|
Corundum
Corundum is a crystalline form of aluminium oxide () typically containing traces of iron, titanium, vanadium and chromium. It is a rock-forming mineral. It is a naturally transparent material, but can have different colors depending on the presence of transition metal impurities in its crystalline structure. Corundum has two primary gem varieties: ruby and sapphire. Rubies are red due to the presence of chromium, and sapphires exhibit a range of colors depending on what transition metal is present. A rare type of sapphire, padparadscha sapphire, is pink-orange. The name "corundum" is derived from the Tamil- Dravidian word ''kurundam'' (ruby-sapphire) (appearing in Sanskrit as ''kuruvinda''). Because of corundum's hardness (pure corundum is defined to have 9.0 on the Mohs scale), it can scratch almost all other minerals. It is commonly used as an abrasive on sandpaper and on large tools used in machining metals, plastics, and wood. Emery, a variety of corundum with no value a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sapphire
Sapphire is a precious gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum, consisting of aluminium oxide () with trace amounts of elements such as iron, titanium, chromium, vanadium, or magnesium. The name sapphire is derived via the Latin "sapphirus" from the Greek "sappheiros", which referred to Lapis lazuli, lapis lazuli. It is typically blue, but natural "fancy" sapphires also occur in yellow, purple, orange, and green colors; "parti sapphires" show two or more colors. Red corundum stones also occur, but are called ruby, rubies rather than sapphires. Pink-colored corundum may be classified either as ruby or sapphire depending on locale. Commonly, natural sapphires are cut and polished into gemstones and worn in jewellery, jewelry. They also may be created synthetically in laboratories for industrial or decorative purposes in large boule (crystal), crystal boules. Because of the remarkable hardness of sapphires 9 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness, Mohs scale (the third hardest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sapphire
Sapphire is a precious gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum, consisting of aluminium oxide () with trace amounts of elements such as iron, titanium, chromium, vanadium, or magnesium. The name sapphire is derived via the Latin "sapphirus" from the Greek "sappheiros", which referred to Lapis lazuli, lapis lazuli. It is typically blue, but natural "fancy" sapphires also occur in yellow, purple, orange, and green colors; "parti sapphires" show two or more colors. Red corundum stones also occur, but are called ruby, rubies rather than sapphires. Pink-colored corundum may be classified either as ruby or sapphire depending on locale. Commonly, natural sapphires are cut and polished into gemstones and worn in jewellery, jewelry. They also may be created synthetically in laboratories for industrial or decorative purposes in large boule (crystal), crystal boules. Because of the remarkable hardness of sapphires 9 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness, Mohs scale (the third hardest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
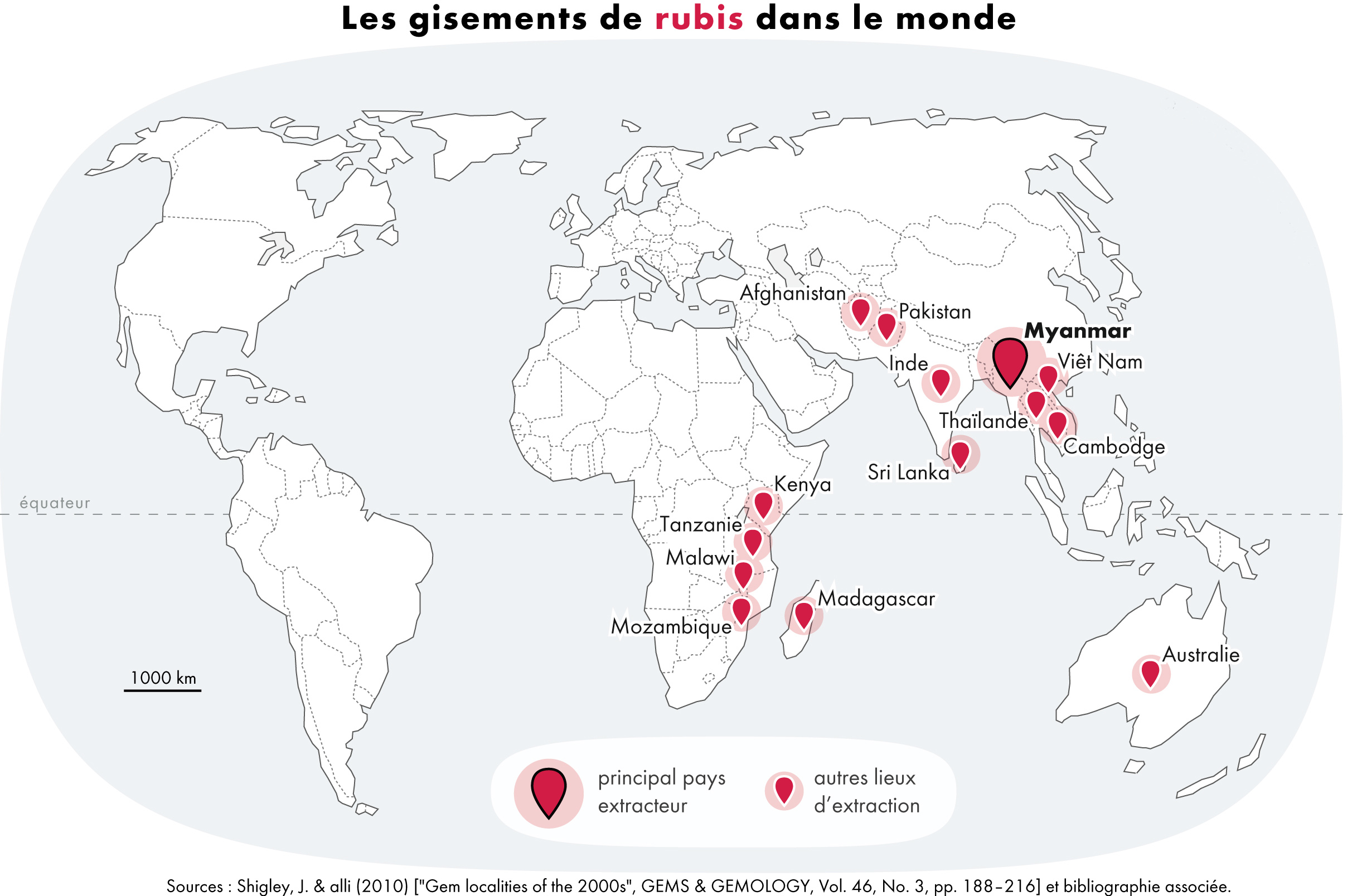
Ruby
A ruby is a pinkish red to blood-red colored gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum ( aluminium oxide). Ruby is one of the most popular traditional jewelry gems and is very durable. Other varieties of gem-quality corundum are called sapphires. Ruby is one of the traditional cardinal gems, alongside amethyst, sapphire, emerald, and diamond. The word ''ruby'' comes from ''ruber'', Latin for red. The color of a ruby is due to the element chromium. Some gemstones that are popularly or historically called rubies, such as the Black Prince's Ruby in the British Imperial State Crown, are actually spinels. These were once known as "Balas rubies". The quality of a ruby is determined by its color, cut, and clarity, which, along with carat weight, affect its value. The brightest and most valuable shade of red, called blood-red or pigeon blood, commands a large premium over other rubies of similar quality. After color follows clarity: similar to diamonds, a clear stone will com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruby
A ruby is a pinkish red to blood-red colored gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum ( aluminium oxide). Ruby is one of the most popular traditional jewelry gems and is very durable. Other varieties of gem-quality corundum are called sapphires. Ruby is one of the traditional cardinal gems, alongside amethyst, sapphire, emerald, and diamond. The word ''ruby'' comes from ''ruber'', Latin for red. The color of a ruby is due to the element chromium. Some gemstones that are popularly or historically called rubies, such as the Black Prince's Ruby in the British Imperial State Crown, are actually spinels. These were once known as "Balas rubies". The quality of a ruby is determined by its color, cut, and clarity, which, along with carat weight, affect its value. The brightest and most valuable shade of red, called blood-red or pigeon blood, commands a large premium over other rubies of similar quality. After color follows clarity: similar to diamonds, a clear stone will com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxide Mineral
The oxide mineral class includes those minerals in which the oxide anion (O2−) is bonded to one or more metal alloys. The hydroxide-bearing minerals are typically included in the oxide class. The minerals with complex anion groups such as the silicates, sulfates, carbonates and phosphates are classed separately. Simple oxides: *XO **Periclase group ***Periclase ***Manganosite **Zincite group ***Zincite *** Bromellite ***Tenorite ***Litharge * **Cuprite **Ice * **Hematite group ***Corundum ***Hematite ***Ilmenite * **Rutile group ***Rutile ***Pyrolusite ***Cassiterite **Baddeleyite **Uraninite **Thorianite * **Spinel group ***Spinel ***Gahnite ***Magnetite ***Franklinite ***Chromite **Chrysoberyl **Columbite *Hydroxide subgroup: **Brucite **Manganite ** Romanèchite **Goethite group: ***Diaspore ***Goethite Nickel–Strunz Classification -04- Oxides IMA-CNMNC proposes a new hierarchical scheme (Mills et al., 2009). This list uses it to modify ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2011): Minerals'; p. 1. In the series ''Geology: Landforms, Minerals, and Rocks''. Rosen Publishing Group. The geological definition of mineral normally excludes compounds that occur only in living organisms. However, some minerals are often biogenic (such as calcite) or are organic compounds in the sense of chemistry (such as mellite). Moreover, living organisms often synthesize inorganic minerals (such as hydroxylapatite) that also occur in rocks. The concept of mineral is distinct from rock, which is any bulk solid geologic material that is relatively homogeneous at a large enough scale. A rock may consist of one type of mineral, or may be an aggregate of two or more different types of minerals, spacially segregated into distinct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mohs Scale Of Mineral Hardness
The Mohs scale of mineral hardness () is a qualitative ordinal scale, from 1 to 10, characterizing scratch resistance of various minerals through the ability of harder material to scratch softer material. The scale was introduced in 1812 by the German geologist and mineralogist Friedrich Mohs, in his book ''"Versuch einer Elementar-Methode zur naturhistorischen Bestimmung und Erkennung der Fossilien"''; it is one of several definitions of hardness in materials science, some of which are more quantitative. The method of comparing hardness by observing which minerals can scratch others is of great antiquity, having been mentioned by Theophrastus in his treatise ''On Stones'', , followed by Pliny the Elder in his ''Naturalis Historia'', . The Mohs scale is useful for identification of minerals in the field, but is not an accurate predictor of how well materials endure in an industrial setting – ''toughness''. Minerals The Mohs scale of mineral hardness is based on the ability ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abrasive
An abrasive is a material, often a mineral, that is used to shape or finish a workpiece through rubbing which leads to part of the workpiece being worn away by friction. While finishing a material often means polishing it to gain a smooth, reflective surface, the process can also involve roughening as in satin, matte or beaded finishes. In short, the ceramics which are used to cut, grind and polish other softer materials are known as abrasives. Abrasives are extremely commonplace and are used very extensively in a wide variety of industrial, domestic, and technological applications. This gives rise to a large variation in the physical and chemical composition of abrasives as well as the shape of the abrasive. Some common uses for abrasives include grinding, polishing, buffing, honing, cutting, drilling, sharpening, lapping, and sanding (see abrasive machining). (For simplicity, "mineral" in this article will be used loosely to refer to both minerals and mineral-like substances ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emery (rock)
Emery, or corundite, is a dark granular rock used to make abrasive powder. It largely consists of corundum ( aluminium oxide), mixed with other minerals such as the iron-bearing spinels, hercynite, and magnetite, and also rutile ( titania). Industrial emery may contain a variety of other minerals and synthetic compounds such as magnesia, mullite, and silica. It is black or dark grey in colour, less dense than translucent-brown corundum with a specific gravity of between 3.5 and 3.8. Because it can be a mixture of minerals, no definite Mohs hardness can be assigned: the hardness of corundum is 9 and that of some spinel-group minerals is near 8, but the hardness of others such as magnetite is near 6. Crushed or naturally eroded emery (known as ''black sand'') is used as an abrasive—for example, on emery boards and emery cloth. It is also used as a traction enhancer in asphalt and tarmac mixtures. Turkey and Greece are the main suppliers of the world's emery. These two countr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emery (mineral)
Emery, or corundite, is a dark granular rock used to make abrasive powder. It largely consists of corundum (aluminium oxide), mixed with other minerals such as the iron-bearing spinels, hercynite, and magnetite, and also rutile (Titanium dioxide, titania). Industrial emery may contain a variety of other minerals and synthetic compounds such as Magnesia (mineral), magnesia, mullite, and silica. It is black or dark grey in colour, less dense than translucent-brown corundum with a specific gravity of between 3.5 and 3.8. Because it can be a mixture of minerals, no definite Mohs scale of mineral hardness, Mohs hardness can be assigned: the hardness of corundum is 9 and that of some spinel-group minerals is near 8, but the hardness of others such as magnetite is near 6. Crushed or naturally eroded emery (known as ''black sand'') is used as an abrasive—for example, on emery boards and emery cloth. It is also used as a traction enhancer in asphalt and Tarmacadam, tarmac mixtures. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rock (geology)
In geology, rock (or stone) is any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals or mineraloid matter. It is categorized by the minerals included, its chemical composition, and the way in which it is formed. Rocks form the Earth's outer solid layer, the crust, and most of its interior, except for the liquid outer core and pockets of magma in the asthenosphere. The study of rocks involves multiple subdisciplines of geology, including petrology and mineralogy. It may be limited to rocks found on Earth, or it may include planetary geology that studies the rocks of other celestial objects. Rocks are usually grouped into three main groups: igneous rocks, sedimentary rocks and metamorphic rocks. Igneous rocks are formed when magma cools in the Earth's crust, or lava cools on the ground surface or the seabed. Sedimentary rocks are formed by diagenesis and lithification of sediments, which in turn are formed by the weathering, transport, and deposition of existing ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanskrit Language
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late Bronze Age. Sanskrit is the sacred language of Hinduism, the language of classical Hindu philosophy, and of historical texts of Buddhism and Jainism. It was a link language in ancient and medieval South Asia, and upon transmission of Hindu and Buddhist culture to Southeast Asia, East Asia and Central Asia in the early medieval era, it became a language of religion and high culture, and of the political elites in some of these regions. As a result, Sanskrit had a lasting impact on the languages of South Asia, Southeast Asia and East Asia, especially in their formal and learned vocabularies. Sanskrit generally connotes several Old Indo-Aryan language varieties. The most archaic of these is the Vedic Sanskrit found in the Rig Veda, a col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







_slabbed_Naxos_Emery_Deposits.jpg)

