|
Crista Ampullaris
The crista ampullaris is the sensory organ of rotation. They are found in the osseous ampullae, ampullae of each of the semicircular canals of the inner ear, meaning that there are three pairs in total. The function of the crista ampullaris is to sense angular acceleration and deceleration. Background The inner ear comprises three specialized regions of the membranous labyrinth: the vestibular sacs – the utricle (ear), utricle and saccule, and the semicircular canals, which are the vestibular organs, as well as the cochlear duct, which is involved in the special sense of Hearing (sense), hearing. The semicircular canals are filled with endolymph due to its connection with the cochlear duct via the saccule, which also contains endolymph. It also contains an inner membranous sleeve that lines the semicircular canals. The canals also contain the crista ampullaris. The hair cell, receptor cells located in the semicircular ducts are innervated by the eighth cranial nerve, the vestib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semicircular Canals
The semicircular canals or semicircular ducts are three semicircular, interconnected tubes located in the innermost part of each ear, the inner ear. The three canals are the horizontal, superior and posterior semicircular canals. Structure The semicircular canals are a component of the bony labyrinth that are at right angles from each other. At one end of each of the semicircular canals is a dilated sac called an osseous ampulla, which is more than twice the diameter of the canal. Each ampulla contains an ampullary crest, the crista ampullaris which consists of a thick gelatinous cap called a ampullary cupula, cupula and many hair cells. The superior and posterior semicircular canals are oriented vertically at right angles to each other. The lateral semicircular canal is about a 30-degree angle from the horizontal plane. The orientations of the canals cause a different canal to be stimulated by movement of the head in different planes, and more than one canal is stimulated at onc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
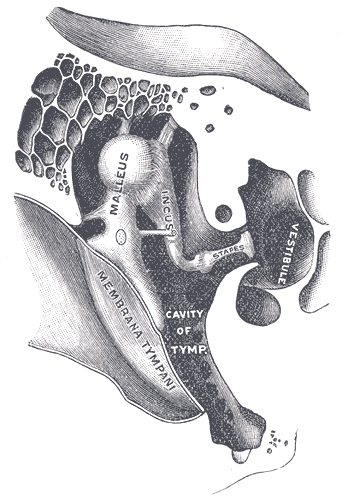
Inner Ear
The inner ear (internal ear, auris interna) is the innermost part of the vertebrate ear. In vertebrates, the inner ear is mainly responsible for sound detection and balance. In mammals, it consists of the bony labyrinth, a hollow cavity in the temporal bone of the skull with a system of passages comprising two main functional parts: * The cochlea, dedicated to hearing; converting sound pressure patterns from the outer ear into electrochemical impulses which are passed on to the brain via the auditory nerve. * The vestibular system, dedicated to balance The inner ear is found in all vertebrates, with substantial variations in form and function. The inner ear is innervated by the eighth cranial nerve in all vertebrates. Structure The labyrinth can be divided by layer or by region. Bony and membranous labyrinths The bony labyrinth, or osseous labyrinth, is the network of passages with bony walls lined with periosteum. The three major parts of the bony labyrinth are the vestib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osseous Ampullae
The semicircular canals or semicircular ducts are three semicircular, interconnected tubes located in the innermost part of each ear, the inner ear. The three canals are the horizontal, superior and posterior semicircular canals. Structure The semicircular canals are a component of the bony labyrinth that are at right angles from each other. At one end of each of the semicircular canals is a dilated sac called an osseous ampulla, which is more than twice the diameter of the canal. Each ampulla contains an ampullary crest, the crista ampullaris which consists of a thick gelatinous cap called a cupula and many hair cells. The superior and posterior semicircular canals are oriented vertically at right angles to each other. The lateral semicircular canal is about a 30-degree angle from the horizontal plane. The orientations of the canals cause a different canal to be stimulated by movement of the head in different planes, and more than one canal is stimulated at once if the movement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semicircular Canals
The semicircular canals or semicircular ducts are three semicircular, interconnected tubes located in the innermost part of each ear, the inner ear. The three canals are the horizontal, superior and posterior semicircular canals. Structure The semicircular canals are a component of the bony labyrinth that are at right angles from each other. At one end of each of the semicircular canals is a dilated sac called an osseous ampulla, which is more than twice the diameter of the canal. Each ampulla contains an ampullary crest, the crista ampullaris which consists of a thick gelatinous cap called a ampullary cupula, cupula and many hair cells. The superior and posterior semicircular canals are oriented vertically at right angles to each other. The lateral semicircular canal is about a 30-degree angle from the horizontal plane. The orientations of the canals cause a different canal to be stimulated by movement of the head in different planes, and more than one canal is stimulated at onc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Membranous Labyrinth
The membranous labyrinth is a collection of fluid filled tubes and chambers which contain the receptors for the senses of equilibrium and hearing. It is lodged within the bony labyrinth in the inner ear and has the same general form; it is, however, considerably smaller and is partly separated from the bony walls by a quantity of fluid, the perilymph. In certain places, it is fixed to the walls of the cavity. The membranous labyrinth contains fluid called endolymph. The walls of the membranous labyrinth are lined with distributions of the cochlear nerve, one of the two branches of the vestibulocochlear nerve. The other branch is the vestibular nerve. Within the vestibule, the membranous labyrinth does not quite preserve the form of the bony labyrinth, but consists of two membranous sacs, the utricle, and the saccule The saccule is a bed of sensory cells in the inner ear. It translates head movements into neural impulses for the brain to interpret. The saccule detects line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utricle (ear)
The utricle and saccule are the two otolith organs in the vertebrate inner ear. They are part of the balancing system (membranous labyrinth) in the vestibule of the bony labyrinth (small oval chamber). They use small stones and a viscous fluid to stimulate hair cells to detect motion and orientation. The utricle detects linear accelerations and head-tilts in the horizontal plane. The word utricle comes . Structure The utricle is larger than the saccule and is of an oblong form, compressed transversely, and occupies the upper and back part of the vestibule, lying in contact with the recessus ellipticus and the part below it. Macula The macula of utricle (macula acustica utriculi) is a small (2 by 3 mm) thickening lying horizontally on the floor of the utricle where the epithelium contains vestibular hair cells that allow a person to perceive changes in latitudinal acceleration as well as the effects of gravity; it receives the utricular filaments of the acoustic nerve. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saccule
The saccule is a bed of sensory cells in the inner ear. It translates head movements into neural impulses for the brain to interpret. The saccule detects linear accelerations and head tilts in the vertical plane. When the head moves vertically, the sensory cells of the saccule are disturbed and the neurons connected to them begin transmitting impulses to the brain. These impulses travel along the vestibular portion of the eighth cranial nerve to the vestibular nuclei in the brainstem. The vestibular system is important in maintaining balance, or equilibrium. The vestibular system includes the saccule, utricle, and the three semicircular canals. The vestibule is the name of the fluid-filled, membranous duct that contains these organs of balance. The vestibule is encased in the temporal bone of the skull. Structure The saccule, or sacculus, is the smaller of the two vestibular sacs. It is globular in form and lies in the recessus sphæricus near the opening of the vest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vestibular Organs
The vestibular system, in vertebrates, is a sensory system that creates the sense of balance and spatial orientation for the purpose of coordinating movement with balance. Together with the cochlea, a part of the auditory system, it constitutes the labyrinth of the inner ear in most mammals. As movements consist of rotations and translations, the vestibular system comprises two components: the semicircular canals, which indicate rotational movements; and the otoliths, which indicate linear accelerations. The vestibular system sends signals primarily to the neural structures that control eye movement; these provide the anatomical basis of the vestibulo-ocular reflex, which is required for clear vision. Signals are also sent to the muscles that keep an animal upright and in general control posture; these provide the anatomical means required to enable an animal to maintain its desired position in space. The brain uses information from the vestibular system in the head and from p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cochlear Duct
The cochlear duct (bounded by the scala media) is an endolymph filled cavity inside the cochlea, located between the tympanic duct and the vestibular duct, separated by the basilar membrane and the vestibular membrane (Reissner's membrane) respectively. The cochlear duct houses the organ of Corti. Structure The cochlear duct is part of the cochlea. It is separated from the tympanic duct (scala tympani) by the basilar membrane. It is separated from the vestibular duct (scala vestibuli) by the vestibular membrane (Reissner's membrane). The stria vascularis is located in the wall of the cochlear duct. Development The cochlear duct develops from the ventral otic vesicle (otocyst). It grows slightly flattened between the middle and outside of the body. This development may be regulated by the genes EYA1, SIX1, GATA3, and TBX1. The organ of Corti develops inside the cochlear duct. Function The cochlear duct contains the organ of Corti. This is attached to the basilar membran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Sense
In medicine and anatomy, the special senses are the senses that have specialized organs devoted to them: * vision (the eye) * hearing and balance (the ear, which includes the auditory system and vestibular system) * smell (the nose) * taste (the tongue) The distinction between special and general senses is used to classify nerve fibers running to and from the central nervous system – information from special senses is carried in special somatic afferents and special visceral afferents. In contrast, the other sense, touch, is a somatic sense which does not have a specialized organ but comes from all over the body, most noticeably the skin but also the internal organs (viscera). Touch includes mechanoreception (pressure, vibration and proprioception), pain (nociception) and heat (thermoception), and such information is carried in general somatic afferents and general visceral afferents. Vision Visual perception is the ability to interpret the surrounding environment using lig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hearing (sense)
Hearing, or auditory perception, is the ability to perceive sounds through an organ, such as an ear, by detecting vibrations as periodic changes in the pressure of a surrounding medium. The academic field concerned with hearing is auditory science. Sound may be heard through solid, liquid, or gaseous matter. It is one of the traditional five senses. Partial or total inability to hear is called hearing loss. In humans and other vertebrates, hearing is performed primarily by the auditory system: mechanical waves, known as vibrations, are detected by the ear and transduced into nerve impulses that are perceived by the brain (primarily in the temporal lobe). Like touch, audition requires sensitivity to the movement of molecules in the world outside the organism. Both hearing and touch are types of mechanosensation. Hearing mechanism There are three main components of the human auditory system: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. Outer ear The outer ear in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endolymph
Endolymph is the fluid contained in the membranous labyrinth of the inner ear. The major cation in endolymph is potassium, with the values of sodium and potassium concentration in the endolymph being 0.91 mM and 154 mM, respectively. It is also called ''Scarpa's fluid'', after Antonio Scarpa. Structure The inner ear has two parts: the bony labyrinth and the membranous labyrinth. The membranous labyrinth is contained within the bony labyrinth, and within the membranous labyrinth is a fluid called endolymph. Between the outer wall of the membranous labyrinth and the wall of the bony labyrinth is the location of perilymph. Composition Perilymph and endolymph have unique ionic compositions suited to their functions in regulating electrochemical impulses of hair cells. The electric potential of endolymph is ~80-90 mV more positive than perilymph due to a higher concentration of K compared to Na. The main component of this unique extracellular fluid is potassium, which is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |