|
Cost-of-production Theory Of Value
In economics, the cost-of-production theory of value is the theory that the price of an object or condition is determined by the sum of the cost of the resources that went into making it. The cost can comprise any of the factors of production (including labor, capital, or land) and taxation. The theory makes the most sense under assumptions of constant returns to scale and the existence of just one non-produced factor of production. With these assumptions, minimal price theorem, a dual version of the so-called non-substitution theorem by Paul Samuelson, holds.Y. Shiozawa, M. Morioka and K. Taniguchi 2019 Microfoundations of Evolutionary Economics, Tokyo, Springer. Under these assumptions, the long-run price of a commodity is equal to the sum of the cost of the inputs into that commodity, including interest charges. Historical development of the theory Historically, the best-known proponent of such theories is probably Adam Smith. Piero Sraffa, in his introduction to the first volu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economics
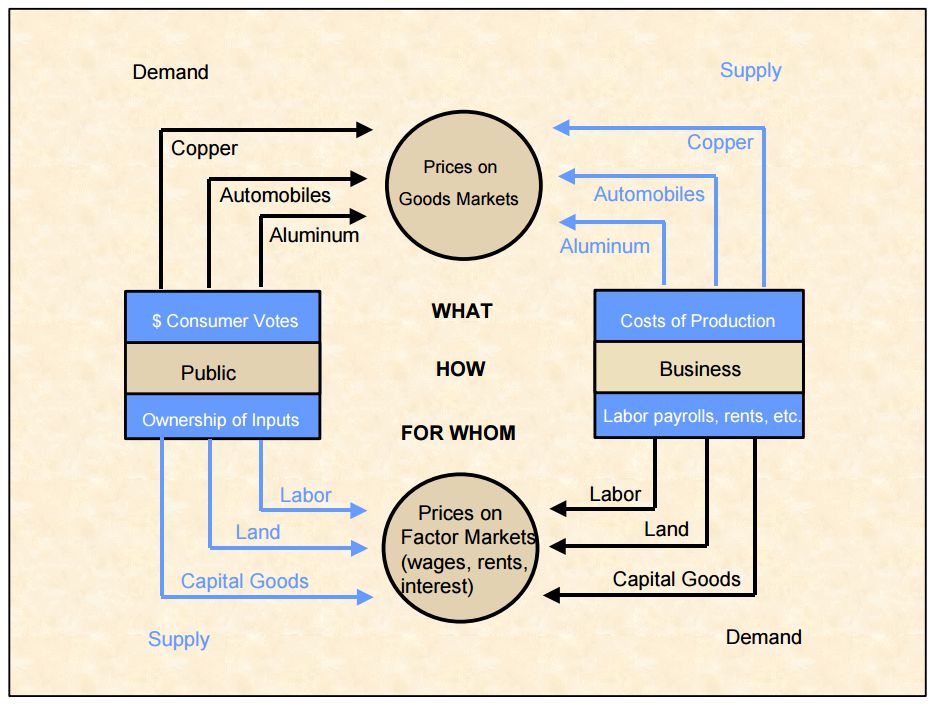
Economics () is the social science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goods and services. Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of Agent (economics), economic agents and how economy, economies work. Microeconomics analyzes what's viewed as basic elements in the economy, including individual agents and market (economics), markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyzes the economy as a system where production, consumption, saving, and investment interact, and factors affecting it: employment of the resources of labour, capital, and land, currency inflation, economic growth, and public policies that have impact on glossary of economics, these elements. Other broad distinctions within economics include those between positive economics, desc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rational Expectations
In economics, "rational expectations" are model-consistent expectations, in that agents inside the model A model is an informative representation of an object, person or system. The term originally denoted the plans of a building in late 16th-century English, and derived via French and Italian ultimately from Latin ''modulus'', a measure. Models c ... are assumed to "know the model" and on average take the model's predictions as valid. Rational expectations ensure internal consistency in models involving uncertainty. To obtain consistency within a model, the predictions of future values of economically relevant variables from the model are assumed to be the same as that of the decision-makers in the model, given their information set, the nature of the random processes involved, and model structure. The rational expectations assumption is used especially in many contemporary macroeconomic models. Since most macroeconomic models today study decisions under uncertainty and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
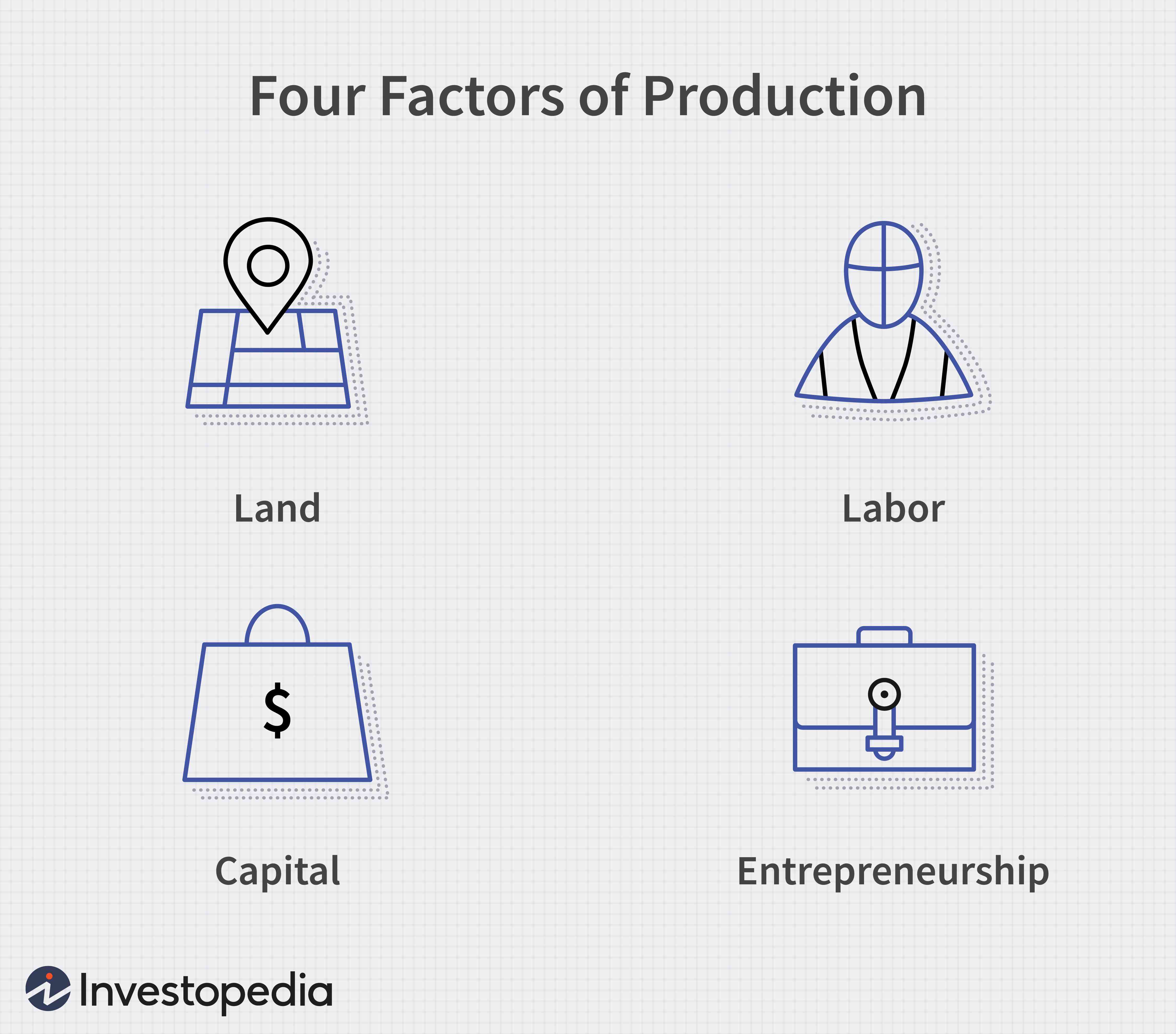
Production Economics
Production is the process of combining various inputs, both material (such as metal, wood, glass, or plastics) and immaterial (such as plans, or knowledge) in order to create output. Ideally this output will be a good or service which has value and contributes to the utility of individuals. The area of economics that focuses on production is called production theory, and it is closely related to the consumption (or consumer) theory of economics. The production process and output directly result from productively utilising the original inputs (or factors of production). Known as primary producer goods or services, land, labour, and capital are deemed the three fundamental production factors. These primary inputs are not significantly altered in the output process, nor do they become a whole component in the product. Under classical economics, materials and energy are categorised as secondary factors as they are byproducts of land, labour and capital. Delving further, primary factors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Production (economics)
Production is the process of combining various inputs, both material (such as metal, wood, glass, or plastics) and immaterial (such as plans, or knowledge) in order to create output. Ideally this output will be a good or service which has value and contributes to the utility of individuals. The area of economics that focuses on production is called production theory, and it is closely related to the consumption (or consumer) theory of economics. The production process and output directly result from productively utilising the original inputs (or factors of production). Known as primary producer goods or services, land, labour, and capital are deemed the three fundamental production factors. These primary inputs are not significantly altered in the output process, nor do they become a whole component in the product. Under classical economics, materials and energy are categorised as secondary factors as they are byproducts of land, labour and capital. Delving further, primary factor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pricing Strategies
A business can use a variety of pricing strategies when selling a product (business), product or Service (economics), service. To determine the most effective pricing strategy for a company, senior executives need to first identify the company's pricing position, pricing segment, pricing capability and their competitive pricing reaction strategy. Pricing strategies and tactics vary from company to company, and also differ across countries, cultures, industries and over time, with the maturing of industries and markets and changes in wider economic conditions. Pricing strategies determine the price companies set for their products. The price can be set to maximize profitability for each unit sold or from the market overall. It can also be used to defend an existing market from new entrants, to increase market share within a market or to enter a new market. Pricing strategies can bring both competitive advantages and disadvantages to its firm and often dictate the success or failure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prices Of Production
Prices of production (or "production prices"; in German ''Produktionspreise'') is a concept in Karl Marx's critique of political economy, defined as "cost-price + average profit". A production price can be thought of as a type of supply price for products; it refers to the price levels at which newly produced goods and services would have to be sold by the producers, in order to reach a normal, average ''profit rate'' on the ''capital'' invested to produce the products (not the same as the profit on the turnover). The importance of these price levels is, that a lot of other prices are based on them, or derived from them: in Marx's theory, they determine the cost structure of capitalist production. The market prices of products normally oscillate around their production prices, while production prices themselves oscillate around product-''values'' (the average current replacement cost in labour-time required to make each type of product). This understanding already existed in clas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Price
A price is the (usually not negative) quantity of payment or compensation given by one party to another in return for goods or services. In some situations, the price of production has a different name. If the product is a "good" in the commercial exchange, the payment for this product will likely be called its "price". However, if the product is "service", there will be other possible names for this product's name. For example, the graph on the bottom will show some situations A good's price is influenced by production costs, supply of the desired item, and demand for the product. A price may be determined by a monopolist or may be imposed on the firm by market conditions. Price can be quoted to currency, quantities of goods or vouchers. * In modern economies, prices are generally expressed in units of some form of currency. (More specifically, for raw materials they are expressed as currency per unit weight, e.g. euros per kilogram or Rands per KG.) * Although prices ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Economics Topics
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to economics: Economics – analyzes the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. It aims to explain how economies work and how economic agents interact. Description of economics Economics can be described as all of the following: * Academic discipline – body of knowledge given to, or received by, a disciple (student); a branch or sphere of knowledge, or field of study, that an individual has chosen to specialize in. * Field of science – widely recognized category of specialized expertise within science, and typically embodies its own terminology and nomenclature. Such a field will usually be represented by one or more scientific journals, where peer-reviewed research is published. There are many economics-related scientific journals. * Social science – field of academic scholarship that explores aspects of human society. Branches of economics * Macroec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Output (economics)
Output in economics is the "quantity of goods or Service (economics), services Production (economics), produced in a given time period, by a firm, industry, or country", whether consumed or used for further production. The concept of national output is essential in the field of macroeconomics. It is national output that makes a country rich, not large amounts of money. Definition Output is the result of an economic process that has used input (economics), inputs to produce a product or service that is available for sale or use somewhere else. ''Net output'', sometimes called ''netput'' is a quantity, in the context of production, that is positive if the quantity is output by the production process and negative if it is an input to the production process. Microeconomics Output condition The profit-maximizing output condition for producers equates the relative marginal cost of any two goods to the relative selling price of those goods; i.e. \frac = \frac One may als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outline Of Production
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to production: Production – act of creating 'use' value or 'utility' that can satisfy a want or need. The act may or may not include factors of production other than labor. Any effort directed toward the realization of a desired product or service is a "productive" effort and the performance of such act is production. The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to production: Types * Industry – production of an economic good or service within an economy. Industry is divided into four sectors, or types of production; they are: Primary sector * Primary sector – this involves the extraction of resources directly from the Earth, this includes agricultural and resource extraction industries. In these industries, the product (that is, the focus of production) is a natural resource. ** Agriculture ( outline) – cultivation of animals, plants, fungi, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outline Of Industrial Organization
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to industrial organization: Industrial organization – describes the behavior of firms in the marketplace with regard to production, pricing, employment and other decisions. Issues underlying these decisions range from classical issues such as opportunity cost to neoclassical concepts such as factors of production. Overview * a field of economics that studies: ** the strategic behavior of firms ** the structure of markets *** Perfect competition *** Monopolistic competition *** Oligopoly *** Oligopsony *** Monopoly *** Monopsony ** and the interactions between them Concepts Production side of Industry: *Production theory ** productive efficiency ** factors of production ** total, average, and marginal product curves ** marginal productivity ** isoquants & isocosts ** the marginal rate of technical substitution *Production function **inputs **diminishing returns to inputs **the stages of produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Price
A price is the (usually not negative) quantity of payment or compensation given by one party to another in return for goods or services. In some situations, the price of production has a different name. If the product is a "good" in the commercial exchange, the payment for this product will likely be called its "price". However, if the product is "service", there will be other possible names for this product's name. For example, the graph on the bottom will show some situations A good's price is influenced by production costs, supply of the desired item, and demand for the product. A price may be determined by a monopolist or may be imposed on the firm by market conditions. Price can be quoted to currency, quantities of goods or vouchers. * In modern economies, prices are generally expressed in units of some form of currency. (More specifically, for raw materials they are expressed as currency per unit weight, e.g. euros per kilogram or Rands per KG.) * Although prices ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |