenium were first reported by Ronald Breslow in 1957. The salt was prepared in two steps starting with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphenylacetylene
Diphenylacetylene is the chemical compound C6H5C≡CC6H5. The molecule consists of two phenyl groups attached to a C2 unit. A colorless solid, it is used as a building block in organic synthesis and as a ligand in organometallic chemistry. Preparation and structure In one preparation for this compound, benzil is condensed with hydrazine to give the bis(hydrazone), which is oxidized with mercury(II) oxide. Alternatively stilbene is brominated, and the resulting dibromodiphenylethane is subjected to dehydrohalogenation, Yet another method starts involves the coupling iodobenzene and the copper salt of phenylacetylene in the Castro-Stephens coupling. Diphenylacetylene is a planar molecule. The central C≡C distance is 119.8 picometers. Derivatives Reaction of diphenylacetylene with tetraphenylcyclopentadienone results in the formation of hexaphenylbenzene in a Diels–Alder reaction. Reaction of Ph2C2 with benzal chloride in the presence of potassium ''t''-butoxide affords t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aromatic
In chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property of cyclic ( ring-shaped), ''typically'' planar (flat) molecular structures with pi bonds in resonance (those containing delocalized electrons) that gives increased stability compared to saturated compounds having single bonds, and other geometric or connective non-cyclic arrangements with the same set of atoms. Aromatic rings are very stable and do not break apart easily. Organic compounds that are not aromatic are classified as aliphatic compounds—they might be cyclic, but only aromatic rings have enhanced stability. The term ''aromaticity'' with this meaning is historically related to the concept of having an aroma, but is a distinct property from that meaning. Since the most common aromatic compounds are derivatives of benzene (an aromatic hydrocarbon common in petroleum and its distillates), the word ''aromatic'' occasionally refers informally to benzene derivatives, and so it was first defined. Nevertheless, many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrachlorocyclopropene
Tetrachlorocyclopropene is a chemical compound with the formula C3Cl4. A colorless liquid, the compound is a reagent used to prepare acetylene derivatives and in organic synthesis. It is prepared by addition of dichlorocarbene to trichloroethylene.{{cite journal, last1=Glück, first1=C, last2=Poingée, first2=V, last3=Schwager, first3=H, title=Improved Synthesis of 7,7-Difluorocyclopropabenzene, journal=Synthesis, volume=1987, issue=3, year=1987, pages=260–262, doi=10.1055/s-1987-27908, url=https://www.thieme-connect.com/products/ejournals/abstract/10.1055/s-1987-27908 The compound is used to prepare arylpropiolic acids: :C3Cl4 + ArH + 2 H2O → ArC2CO2H + 4 HCl Under some circumstances, diarylation occurs, giving diarylcyclopropenones, which decarbonylate to give diarylacetylenes. These reactions are thought to proceed via the intermediacy of trichlorocyclopropenium The cyclopropenium ion is the cation with the formula . It has attracted attention as the smallest e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrachlorocyclopropene
Tetrachlorocyclopropene is a chemical compound with the formula C3Cl4. A colorless liquid, the compound is a reagent used to prepare acetylene derivatives and in organic synthesis. It is prepared by addition of dichlorocarbene to trichloroethylene.{{cite journal, last1=Glück, first1=C, last2=Poingée, first2=V, last3=Schwager, first3=H, title=Improved Synthesis of 7,7-Difluorocyclopropabenzene, journal=Synthesis, volume=1987, issue=3, year=1987, pages=260–262, doi=10.1055/s-1987-27908, url=https://www.thieme-connect.com/products/ejournals/abstract/10.1055/s-1987-27908 The compound is used to prepare arylpropiolic acids: :C3Cl4 + ArH + 2 H2O → ArC2CO2H + 4 HCl Under some circumstances, diarylation occurs, giving diarylcyclopropenones, which decarbonylate to give diarylacetylenes. These reactions are thought to proceed via the intermediacy of trichlorocyclopropenium The cyclopropenium ion is the cation with the formula . It has attracted attention as the smallest e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid Chloride
In organic chemistry, an acyl chloride (or acid chloride) is an organic compound with the functional group . Their formula is usually written , where R is a side chain. They are reactive derivatives of carboxylic acids (). A specific example of an acyl chloride is acetyl chloride, . Acyl chlorides are the most important subset of acyl halides. Nomenclature Where the acyl chloride moiety takes priority, acyl chlorides are named by taking the name of the parent carboxylic acid, and substituting ''-yl chloride'' for ''-ic acid''. Thus: : : When other functional groups take priority, acyl chlorides are considered prefixes — ''chlorocarbonyl-'': : Properties Lacking the ability to form hydrogen bonds, acyl chlorides have lower boiling and melting points than similar carboxylic acids. For example, acetic acid boils at 118 °C, whereas acetyl chloride boils at 51 °C. Like most carbonyl compounds, infrared spectroscopy reveals a band near 1750 cm−1. The simplest s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclopropenone
Cyclopropenone is an organic compound with molecular formula C3H2O consisting of a cyclopropene carbon framework with a ketone functional group. It is a colorless, volatile liquid that boils near room temperature. Neat cyclopropenone polymerizes upon standing at room temperature. The chemical properties of the compound are dominated by the strong polarization of the carbonyl group, which gives a partial positive charge with aromatic stabilization on the ring and a partial negative charge on oxygen. It is an aromatic compound. See also * Diphenylcyclopropenone * Deltic acid *Tropone Tropone or 2,4,6-cycloheptatrien-1-one is an organic compound with some importance in organic chemistry as a non-benzenoid aromatic. The compound consists of a ring of seven carbon atoms with three conjugated alkene groups and a ketone group. Th ... References {{Molecules detected in outer space Enones Simple aromatic rings Cyclopropenes Non-benzenoid aromatic carbocycles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
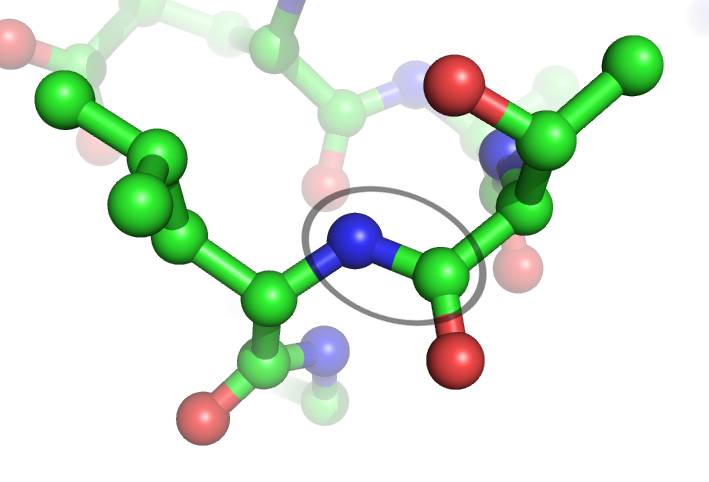
Peptide Bond
In organic chemistry, a peptide bond is an amide type of covalent chemical bond linking two consecutive alpha-amino acids from C1 (carbon number one) of one alpha-amino acid and N2 (nitrogen number two) of another, along a peptide or protein chain. It can also be called a eupeptide bond to distinguish it from an isopeptide bond, which is another type of amide bond between two amino acids. Synthesis When two amino acids form a ''dipeptide'' through a ''peptide bond'', it is a type of condensation reaction. In this kind of condensation, two amino acids approach each other, with the non-side chain (C1) carboxylic acid moiety of one coming near the non-side chain (N2) amino moiety of the other. One loses a hydrogen and oxygen from its carboxyl group (COOH) and the other loses a hydrogen from its amino group (NH2). This reaction produces a molecule of water (H2O) and two amino acids joined by a peptide bond (−CO−NH−). The two joined amino acids are called a dipeptide. The am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha amino acids appear in the genetic code. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups, as Alpha and beta carbon, alpha- , beta- , gamma- or delta- amino acids; other categories relate to Chemical polarity, polarity, ionization, and side chain group type (aliphatic, Open-chain compound, acyclic, aromatic, containing hydroxyl or sulfur, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino acid '' residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)