|
Cultural Psychology
Cultural psychology is the study of how cultures reflect and shape the psychological processes of their members.Heine, S. J. (2011). ''Cultural Psychology. ''New York: W. W. Norton & Company. It is based on the premise that mind and culture are inseparable and mutually constitutive, meaning that people are shaped by their culture and their culture is also shaped by them.Fiske, A.; Kitayama, S.; Markus, H.R.; & Nisbett, R.E. (1998)The cultural matrix of social psychology In D. Gilbert & S. Fiske & G. Lindzey (Eds.), The Handbook of Social Psychology (4th ed., pp. 915–81). San Francisco: McGraw-Hill. Cultural psychology aims to define culture, its nature and function, specifically in relation to psychological phenomena. Gerd Baumann has argued: "Culture is not a real thing, but an abstract and purely analytical notion. In itself «it» does not «cause» behavior, but denotes an abstraction from it, and is thus neither normative nor predictive but a heuristic means towards explain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Shweder
Richard Allan Shweder (born 1945) is an American cultural anthropologist and a figure in cultural psychology. He is currently Harold H. Swift Distinguished Service Professor of Human Development in the Department of Comparative Human Development at the University of Chicago."Richard Shweder" , Department of Comparative Human Development, University of Chicago. He is the author of ''Thinking Through Cultures: Expeditions in Cultural Psychology'' (1991) and ''Why Do Men Barbecue? Recipes for Cultural Psychology'' (2003). Education and career Shweder received his B.A. in anthropology from the in 1966 and his Ph.D. in[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Psychology
Cognitive psychology is the scientific study of mental processes such as attention, language use, memory, perception, problem solving, creativity, and reasoning. Cognitive psychology originated in the 1960s in a break from behaviorism, which held from the 1920s to 1950s that unobservable mental processes were outside the realm of empirical science. This break came as researchers in linguistics and cybernetics, as well as applied psychology, used models of mental processing to explain human behavior. Work derived from cognitive psychology was integrated into other branches of psychology and various other modern disciplines like cognitive science, linguistics, and economics. The domain of cognitive psychology overlaps with that of cognitive science, which takes a more interdisciplinary approach and includes studies of non-human subjects and artificial intelligence. History Philosophically, ruminations on the human mind and its processes have been around since the times of the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher learning in the United States and one of the most prestigious and highly ranked universities in the world. The university is composed of ten academic faculties plus Harvard Radcliffe Institute. The Faculty of Arts and Sciences offers study in a wide range of undergraduate and graduate academic disciplines, and other faculties offer only graduate degrees, including professional degrees. Harvard has three main campuses: the Cambridge campus centered on Harvard Yard; an adjoining campus immediately across Charles River in the Allston neighborhood of Boston; and the medical campus in Boston's Longwood Medical Area. Harvard's endowment is valued at $50.9 billion, making it the wealthiest academic institution in the world. Endowment inco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hazel Rose Markus
Hazel June Linda Rose Markus (born 9 March 1949) is a social psychologist and a pioneer in the field of cultural psychology. She is the Davis-Brack Professor in the Behavioral Sciences at Stanford University in Stanford, California. She is also a founder and faculty director oStanford SPARQ a "do tank" that partners with industry leaders to tackle disparities and inspire culture change using insights from behavioral science. She is a founder and former director of the Research Institute of the Center for Comparative Studies in Race and Ethnicity (CCSRE). Her research focuses on how culture shapes mind and behavior. She examines how many forms of culture (e.g., region of origin, ethnicity, race, social class, gender and occupation) influence the self, and in turn, how we think, feel, and act. Markus is a member of the National Academy of Sciences, a member of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences, and a Corresponding Fellow of the British Academy. A former president of the Soci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culture Of Honor (Southern United States)
The traditional culture of the Southern United States has been called a "culture of honor", that is, a culture where people avoid intentionally offending others, and maintain a reputation for not accepting improper conduct by others. A theory as to why the American South had or may have this culture is an assumed regional belief in retribution to enforce one's rights and deter predation against one's family, home, and possessions.Nisbett, R.E., & Cohen, D. (1996). ''Culture of honor: The psychology of violence in the South''. Boulder, CO: Westview Press. Background The "culture of honor" in the Southern United States is hypothesized by some social scientists to have its roots in the livelihoods of the early settlers who first inhabited the region. Unlike settlers with an agricultural heritage (mainly from the densely populated South East England and East Anglia) who settled in New England, the Southern United States was settled by herders from Scotland, Northern Ireland, Northe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereotyping
In social psychology, a stereotype is a generalized belief about a particular category of people. It is an expectation that people might have about every person of a particular group. The type of expectation can vary; it can be, for example, an expectation about the group's personality, preferences, appearance or ability. Stereotypes are sometimes overgeneralized, inaccurate, and resistant to new information, but can sometimes be accurate. While such generalizations about groups of people may be useful when making quick decisions, they may be erroneous when applied to particular individuals and are among the reasons for prejudicial attitudes. Explicit stereotypes An explicit stereotype refers to stereotypes that one is aware that one holds, and is aware that one is using to judge people. If person ''A ''is making judgments about a ''particular'' person ''B'' from a group ''G'', and person ''A'' has an explicit stereotype for group ''G'', their decision bias can be partial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self (sociology)
The self is an individual as the object of that individual’s own reflective consciousness. Since the ''self'' is a reference by a subject to the same subject, this reference is necessarily subjective. The sense of having a self—or ''selfhood''—should, however, not be confused with subjectivity itself. Ostensibly, this sense is directed outward from the subject to refer inward, back to its "self" (or itself). Examples of psychiatric conditions where such "sameness" may become broken include depersonalization, which sometimes occurs in schizophrenia: the self appears different from the subject. The first-person perspective distinguishes selfhood from personal identity. Whereas "identity" is (literally) sameness and may involve categorization and labeling, selfhood implies a first-person perspective and suggests potential uniqueness. Conversely, we use "person" as a third-person reference. Personal identity can be impaired in late-stage Alzheimer's disease and in other neurode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognition
Cognition refers to "the mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses". It encompasses all aspects of intellectual functions and processes such as: perception, attention, thought, intelligence, the formation of knowledge, memory and working memory, judgment and evaluation, reasoning and computation, problem solving and decision making, comprehension and production of language. Imagination is also a cognitive process, it is considered as such because it involves thinking about possibilities. Cognitive processes use existing knowledge and discover new knowledge. Cognitive processes are analyzed from different perspectives within different contexts, notably in the fields of linguistics, musicology, anesthesia, neuroscience, psychiatry, psychology, education, philosophy, anthropology, biology, systemics, logic, and computer science. These and other approaches to the analysis of cognition (such as embodied cognition) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perception
Perception () is the organization, identification, and interpretation of sensory information in order to represent and understand the presented information or environment. All perception involves signals that go through the nervous system, which in turn result from physical or chemical stimulation of the sensory system.Goldstein (2009) pp. 5–7 Vision involves light striking the retina of the eye; smell is mediated by odor molecules; and hearing involves pressure waves. Perception is not only the passive receipt of these signals, but it is also shaped by the recipient's learning, memory, expectation, and attention. Gregory, Richard. "Perception" in Gregory, Zangwill (1987) pp. 598–601. Sensory input is a process that transforms this low-level information to higher-level information (e.g., extracts shapes for object recognition). The process that follows connects a person's concepts and expectations (or knowledge), restorative and selective mechanisms (such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attention
Attention is the behavioral and cognitive process of selectively concentrating on a discrete aspect of information, whether considered subjective or objective, while ignoring other perceivable information. William James (1890) wrote that "Attention is the taking possession by the mind, in clear and vivid form, of one out of what seem several simultaneously possible objects or trains of thought. Focalization, concentration, of consciousness are of its essence." Attention has also been described as the allocation of limited cognitive processing resources. Attention is manifested by an attentional bottleneck, in terms of the amount of data the brain can process each second; for example, in human vision, only less than 1% of the visual input data (at around one megabyte per second) can enter the bottleneck, leading to inattentional blindness. Attention remains a crucial area of investigation within education, psychology, neuroscience, cognitive neuroscience, and neuropsychology. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shinobu Kitayama
Shinobu Kitayama (born March 9, 1957) is a Japanese social psychologist and the Robert B. Zajonc Collegiate Professor of Psychology at the University of Michigan. He is also the Social Psychology Area Chair and Director of the Culture & Cognition Program at the University of Michigan. He is the editor-in-chief of the Attitudes and Social Cognition section of the ''Journal of Personality and Social Psychology''. He received his bachelor's degree and master's degree from Kyoto University and his doctorate from the University of Michigan. Together with Mayumi Karasawa, he discovered the birthday-number effect, the subconscious tendency of people to prefer the numbers in the date of their birthday over other numbers. Prof. Kitayama is best known for his work on the social psychology of culture as it relates to the self. He and Hazel Rose Markus have argued that Western selves are constructed as independent from others, and people from many East Asian cultures construct interdependent se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
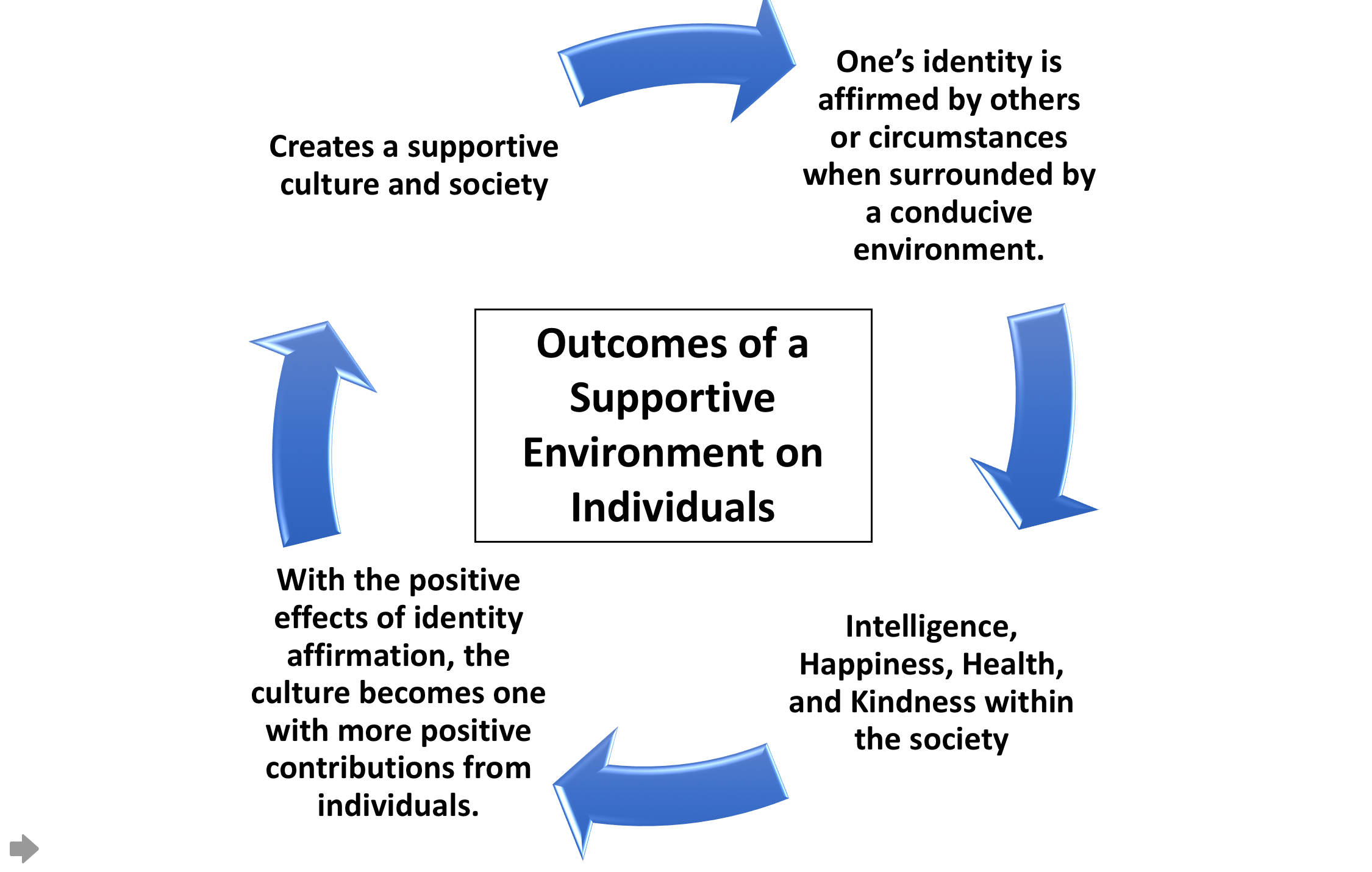
Positive Example Of Mutual Constitution In Society
Positive is a property of Positivity (other), positivity and may refer to: Mathematics and science * Positive formula, a logical formula not containing negation * Positive number, a number that is greater than 0 * Plus sign, the sign "+" used to indicate a positive number * Positive operator, a type of linear operator in mathematics * Positive result, a result that has been found significant in statistical hypothesis testing * Positive test, a diagnostic test result that indicates some parameter being evaluated was present * Positive charge, one of the two types of electrical charge * Positive (electrical polarity), in electrical circuits * Positive lens, in optics * Positive (photography), a positive image, in which the color and luminance correlates directly with that in the depicted scene * Positive sense, said of an RNA sequence that codes for a protein Philosophy and humanities * Affirmative (policy debate), the team which affirms the resolution * Negative and po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |