|
Cremasteric Reflex
The cremasteric reflex is a superficial (i.e., close to the skin's surface) reflex observed in human males. This reflex is elicited by lightly stroking or poking the superior and medial (inner) part of the thigh—regardless of the direction of stroke. The normal response is an immediate contraction of the cremaster muscle that pulls up the testis ipsilaterally (on the same side of the body). The reflex utilizes sensory and motor fibers from two different nerves. When the inner thigh is stroked, sensory fibers of the ilioinguinal nerve are stimulated. These activate the motor fibers of the genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve which causes the cremaster muscle to contract and elevate the testis. Clinical conditions In boys, this reflex may be exaggerated which can occasionally lead to a misdiagnosis of cryptorchidism. The cremasteric reflex may be absent with testicular torsion, upper and lower motor neuron disorders, as well as a spine injury of L1-L2. It can also occur if ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cremasteric Reflex
The cremasteric reflex is a superficial (i.e., close to the skin's surface) reflex observed in human males. This reflex is elicited by lightly stroking or poking the superior and medial (inner) part of the thigh—regardless of the direction of stroke. The normal response is an immediate contraction of the cremaster muscle that pulls up the testis ipsilaterally (on the same side of the body). The reflex utilizes sensory and motor fibers from two different nerves. When the inner thigh is stroked, sensory fibers of the ilioinguinal nerve are stimulated. These activate the motor fibers of the genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve which causes the cremaster muscle to contract and elevate the testis. Clinical conditions In boys, this reflex may be exaggerated which can occasionally lead to a misdiagnosis of cryptorchidism. The cremasteric reflex may be absent with testicular torsion, upper and lower motor neuron disorders, as well as a spine injury of L1-L2. It can also occur if ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
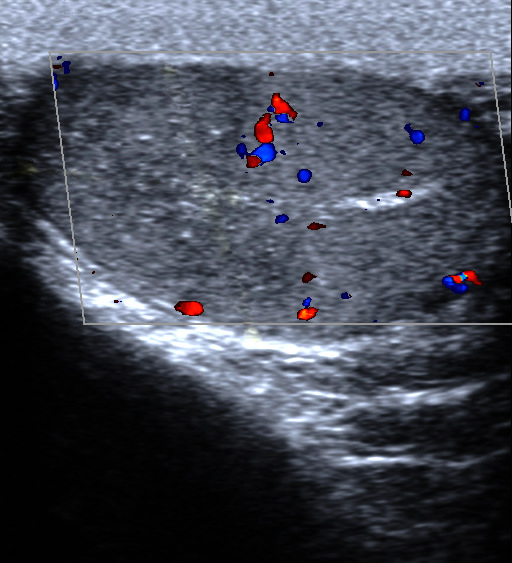
Testicular Torsion
Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord (from which the testicle is suspended) twists, cutting off the blood supply to the testicle. The most common symptom in children is sudden, severe testicular pain. The testicle may be higher than usual in the scrotum and vomiting may occur. In newborns, pain is often absent and instead the scrotum may become discolored or the testicle may disappear from its usual place. Most of those affected have no obvious prior underlying health problems. Testicular tumor or prior trauma may increase risk. Other risk factors include a congenital malformation known as a "bell-clapper deformity" wherein the testis is inadequately attached to the scrotum allowing it to move more freely and thus potentially twist. Cold temperatures may also be a risk factor. The diagnosis should usually be made based on the presenting symptoms, but requires timely diagnosis and treatment to avoid testicular loss. An ultrasound can be useful when the diagnosis is u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Necrosis
Necrosis () is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. Necrosis is caused by factors external to the cell or tissue, such as infection, or trauma which result in the unregulated digestion of cell components. In contrast, apoptosis is a naturally occurring programmed and targeted cause of cellular death. While apoptosis often provides beneficial effects to the organism, necrosis is almost always detrimental and can be fatal. Cellular death due to necrosis does not follow the apoptotic signal transduction pathway, but rather various receptors are activated and result in the loss of cell membrane integrity and an uncontrolled release of products of cell death into the extracellular space. This initiates in the surrounding tissue an inflammatory response, which attracts leukocytes and nearby phagocytes which eliminate the dead cells by phagocytosis. However, microbial damaging substances released by leukocytes would cre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
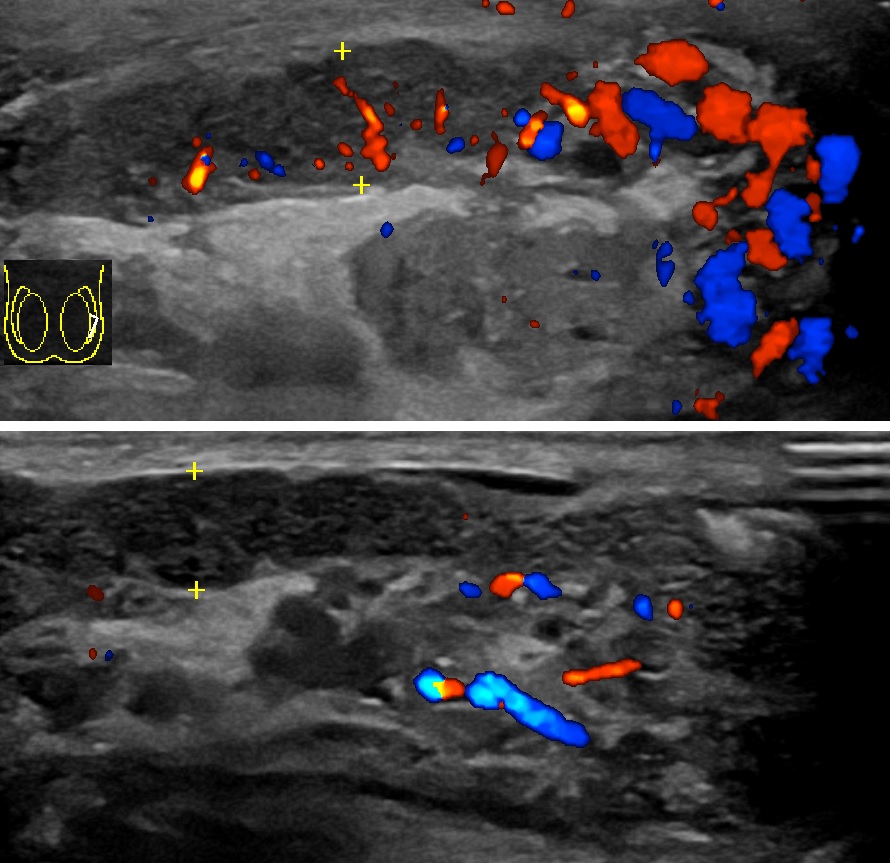
Medical Ultrasonography
Medical ultrasound includes diagnostic techniques (mainly imaging techniques) using ultrasound, as well as therapeutic applications of ultrasound. In diagnosis, it is used to create an image of internal body structures such as tendons, muscles, joints, blood vessels, and internal organs, to measure some characteristics (e.g. distances and velocities) or to generate an informative audible sound. Its aim is usually to find a source of disease or to exclude pathology. The usage of ultrasound to produce visual images for medicine is called medical ultrasonography or simply sonography. The practice of examining pregnant women using ultrasound is called obstetric ultrasonography, and was an early development of clinical ultrasonography. Ultrasound is composed of sound waves with frequencies which are significantly higher than the range of human hearing (>20,000 Hz). Ultrasonic images, also known as sonograms, are created by sending pulses of ultrasound into tissue usin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testicular Pain
Testicular pain, also known as scrotal pain, occurs when part or all of either one or both testicles hurt. Pain in the scrotum is also often included. Testicular pain may be of sudden onset or of long duration. Causes range from non serious muscular skeletal problems to emergency conditions such as Fournier gangrene and testicular torsion. The diagnostic approach involves making sure no serious conditions are present. Diagnosis may be supported by ultrasound, urine tests, and blood tests. Pain management is typically given with definitive management depending on the underlying cause. Definition Testicular pain is when part or all of either one or both testicles hurt. Pain of the scrotum is often included. It may be either acute, subacute or chronic depending on its duration. Chronic scrotal pain Chronic scrotal pain (pain for greater than 3 months) may occur due to a number of underlying conditions. It occurs in 15-19% of men post vasectomy, due to infections such as epidid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epididymitis
Epididymitis is a medical condition characterized by inflammation of the epididymis, a curved structure at the back of the testicle. Onset of pain is typically over a day or two. The pain may improve with raising the testicle. Other symptoms may include swelling of the testicle, burning with urination, or frequent urination. Inflammation of the testicle is commonly also present. In those who are young and sexually active gonorrhea and chlamydia are frequently the underlying cause. In older males and men who practice insertive anal sex, enteric bacteria are a common cause. Diagnosis is typically based on symptoms. Conditions that may result in similar symptoms include testicular torsion, inguinal hernia, and testicular cancer. Ultrasound can be useful if the diagnosis is unclear. Treatment may include pain medications, NSAIDs, and elevation. Recommended antibiotics in those who are young and sexually active are ceftriaxone and doxycycline. Among those who are older, ofloxacin m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hernia
A hernia is the abnormal exit of tissue or an organ, such as the bowel, through the wall of the cavity in which it normally resides. Various types of hernias can occur, most commonly involving the abdomen, and specifically the groin. Groin hernias are most commonly of the inguinal type but may also be femoral. Other types of hernias include hiatus, incisional, and umbilical hernias. Symptoms are present in about 66% of people with groin hernias. This may include pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen, especially with coughing, exercise, or urinating or defecating. Often, it gets worse throughout the day and improves when lying down. A bulge may appear at the site of hernia, that becomes larger when bending down. Groin hernias occur more often on the right than left side. The main concern is bowel strangulation, where the blood supply to part of the bowel is blocked. This usually produces severe pain and tenderness in the area. Hiatus, or hiatal hernias often result in hear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuron
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. Non-animals like plants and fungi do not have nerve cells. Neurons are typically classified into three types based on their function. Sensory neurons respond to stimuli such as touch, sound, or light that affect the cells of the sensory organs, and they send signals to the spinal cord or brain. Motor neurons receive signals from the brain and spinal cord to control everything from muscle contractions to glandular output. Interneurons connect neurons to other neurons within the same region of the brain or spinal cord. When multiple neurons are connected together, they form what is called a neural circuit. A typical neuron consists of a cell body ( soma), dendrites, and a single axon. The soma is a compact structure, and the axo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptorchidism
Cryptorchidism, also known as undescended testis, is the failure of one or both testes to descend into the scrotum. The word is from Greek () 'hidden' and () 'testicle'. It is the most common birth defect of the male genital tract. About 3% of full-term and 30% of premature infant boys are born with at least one undescended testis. However, about 80% of cryptorchid testes descend by the first year of life (the majority within three months), making the true incidence of cryptorchidism around 1% overall. Cryptorchidism may develop after infancy, sometimes as late as young adulthood, but that is exceptional. Cryptorchidism is distinct from monorchism, the condition of having only one testicle. Though the condition may occur on one or both sides, it more commonly affects the right testis. A testis absent from the normal scrotal position may be: # Anywhere along the "path of descent" from high in the posterior (retroperitoneal) abdomen, just below the kidney, to the inguinal ring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cremasteric Reflex
The cremasteric reflex is a superficial (i.e., close to the skin's surface) reflex observed in human males. This reflex is elicited by lightly stroking or poking the superior and medial (inner) part of the thigh—regardless of the direction of stroke. The normal response is an immediate contraction of the cremaster muscle that pulls up the testis ipsilaterally (on the same side of the body). The reflex utilizes sensory and motor fibers from two different nerves. When the inner thigh is stroked, sensory fibers of the ilioinguinal nerve are stimulated. These activate the motor fibers of the genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve which causes the cremaster muscle to contract and elevate the testis. Clinical conditions In boys, this reflex may be exaggerated which can occasionally lead to a misdiagnosis of cryptorchidism. The cremasteric reflex may be absent with testicular torsion, upper and lower motor neuron disorders, as well as a spine injury of L1-L2. It can also occur if ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genital Branch
The genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve, also known as the external spermatic nerve in males, is a nerve in the abdomen that arises from the genitofemoral nerve. The genital branch supplies the cremaster muscle and anterior scrotal skin in males, and the skin of the mons pubis and labia majora in females. Structure The genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve arises from the ventral primary divisions of L1-L2 spinal nerve roots. It passes outward on the psoas major muscle, and pierces the fascia transversalis, or passes through the deep inguinal ring. It then descends within the spermatic cord. In males, it passes through to the scrotum, where it supplies the cremaster, dartos muscle and gives a few filaments to the skin of the scrotum. In females, it accompanies the round ligament of the uterus, where it terminates as the nerve supplying the skin of the labia majora and mons pubis. Function The genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve is responsible for the motor po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis), or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see spelling differences), is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action potentials away from the nerve cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles, and glands. In certain sensory neurons ( pseudounipolar neurons), such as those for touch and warmth, the axons are called afferent nerve fibers and the electrical impulse travels along these from the periphery to the cell body and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction can be the cause of many inherited and acquired neurological disorders that affect both the peripheral and central neurons. Nerve fibers are classed into three types group A nerve fibers, group B nerve fibers, and group C nerve fibers. Groups A and B are myelinated, and group C are unmyelinated. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)