|
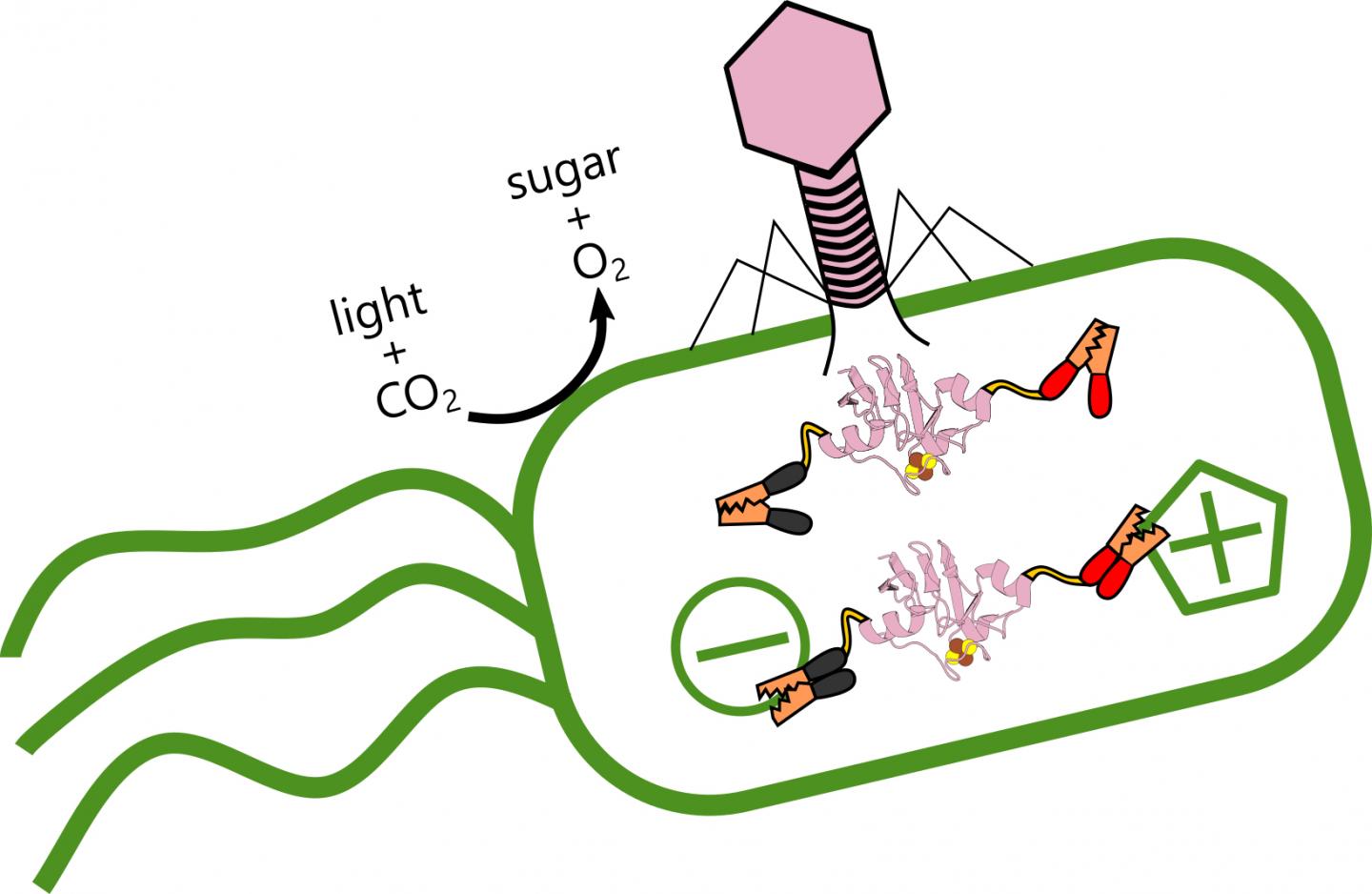
Cyanophage LPP-1
Cyanophages are viruses that infect cyanobacteria, also known as Cyanophyta or blue-green algae. Cyanobacteria are a phylum of bacteria that obtain their energy through the process of photosynthesis. Although cyanobacteria metabolize photoautotrophically like eukaryotic plants, they have prokaryotic cell structure. Cyanophages can be found in both freshwater and marine environments. Marine and freshwater cyanophages have icosahedral heads, which contain double-stranded DNA, attached to a tail by connector proteins. The size of the head and tail vary among species of cyanophages. Cyanophages infect a wide range of cyanobacteria and are key regulators of the cyanobacterial populations in aquatic environments, and may aid in the prevention of cyanobacterial blooms in freshwater and marine ecosystems. These blooms can pose a danger to humans and other animals, particularly in eutrophic freshwater lakes. Infection by these viruses is highly prevalent in cells belonging to ''Synechococcus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanophages
Cyanophages are viruses that infect cyanobacteria, also known as Cyanophyta or blue-green algae. Cyanobacteria are a phylum of bacteria that obtain their energy through the process of photosynthesis. Although cyanobacteria metabolize photoautotrophically like eukaryotic plants, they have Prokaryote, prokaryotic cell structure. Cyanophages can be found in both freshwater and marine environments. Marine and freshwater cyanophages have Regular icosahedron, icosahedral heads, which contain double-stranded DNA, attached to a tail by connector proteins. The size of the head and tail vary among species of cyanophages. Cyanophages infect a wide range of cyanobacteria and are key regulators of the cyanobacterial populations in aquatic environments, and may aid in the prevention of cyanobacterial blooms in freshwater and marine ecosystems. These blooms can pose a danger to humans and other animals, particularly in eutrophic freshwater lakes. Infection by these viruses is highly prevalent in c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CRC Press
The CRC Press, LLC is an American publishing group that specializes in producing technical books. Many of their books relate to engineering, science and mathematics. Their scope also includes books on business, forensics and information technology. CRC Press is now a division of Taylor & Francis, itself a subsidiary of Informa. History The CRC Press was founded as the Chemical Rubber Company (CRC) in 1903 by brothers Arthur, Leo and Emanuel Friedman in Cleveland, Ohio, based on an earlier enterprise by Arthur, who had begun selling rubber laboratory aprons in 1900. The company gradually expanded to include sales of laboratory equipment to chemists. In 1913 the CRC offered a short (116-page) manual called the ''Rubber Handbook'' as an incentive for any purchase of a dozen aprons. Since then the ''Rubber Handbook'' has evolved into the CRC's flagship book, the '' CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics''. In 1964, Chemical Rubber decided to focus on its publishing ventures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nostoc
''Nostoc'', also known as star jelly, troll’s butter, spit of moon, fallen star, witch's butter (not to be confused with the fungi commonly known as witches' butter), and witch’s jelly, is the most common genus of cyanobacteria found in various environments that may form colonies composed of filaments of moniliform cells in a gelatinous sheath of polysaccharides. ''Nostoc'' is a genus of photosynthetic, Gram-negative cyanobacteria that can be found in both terrestrial and aquatic environments. It may also grow symbiotically within the tissues of plants, providing nitrogen to its host through the action of terminally differentiated cells known as heterocysts. ''Nostoc'' is a genus that includes many species that are diverse in morphology, habitat distribution, and ecological function. ''Nostoc'' can be found in soil, on moist rocks, at the bottom of lakes and springs, and rarely in marine habitats. It may also be found in terrestrial temperate, desert, tropical, or polar env ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcystis
''Microcystis'' is a genus of freshwater cyanobacteria that includes the harmful algal bloom-forming ''Microcystis aeruginosa''. Many members of a ''Microcystis'' community can produce neurotoxins and hepatotoxins, such as microcystin and cyanopeptolin. Communities are often a mix of toxin-producing and nonproducing isolates. Etymology The genus ''Microcystis'' derives from the Greek ''mikros'' (small) + ''kystis'' (bladder) Physical characteristics As the etymological derivation implies, ''Microcystis'' is characterized by small cells (a few micrometre, micrometers in diameter), possessing gas-filled vesicles (also lacking individual sheaths). The cells are usually organized into colonies (aggregations of which are visible with the naked eye) that begin in a spherical shape, losing coherence to become perforated or irregularly shaped over time. These colonies are bound by a thick mucilage composed of complex polysaccharide compounds, including xylose, mannose, glucose, fuc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myovirus
''Myoviridae'' is a family of bacteriophages in the order ''Caudovirales''. Bacteria and archaea serve as natural hosts. There are 625 species in this family, assigned to eight subfamilies and 217 genera. Subdivisions The subfamily ''Tevenvirinae'' (synonym: ''Tequatrovirinae'') is named after its type species ''Enterobacteria phage T4''. Members of this subfamily are morphologically indistinguishable and have moderately elongated heads of about 110 nanometers (nm) in length, 114 nm long tails with a collar, base plates with short spikes and six long kinked tail fibers. The genera within this subfamily are divided on the basis of head morphology with the genus ''Tequatrovirus'' (Provisional name: ''T4virus'') having a head length of 137 nm and those in the genus ''Schizot4virus'' being 111 nm in length. Within the genera on the basis of protein homology the species have been divided into a number of groups. The subfamily ''Peduovirinae'' have virions with heads of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyngbya
''Lyngbya'' is a genus of cyanobacteria, unicellular autotrophs that form the basis of the oceanic food chain. As a result of recent genetic analyses, several new genera were erected from this genus: ''e.g.'', ''Moorea'', '' Limnoraphis'', '' Okeania'', '' Microseira'', and '' Dapis''. ''Lyngbya'' species form long, unbranching filaments inside a rigid mucilaginous sheath. Sheaths may form tangles or mats, intermixed with other phytoplankton species. They reproduce asexually. Their filaments break apart and each cell forms a new filament. The mats grow around atolls, salt marshes, or fresh water. Some ''Lyngbya'' species cause the human skin irritation called seaweed dermatitis. Some ''Lyngbya'' species can also temporarily monopolize aquatic ecosystems when they form dense, floating mats in the water. Ingestion of ''Lyngbya'' is potentially lethal. Most commonly, poisoning is caused by eating fish which have fed on ''Lyngbya'' or which have fed on other fish which have co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lysis
Lysis ( ) is the breaking down of the membrane of a cell, often by viral, enzymic, or osmotic (that is, "lytic" ) mechanisms that compromise its integrity. A fluid containing the contents of lysed cells is called a ''lysate''. In molecular biology, biochemistry, and cell biology laboratories, cell cultures may be subjected to lysis in the process of purifying their components, as in protein purification, DNA extraction, RNA extraction, or in purifying organelles. Many species of bacteria are subject to lysis by the enzyme lysozyme, found in animal saliva, egg white, and other secretions. Phage lytic enzymes (lysins) produced during bacteriophage infection are responsible for the ability of these viruses to lyse bacterial cells. Penicillin and related β-lactam antibiotics cause the death of bacteria through enzyme-mediated lysis that occurs after the drug causes the bacterium to form a defective cell wall. If the cell wall is completely lost and the penicillin was used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Host Organism
In biology and medicine, a host is a larger organism that harbours a smaller organism; whether a parasite, parasitic, a mutualism (biology), mutualistic, or a commensalism, commensalist ''guest'' (symbiont). The guest is typically provided with nourishment and shelter. Examples include animals playing host to parasitic worms (e.g. nematodes), cell (biology), cells harbouring pathogenic (disease-causing) viruses, a Fabaceae, bean plant hosting mutualistic (helpful) Rhizobia, nitrogen-fixing bacteria. More specifically in botany, a host plant supplies nutrient, food resources to micropredators, which have an evolutionarily stable strategy, evolutionarily stable relationship with their hosts similar to ectoparasitism. The host range is the collection of hosts that an organism can use as a partner. Symbiosis Symbiosis spans a wide variety of possible relationships between organisms, differing in their permanence and their effects on the two parties. If one of the partners in an ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxonomy (biology)
In biology, taxonomy () is the scientific study of naming, defining ( circumscribing) and classifying groups of biological organisms based on shared characteristics. Organisms are grouped into taxa (singular: taxon) and these groups are given a taxonomic rank; groups of a given rank can be aggregated to form a more inclusive group of higher rank, thus creating a taxonomic hierarchy. The principal ranks in modern use are domain, kingdom, phylum (''division'' is sometimes used in botany in place of ''phylum''), class, order, family, genus, and species. The Swedish botanist Carl Linnaeus is regarded as the founder of the current system of taxonomy, as he developed a ranked system known as Linnaean taxonomy for categorizing organisms and binomial nomenclature for naming organisms. With advances in the theory, data and analytical technology of biological systematics, the Linnaean system has transformed into a system of modern biological classification intended to reflect the evolu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family (taxonomy), family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anabaena Circinalis
''Anabaena circinalis'' is a species of Gram-negative, photosynthetic cyanobacteria common to freshwater environments throughout the world. Much of the scientific interest in '' A. circinalis '' owes to its production of several potentially harmful cyanotoxins, ranging in potency from irritating to lethal. Under favorable conditions for growth, '' A. circinalis '' forms large algae-like blooms, potentially harming the flora and fauna of an area. Morphology ''Anabaena circinalis'' exhibits a filamentous morphology, each filament a string of task-specific cells. The appearance of cell differentiation was a great evolutionary leap; marking cyanobacteria as one of the first multicellular organisms on Earth. On the '' A. circinalis '' filament, the most numerous structures are vegetative cells, responsible for the Photosynthesis#Cyanobacteria and the evolution of photosynthesis, photosynthesis of high-energy sugars from environmental carbon, water, and sunlight. The energy from p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_Figure_2.jpg)


.jpg)


