|
Cortical Remapping
Cortical remapping, also referred to as cortical reorganization, is the process by which an existing cortical map is affected by a stimulus resulting in the creating of a 'new' cortical map. Every part of the body is connected to a corresponding area in the brain which creates a cortical map. When something happens to disrupt the cortical maps such as an amputation or a change in neuronal characteristics, the map is no longer relevant. The part of the brain that is in charge of the amputated limb or neuronal change will be dominated by adjacent cortical regions that are still receiving input, thus creating a remapped area. Remapping can occur in the sensory or motor system. The mechanism for each system may be quite different. Cortical remapping in the somatosensory system happens when there has been a decrease in sensory input to the brain due to deafferentation or amputation, as well as a sensory input increase to an area of the brain. Motor system remapping receives more l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
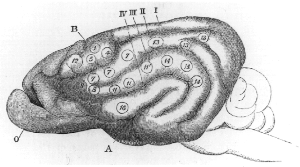
Cortical Map
Cortical maps are collections (areas) of minicolumns in the brain cortex that have been identified as performing a specific information processing function (texture maps, color maps, contour maps, etc.). Cortical maps Cortical organization, especially for the sensory systems, is often described in terms of maps. For example, sensory information from the foot projects to one cortical site and the projections from the hand target in another site. As the result of this somatotopic organization of sensory inputs to the cortex, cortical representation of the body resembles a map (or homunculus). In the late 1970s and early 1980s, several groups began exploring the impacts of removing portions of the sensory inputs. Michael Merzenich and Jon Kaas and Doug Rasmusson used the cortical map as their dependent variable. They found—and this has been since corroborated by a wide range of labs—that if the cortical map is deprived of its input it will become activated at a late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long-term Potentiation
In neuroscience, long-term potentiation (LTP) is a persistent strengthening of synapses based on recent patterns of activity. These are patterns of synaptic activity that produce a long-lasting increase in signal transmission between two neurons. The opposite of LTP is long-term depression, which produces a long-lasting decrease in synaptic strength. It is one of several phenomena underlying synaptic plasticity, the ability of chemical synapses to change their strength. As memories are thought to be encoded by modification of synaptic strength, LTP is widely considered one of the major cellular mechanisms that underlies learning and memory. LTP was discovered in the rabbit hippocampus by Terje Lømo in 1966 and has remained a popular subject of research since. Many modern LTP studies seek to better understand its basic biology, while others aim to draw a causal link between LTP and behavioral learning. Still, others try to develop methods, pharmacologic or otherwise, of enhanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penguin Group
Penguin Group is a British trade book publisher and part of Penguin Random House, which is owned by the German media conglomerate Bertelsmann. The new company was created by a merger that was finalised on 1 July 2013, with Bertelsmann initially owning 53% of the joint venture, and Pearson PLC initially owning the remaining 47%. Since 18 December 2019, Penguin Random House has been wholly owned by Bertelsmann. Penguin Books has its registered office in City of Westminster, London.Maps ." City of Westminster. Retrieved 28 August 2009. Its British division is Penguin Books Ltd. Other separate divisions are located in the |
The Brain That Changes Itself
''The Brain That Changes Itself: Stories of Personal Triumph from the Frontiers of Brain Science'' is a book on neuroplasticity by psychiatrist and psychoanalyst Norman Doidge. Content The book is a collection of stories of doctors and patients showing that the human brain is capable of undergoing change, including stories of recovering use of paralyzed body parts, deaf people learning to hear, and others getting relief from pain using exercises to retrain neural pathways. Doidge also covers scientists who first identified neuroplasticity, the subjects of persistent pain, sexual attraction and love, how culture impacts the changing brain, the developing pediatric brain and the preservation of the geriatric brain. Reception ''The New York Times'' gave a mostly positive review of the book. In contrast ''The International Journal of Psychoanalysis'' published a negative book review essay critical of Doidge's writings. The review claims that neuroscience is irrelevant to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael M
Michael may refer to: People * Michael (given name), a given name * Michael (surname), including a list of people with the surname Michael Given name "Michael" * Michael (archangel), ''first'' of God's archangels in the Jewish, Christian and Islamic religions * Michael (bishop elect), English 13th-century Bishop of Hereford elect * Michael (Khoroshy) (1885–1977), cleric of the Ukrainian Orthodox Church of Canada * Michael Donnellan (1915–1985), Irish-born London fashion designer, often referred to simply as "Michael" * Michael (footballer, born 1982), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born 1983), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born 1993), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born February 1996), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born March 1996), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born 1999), Brazilian footballer Rulers =Byzantine emperors= *Michael I Rangabe (d. 844), married the daughter of Emperor Nikephoros I * Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synaptic Plasticity
In neuroscience, synaptic plasticity is the ability of synapses to strengthen or weaken over time, in response to increases or decreases in their activity. Since memories are postulated to be represented by vastly interconnected neural circuits in the brain, synaptic plasticity is one of the important neurochemical foundations of learning and memory (''see Hebbian theory''). Plastic change often results from the alteration of the number of neurotransmitter receptors located on a synapse. There are several underlying mechanisms that cooperate to achieve synaptic plasticity, including changes in the quantity of neurotransmitters released into a synapse and changes in how effectively cells respond to those neurotransmitters. Synaptic plasticity in both excitatory and inhibitory synapses has been found to be dependent upon postsynaptic calcium release. Historical discoveries In 1973, Terje Lømo and Tim Bliss first described the now widely studied phenomenon of long-term pote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homeostatic Plasticity
In neuroscience, homeostatic plasticity refers to the capacity of neurons to regulate their own excitability relative to network activity. The term homeostatic plasticity derives from two opposing concepts: 'homeostatic' (a product of the Greek words for 'same' and 'state' or 'condition') and plasticity (or 'change'), thus homeostatic plasticity means "staying the same through change". Comparison with Hebbian plasticity Homeostatic synaptic plasticity is a means of maintaining the synaptic basis for learning, respiration, and locomotion, in contrast to the Hebbian plasticity associated with learning and memory. Although Hebbian forms of plasticity, such as long-term potentiation and long-term depression occur rapidly, homeostatic plasticity (which relies on protein synthesis) can take hours or days. TNF-α and microRNAs are important mediators of homeostatic synaptic plasticity. Homeostatic plasticity is thought to balance Hebbian plasticity by modulating the activity of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Cortical Development
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, and language. Humans are highly social and tend to live in complex social structures composed of many cooperating and competing groups, from families and kinship networks to political states. Social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of values, social norms, and rituals, which bolster human society. Its intelligence and its desire to understand and influence the environment and to explain and manipulate phenomena have motivated humanity's development of science, philosophy, mythology, religion, and other fields of study. Although some scientists equate the term ''humans'' with all members of the genus ''Homo'', in common usage, it generally refers to ''Homo sapiens'', the only extant member. Anatomically mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penumbra (medicine)
In pathology and anatomy the penumbra is the area surrounding an ischemic event such as thrombotic or embolic stroke. Immediately following the event, blood flow and therefore oxygen transport is reduced locally, leading to hypoxia of the cells near the location of the original insult. This can lead to hypoxic cell death (infarction) and amplify the original damage from the ischemia; however, the penumbra area may remain viable for several hours after an ischemic event due to the collateral arteries that supply the penumbral zone. As time elapses after the onset of stroke, the extent of the penumbra tends to decrease; therefore, in the emergency department a major concern is to protect the penumbra by increasing oxygen transport and delivery to cells in the danger zone, thereby limiting cell death. The existence of a penumbra implies that salvage of the cells is possible. There is a high correlation between the extent of spontaneous neurological recovery and the volume of penum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebral Infarction
A cerebral infarction is the pathologic process that results in an area of necrotic tissue in the brain (cerebral infarct). It is caused by disrupted blood supply ( ischemia) and restricted oxygen supply ( hypoxia), most commonly due to thromboembolism, and manifests clinically as ischemic stroke. In response to ischemia, the brain degenerates by the process of liquefactive necrosis. Classification There are various classification systems for a cerebral infarction, some of which are described below. * The Oxford Community Stroke Project classification (OCSP, also known as the Bamford or Oxford classification) relies primarily on the initial symptoms. Based on the extent of the symptoms, the stroke episode is classified as total anterior circulation infarct (TACI), partial anterior circulation infarct (PACI), lacunar infarct (LACI) or posterior circulation infarct (POCI). These four entities predict the extent of the stroke, the area of the brain affected, the underlying cause, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
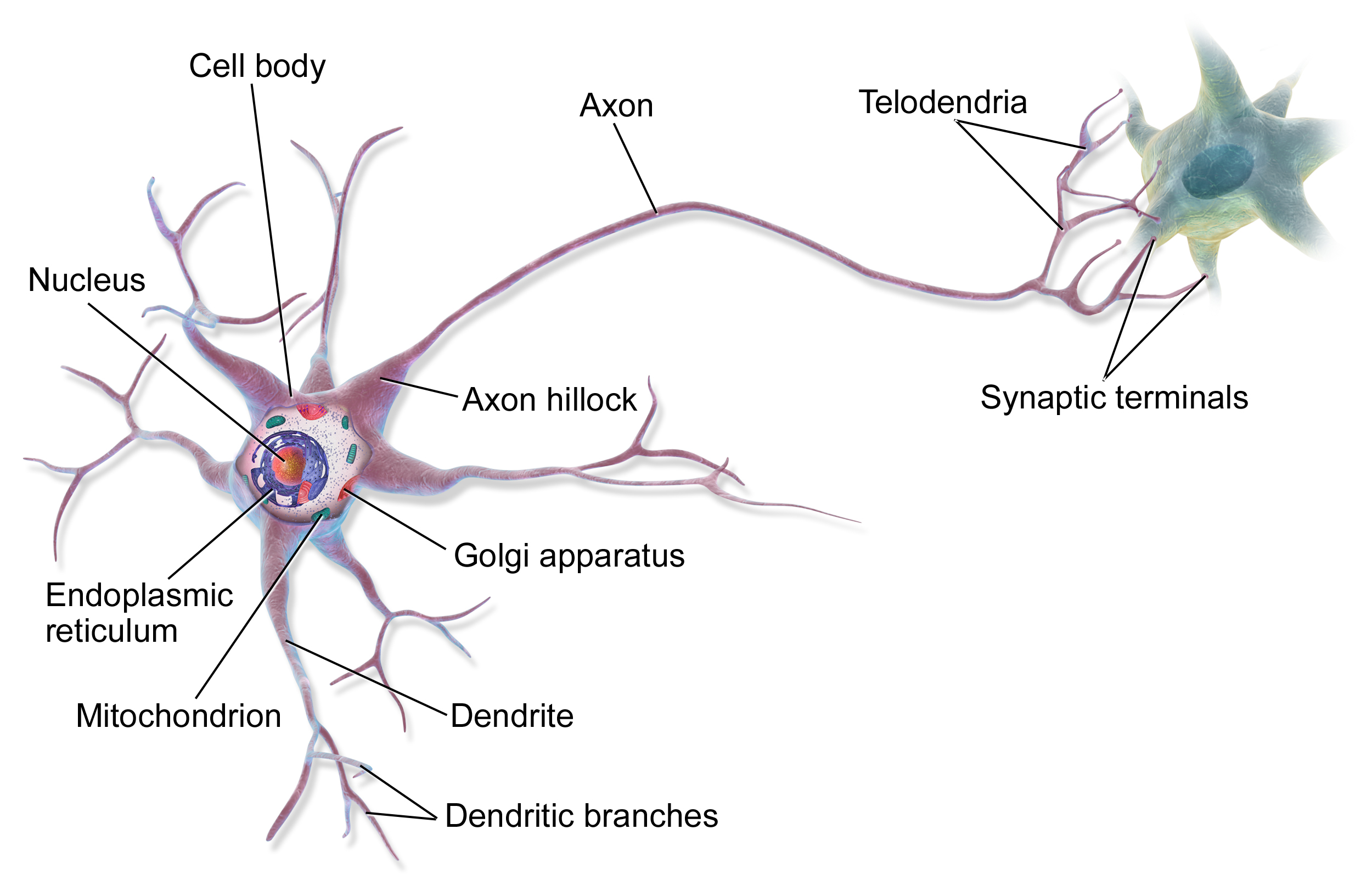
Brain Circuit
A neural circuit is a population of neurons interconnected by synapses to carry out a specific function when activated. Neural circuits interconnect to one another to form large scale brain networks. Biological neural networks have inspired the design of artificial neural networks, but artificial neural networks are usually not strict copies of their biological counterparts. Early study Early treatments of neural networks can be found in Herbert Spencer's ''Principles of Psychology'', 3rd edition (1872), Theodor Meynert's ''Psychiatry'' (1884), William James' ''Principles of Psychology'' (1890), and Sigmund Freud's Project for a Scientific Psychology (composed 1895). The first rule of neuronal learning was described by Hebb in 1949, in the Hebbian theory. Thus, Hebbian pairing of pre-synaptic and post-synaptic activity can substantially alter the dynamic characteristics of the synaptic connection and therefore either facilitate or inhibit signal transmission. In 1959, the neur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stroke
A stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop functioning properly. Signs and symptoms of a stroke may include an inability to move or feel on one side of the body, problems understanding or speaking, dizziness, or loss of vision to one side. Signs and symptoms often appear soon after the stroke has occurred. If symptoms last less than one or two hours, the stroke is a transient ischemic attack (TIA), also called a mini-stroke. A hemorrhagic stroke may also be associated with a severe headache. The symptoms of a stroke can be permanent. Long-term complications may include pneumonia and loss of bladder control. The main risk factor for stroke is high blood pressure. Other risk factors include high blood cholesterol, tobacco smoking, obesity, diabetes mellitus, a previous TIA, end-st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |