|
Cross Modal Plasticity
Cross modal plasticity is the adaptive reorganization of neurons to integrate the function of two or more sensory systems. Cross modal plasticity is a type of neuroplasticity and often occurs after sensory deprivation due to disease or brain damage. The reorganization of the neural network is greatest following long-term sensory deprivation, such as congenital blindness or pre-lingual deafness. In these instances, cross modal plasticity can strengthen other sensory systems to compensate for the lack of vision or hearing. This strengthening is due to new connections that are formed to brain cortices that no longer receive sensory input. Plasticity in the blind Even though the blind are no longer able to see, the visual cortex is still in active use, although it deals with information different from visual input. Studies found that the volume of white matter (myelinated nerve connections) was reduced in the optic tract, but not in the primary visual cortex itself. However, grey mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. In a human, the cerebral cortex contains approximately 14–16 billion neurons, and the estimated number of neurons in the cerebellum is 55–70 billion. Each neuron is connected by synapses to several thousand other neurons. These neurons typically communicate with one another by means of long fibers called axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potentials to distant parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipient cells. Physiologically, brains exert centralized control over a body's other organs. They act on the rest of the body both by generating patterns of muscle activity and by driving the secretion of chemicals called hormones. This centralized control allows rapid and coordinated respon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Parietal Cortex
The posterior parietal cortex (the portion of parietal neocortex posterior to the primary somatosensory cortex) plays an important role in planned movements, spatial reasoning, and attention. Damage to the posterior parietal cortex can produce a variety of sensorimotor deficits, including deficits in the perception and memory of spatial relationships, inaccurate reaching and grasping, in the control of eye movement, and inattention. The two most striking consequences of PPC damage are apraxia and hemispatial neglect. Anatomy The posterior parietal cortex receives input from the three sensory systems that play roles in the localization of the body and external objects in space: the visual system, the auditory system, and the somatosensory system. In turn, much of the output of the posterior parietal cortex goes to areas of frontal motor cortex: the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, various areas of the secondary motor cortex, and the frontal eye field. The posterior parietal cortex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auditory System
The auditory system is the sensory system for the sense of hearing. It includes both the sensory organs (the ears) and the auditory parts of the sensory system. System overview The outer ear funnels sound vibrations to the eardrum, increasing the sound pressure in the middle frequency range. The middle-ear ossicles further amplify the vibration pressure roughly 20 times. The base of the stapes couples vibrations into the cochlea via the oval window, which vibrates the perilymph liquid (present throughout the inner ear) and causes the round window to bulb out as the oval window bulges in. Vestibular and tympanic ducts are filled with perilymph, and the smaller cochlear duct between them is filled with endolymph, a fluid with a very different ion concentration and voltage. Vestibular duct perilymph vibrations bend organ of Corti outer cells (4 lines) causing prestin to be released in cell tips. This causes the cells to be chemically elongated and shrunk ( somatic motor), and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ears
An ear is the organ that enables hearing and, in mammals, body balance using the vestibular system. In mammals, the ear is usually described as having three parts—the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. The outer ear consists of the pinna and the ear canal. Since the outer ear is the only visible portion of the ear in most animals, the word "ear" often refers to the external part alone. The middle ear includes the tympanic cavity and the three ossicles. The inner ear sits in the bony labyrinth, and contains structures which are key to several senses: the semicircular canals, which enable balance and eye tracking when moving; the utricle and saccule, which enable balance when stationary; and the cochlea, which enables hearing. The ears of vertebrates are placed somewhat symmetrically on either side of the head, an arrangement that aids sound localisation. The ear develops from the first pharyngeal pouch and six small swellings that develop in the early embryo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sign Language
Sign languages (also known as signed languages) are languages that use the visual-manual modality to convey meaning, instead of spoken words. Sign languages are expressed through manual articulation in combination with non-manual markers. Sign languages are full-fledged natural languages with their own grammar and lexicon. Sign languages are not universal and are usually not mutually intelligible, although there are also similarities among different sign languages. Linguists consider both spoken and signed communication to be types of natural language, meaning that both emerged through an abstract, protracted aging process and evolved over time without meticulous planning. Sign language should not be confused with body language, a type of nonverbal communication. Wherever communities of deaf people exist, sign languages have developed as useful means of communication and form the core of local Deaf cultures. Although signing is used primarily by the deaf and hard of hearing, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
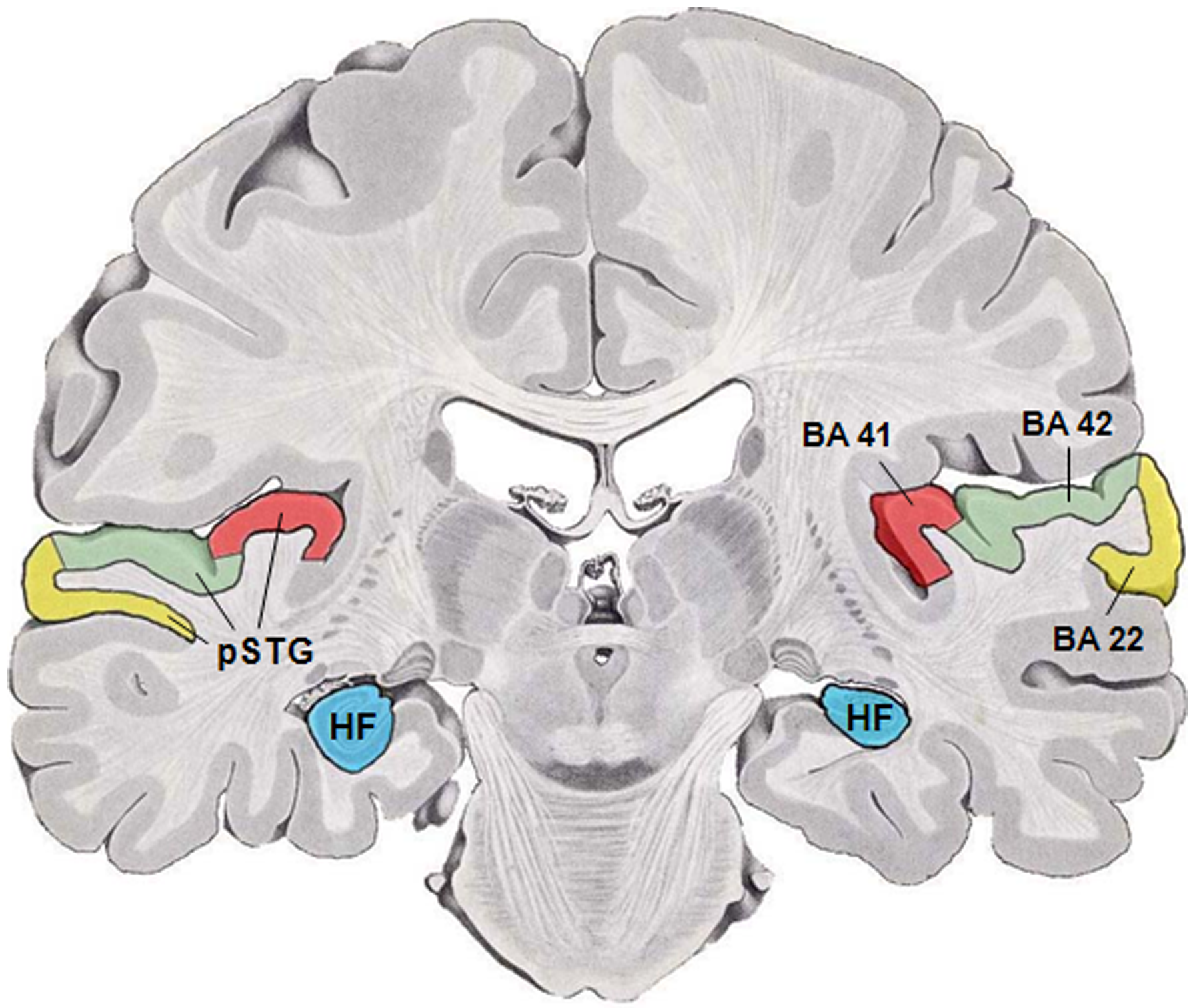
Primary Auditory Cortex
The auditory cortex is the part of the temporal lobe that processes auditory information in humans and many other vertebrates. It is a part of the auditory system, performing basic and higher functions in hearing, such as possible relations to language switching.Cf. Pickles, James O. (2012). ''An Introduction to the Physiology of Hearing'' (4th ed.). Bingley, UK: Emerald Group Publishing Limited, p. 238. It is located bilaterally, roughly at the upper sides of the temporal lobes – in humans, curving down and onto the medial surface, on the superior temporal plane, within the lateral sulcus and comprising parts of the transverse temporal gyri, and the superior temporal gyrus, including the planum polare and planum temporale (roughly Brodmann areas 41 and 42, and partially 22). The auditory cortex takes part in the spectrotemporal, meaning involving time and frequency, analysis of the inputs passed on from the ear. The cortex then filters and passes on the information to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FMRI
Functional magnetic resonance imaging or functional MRI (fMRI) measures brain activity by detecting changes associated with blood flow. This technique relies on the fact that cerebral blood flow and neuronal activation are coupled. When an area of the brain is in use, blood flow to that region also increases. The primary form of fMRI uses the blood-oxygen-level dependent (BOLD) contrast, discovered by Seiji Ogawa in 1990. This is a type of specialized brain and body scan used to map neural activity in the brain or spinal cord of humans or other animals by imaging the change in blood flow (hemodynamic response) related to energy use by brain cells. Since the early 1990s, fMRI has come to dominate brain mapping research because it does not involve the use of injections, surgery, the ingestion of substances, or exposure to ionizing radiation. This measure is frequently corrupted by noise from various sources; hence, statistical procedures are used to extract the underlying signal. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prelingual Deafness
Prelingual deafness refers to deafness that occurs before learning speech or language. Speech and language typically begin to develop very early with infants saying their first words by age one. Therefore, prelingual deafness is considered to occur before the age of one, where a baby is either born deaf (known as congenital deafness) or loses hearing before the age of one. This hearing loss may occur for a variety of reasons and impacts cognitive, social, and language development. Statistics There are approximately 12,000 children with hearing loss in the United States. Profound hearing loss occurs in somewhere between 4 and 11 per every 10,000 children. In 2017, according to the CDC, of the 3,742,608 babies screened, 3,896 were diagnosed with hearing loss before the age of three months or 1.7 babies per 1,000 births were diagnosed with hearing loss in the United States. Causes Prelingual hearing loss can be considered congenital, present at birth, or acquired, occurring after birt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sense Of Touch
In physiology, the somatosensory system is the network of neural structures in the brain and body that produce the perception of touch (haptic perception), as well as temperature (thermoception), body position (proprioception), and pain. It is a subset of the sensory nervous system, which also represents visual, auditory, olfactory, and gustatory stimuli. Somatosensation begins when mechano- and thermosensitive structures in the skin or internal organs sense physical stimuli such as pressure on the skin (see mechanotransduction, nociception). Activation of these structures, or receptors, leads to activation of peripheral sensory neurons that convey signals to the spinal cord as patterns of action potentials. Sensory information is then processed locally in the spinal cord to drive reflexes, and is also conveyed to the brain for conscious perception of touch and proprioception. Note, somatosensory information from the face and head enters the brain through peripheral sen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Braille
Braille (Pronounced: ) is a tactile writing system used by people who are visually impaired, including people who are Blindness, blind, Deafblindness, deafblind or who have low vision. It can be read either on Paper embossing, embossed paper or by using refreshable braille displays that connect to computers and smartphone devices. Braille can be written using a slate and stylus, a braille writer, an electronic braille notetaker or with the use of a computer connected to a braille embosser. Braille is named after its creator, Louis Braille, a Frenchman who lost his sight as a result of a childhood accident. In 1824, at the age of fifteen, he developed the braille code based on the French alphabet as an improvement on night writing. He published his system, which subsequently included musical notation, in 1829. The second revision, published in 1837, was the first Binary numeral system, binary form of writing developed in the modern era. Braille characters are formed using a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Control
A scientific control is an experiment or observation designed to minimize the effects of variables other than the independent variable (i.e. confounding variables). This increases the reliability of the results, often through a comparison between control measurements and the other measurements. Scientific controls are a part of the scientific method. Controlled experiments Controls eliminate alternate explanations of experimental results, especially experimental errors and experimenter bias. Many controls are specific to the type of experiment being performed, as in the molecular markers used in SDS-PAGE experiments, and may simply have the purpose of ensuring that the equipment is working properly. The selection and use of proper controls to ensure that experimental results are valid (for example, absence of confounding variables) can be very difficult. Control measurements may also be used for other purposes: for example, a measurement of a microphone's background noise in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |