|
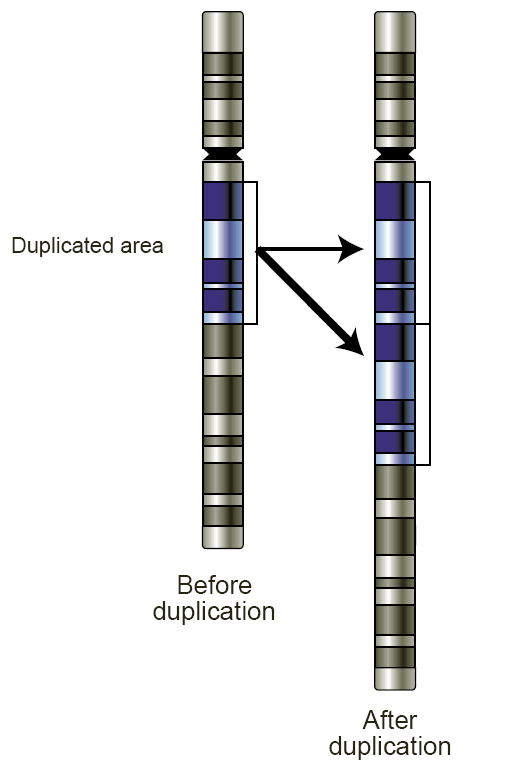
Copy Number Variation
Copy number variation (CNV) is a phenomenon in which sections of the genome are repeated and the number of repeats in the genome varies between individuals. Copy number variation is a type of structural variation: specifically, it is a type of duplication or deletion event that affects a considerable number of base pairs. Approximately two-thirds of the entire human genome may be composed of repeats and 4.8–9.5% of the human genome can be classified as copy number variations. In mammals, copy number variations play an important role in generating necessary variation in the population as well as disease phenotype. Copy number variations can be generally categorized into two main groups: short repeats and long repeats. However, there are no clear boundaries between the two groups and the classification depends on the nature of the loci of interest. Short repeats include mainly dinucleotide repeats (two repeating nucleotides e.g. A-C-A-C-A-C...) and trinucleotide repeats. Long r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, protein or non-coding RNA, and ultimately affect a phenotype, as the final effect. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein-coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) and small nuclear RNA (snRNA), the product is a functional non-coding RNA. Gene expression is summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology first formulated by Francis Crick in 1958, further developed in his 1970 article, and expanded by the subsequent discoveries of reverse transcription and RNA replication. The process of gene expression is used by all known life—eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and utilized by viruses—to generate the macromolecular machinery for life. In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenotype, '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterochromatin
Heterochromatin is a tightly packed form of DNA or '' condensed DNA'', which comes in multiple varieties. These varieties lie on a continue between the two extremes of constitutive heterochromatin and facultative heterochromatin. Both play a role in the expression of genes. Because it is tightly packed, it was thought to be inaccessible to polymerases and therefore not transcribed; however, according to Volpe et al. (2002), and many other papers since, much of this DNA is in fact transcribed, but it is continuously turned over via RNA-induced transcriptional silencing (RITS). Recent studies with electron microscopy and OsO4 staining reveal that the dense packing is not due to the chromatin. Constitutive heterochromatin can affect the genes near itself (e.g. position-effect variegation). It is usually repetitive and forms structural functions such as centromeres or telomeres, in addition to acting as an attractor for other gene-expression or repression signals. Facultative hete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centromere
The centromere links a pair of sister chromatids together during cell division. This constricted region of chromosome connects the sister chromatids, creating a short arm (p) and a long arm (q) on the chromatids. During mitosis, spindle fibers attach to the centromere via the kinetochore. The physical role of the centromere is to act as the site of assembly of the kinetochores – a highly complex multiprotein structure that is responsible for the actual events of chromosome segregation – i.e. binding microtubules and signaling to the cell cycle machinery when all chromosomes have adopted correct attachments to the spindle, so that it is safe for cell division to proceed to completion and for cells to enter anaphase. There are, broadly speaking, two types of centromeres. "Point centromeres" bind to specific proteins that recognize particular DNA sequences with high efficiency. Any piece of DNA with the point centromere DNA sequence on it will typically form a centromere if pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telomere
A telomere (; ) is a region of repetitive nucleotide sequences associated with specialized proteins at the ends of linear chromosomes. Although there are different architectures, telomeres, in a broad sense, are a widespread genetic feature most commonly found in eukaryotes. In most, if not all species possessing them, they protect the terminal regions of chromosomal DNA from progressive degradation and ensure the integrity of linear chromosomes by preventing DNA repair systems from mistaking the very ends of the DNA strand for a double-strand break. Discovery In the early 1970s, Soviet theorist Alexei Olovnikov first recognized that chromosomes could not completely replicate their ends; this is known as the "end replication problem". Building on this, and accommodating Leonard Hayflick's idea of limited somatic cell division, Olovnikov suggested that DNA sequences are lost every time a cell replicates until the loss reaches a critical level, at which point cell division end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsatellite
A microsatellite is a tract of repetitive DNA in which certain DNA motifs (ranging in length from one to six or more base pairs) are repeated, typically 5–50 times. Microsatellites occur at thousands of locations within an organism's genome. They have a higher mutation rate than other areas of DNA leading to high genetic diversity. Microsatellites are often referred to as short tandem repeats (STRs) by forensic geneticists and in genetic genealogy, or as simple sequence repeats (SSRs) by plant geneticists. Microsatellites and their longer cousins, the minisatellites, together are classified as VNTR (variable number of tandem repeats) DNA. The name "satellite" DNA refers to the early observation that centrifugation of genomic DNA in a test tube separates a prominent layer of bulk DNA from accompanying "satellite" layers of repetitive DNA. They are widely used for DNA profiling in cancer diagnosis, in kinship analysis (especially paternity testing) and in forensic identific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
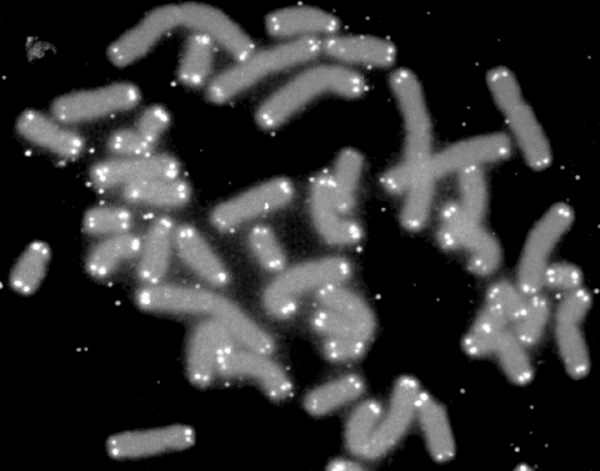
Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization
Fluorescence ''in situ'' hybridization (FISH) is a molecular cytogenetic technique that uses fluorescent probes that bind to only particular parts of a nucleic acid sequence with a high degree of sequence complementarity. It was developed by biomedical researchers in the early 1980s to detect and localize the presence or absence of specific DNA sequences on chromosomes. Fluorescence microscopy can be used to find out where the fluorescent probe is bound to the chromosomes. FISH is often used for finding specific features in DNA for use in genetic counseling, medicine, and species identification. FISH can also be used to detect and localize specific RNA targets (mRNA, lncRNA and miRNA) in cells, circulating tumor cells, and tissue samples. In this context, it can help define the spatial-temporal patterns of gene expression within cells and tissues. Probes – RNA and DNA In biology, a probe is a single strand of DNA or RNA that is complementary to a nucleotide sequence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Diseases
A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosomal abnormality. Although polygenic disorders are the most common, the term is mostly used when discussing disorders with a single genetic cause, either in a gene or chromosome. The mutation responsible can occur spontaneously before embryonic development (a ''de novo'' mutation), or it can be inherited from two parents who are carriers of a faulty gene (autosomal recessive inheritance) or from a parent with the disorder (autosomal dominant inheritance). When the genetic disorder is inherited from one or both parents, it is also classified as a hereditary disease. Some disorders are caused by a mutation on the X chromosome and have X-linked inheritance. Very few disorders are inherited on the Y chromosome or mitochondrial DNA (due to their size). There are well over 6,000 known genet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Variation
Genetic variation is the difference in DNA among individuals or the differences between populations. The multiple sources of genetic variation include mutation and genetic recombination. Mutations are the ultimate sources of genetic variation, but other mechanisms, such as genetic drift, contribute to it, as well. Among individuals within a population Genetic variation can be identified at many levels. Identifying genetic variation is possible from observations of phenotypic variation in either quantitative traits (traits that vary continuously and are coded for by many genes (e.g., leg length in dogs)) or discrete traits (traits that fall into discrete categories and are coded for by one or a few genes (e.g., white, pink, or red petal color in certain flowers)). Genetic variation can also be identified by examining variation at the level of enzymes using the process of protein electrophoresis. Polymorphic genes have more than one allele at each locus. Half of the genes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosomal Rearrangement
In genetics, a chromosomal rearrangement is a mutation that is a type of chromosome abnormality involving a change in the structure of the native chromosome. Such changes may involve several different classes of events, like deletions, duplications, inversions, and translocations. Usually, these events are caused by a breakage in the DNA double helices at two different locations, followed by a rejoining of the broken ends to produce a new chromosomal arrangement of genes, different from the gene order of the chromosomes before they were broken. Structural chromosomal abnormalities are estimated to occur in around 0.5% of newborn infants. Some chromosomal regions are more prone to rearrangement than others and thus are the source of genetic diseases and cancer. This instability is usually due to the propensity of these regions to misalign during DNA repair, exacerbated by defects of the appearance of replication proteins (like FEN1 or Pol δ) that ubiquitously affect the integri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tandem
Tandem, or in tandem, is an arrangement in which a team of machines, animals or people are lined up one behind another, all facing in the same direction. The original use of the term in English was in ''tandem harness'', which is used for two or more draft horses, or other draft animals, harnessed in a single line one behind another, as opposed to a pair, harnessed side by side, or a team of several pairs. The tandem harness allows additional animals to provide pulling power for a vehicle designed for a single animal. The English word ''tandem'' derives from the Latin adverb , meaning ''at length'' or ''finally''. It is a word play, using the Latin phrase (referring to time, not position) for English "at length, lengthwise". Tandem bicycles are named for their tandem seating, a more common arrangement than side-by-side "sociable" seating. ''Tandem'' can also be used more generally to refer to any group of persons or objects working together, not necessarily in line. Automob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Segmental Duplication
Low copy repeats (LCRs), also known as segmental duplications (SDs), are highly homologous sequence elements within the eukaryotic genome. Repeats The repeats, or duplications, are typically 10–300 kb in length, and bear greater than 95% sequence identity. Though rare in most mammals, LCRs comprise a large portion of the human genome owing to a significant expansion during primate evolution. In humans, chromosomes Y and 22 have the greatest proportion of SDs: 50.4% and 11.9% respectively. Misalignment of LCRs during non-allelic homologous recombination (NAHR) is an important mechanism underlying the chromosomal microdeletion disorders as well as their reciprocal duplication partners. Many LCRs are concentrated in "hotspots", such as the 17p11-12 region, 27% of which is composed of LCR sequence. NAHR and non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) within this region are responsible for a wide range of disorders, including Charcot–Marie–Tooth syndrome type 1A, hereditary neuropat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |