|
Contrecoup Injury
In head injury, a coup injury occurs under the site of impact with an object, and a contrecoup injury occurs on the side opposite the area that was hit. Coup and contrecoup injuries are associated with cerebral contusions, a type of traumatic brain injury in which the brain is bruised. Coup and contrecoup injuries can occur individually or together. When a moving object impacts the stationary head, coup injuries are typical, while contrecoup injuries are produced when the moving head strikes a stationary object. Coup and contrecoup injuries are considered focal brain injuries – those that occur in a particular spot in the brain – as opposed to diffuse injuries, which occur over a more widespread area. Diffuse axonal injury is the most prevalent pathology of coup contrecoup. The exact mechanism for the injuries, especially contrecoup injuries, is a subject of much debate. In general, they involve an abrupt deceleration of the head, causing the brain to collide with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contrecoup
Contrecoup may refer to: * Coup contrecoup injury In head injury, a coup injury occurs under the site of impact with an object, and a contrecoup injury occurs on the side opposite the area that was hit. Coup and contrecoup injuries are associated with cerebral contusions, a type of traumatic bra ... * Counter-coup {{dab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis), or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see spelling differences), is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action potentials away from the nerve cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles, and glands. In certain sensory neurons (pseudounipolar neurons), such as those for touch and warmth, the axons are called afferent nerve fibers and the electrical impulse travels along these from the periphery to the cell body and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction can be the cause of many inherited and acquired neurological disorders that affect both the peripheral and central neurons. Nerve fibers are classed into three typesgroup A nerve fibers, group B nerve fibers, and group C nerve fibers. Groups A and B are myelinated, and group C are unmyelinated. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Académie Royale De Chirurgie
An academy (Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of secondary or tertiary higher learning (and generally also research or honorary membership). The name traces back to Plato's school of philosophy, founded approximately 385 BC at Akademia, a sanctuary of Athena, the goddess of wisdom and skill, north of Athens, Greece. Etymology The word comes from the ''Academy'' in ancient Greece, which derives from the Athenian hero, ''Akademos''. Outside the city walls of Athens, the gymnasium was made famous by Plato as a center of learning. The sacred space, dedicated to the goddess of wisdom, Athena, had formerly been an olive grove, hence the expression "the groves of Academe". In these gardens, the philosopher Plato conversed with followers. Plato developed his sessions into a method of teaching philosophy and in 387 BC, established what is known today as the Old Academy. By extension, ''academia'' has come to mean the accumulation, dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antoine Louis
Antoine Louis (; 13 February 1723, Metz – 20 May 1792) was an 18th-century French surgeon and physiologist. He was originally trained in medicine by his father, a sergeant major at a local military hospital. As a young man he moved to Paris, where he served as ''gagnant-maîtrise'' at the Salpêtrière. In 1750 he was appointed professor of physiology, a position he held for 40 years. In 1764 he was appointed lifetime secretary to the Académie Royale de Chirurgie. Louis published numerous articles on surgery, including several biographies of surgeons who died in his lifetime. He also published the surgical aphorisms of Dutch physician Herman Boerhaave (1668–1738). Louis is credited with designing a prototype of the guillotine. For a period of time after its invention, the guillotine was called a ''louisette''. However, it was later named after French physician Joseph Ignace Guillotin (1738–1814), whose advocacy of a more humane method of capital punishment prompted the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Louis Petit
Jean-Louis Petit (13 March 1674 – 20 April 1750) was a French surgeon and the inventor of a screw-type tourniquet. He was first enthusiastic about anatomy and received a master's certificate in surgery in Paris in 1700. He became a member of the French Royal Academy of Sciences in 1715 and was named director of the French Royal Academy of Surgery by the king when it was created in 1731. He acquired great notoriety because of his skill and experience, thanks to his case reports of hemorrhage, lacrimal fistula and operation on the frenum A frenulum (or frenum, plural: frenula or frena, from the Latin ''frēnulum'', "little bridle", the diminutive of ''frēnum'') is a small fold of tissue that secures the motion of a mobile organ (anatomy), organ in the Human body, body. In huma ..., for his treatise on bone diseases and especially for his general treatise on surgical operations, on which he worked for 12 years and which was finished after his death by François-Dominique L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lens (anatomy)
The lens, or crystalline lens, is a transparent biconvex structure in the eye that, along with the cornea, helps to refract light to be focused on the retina. By changing shape, it functions to change the focal length of the eye so that it can focus on objects at various distances, thus allowing a sharp real image of the object of interest to be formed on the retina. This adjustment of the lens is known as '' accommodation'' (see also below). Accommodation is similar to the focusing of a photographic camera via movement of its lenses. The lens is flatter on its anterior side than on its posterior side. In humans, the refractive power of the lens in its natural environment is approximately 18 dioptres, roughly one-third of the eye's total power. Structure The lens is part of the anterior segment of the human eye. In front of the lens is the iris, which regulates the amount of light entering into the eye. The lens is suspended in place by the suspensory ligament of the lens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temporal Lobe
The temporal lobe is one of the four Lobes of the brain, major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The temporal lobe is located beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain. The temporal lobe is involved in processing sensory input into derived meanings for the appropriate retention of visual memory, language comprehension, and emotion association. ''Temporal'' refers to the head's Temple (anatomy), temples. Structure The Temple (anatomy)#Etymology, temporal Lobe (anatomy), lobe consists of structures that are vital for declarative or long-term memory. Declarative memory, Declarative (denotative) or Explicit memory, explicit memory is conscious memory divided into semantic memory (facts) and episodic memory (events). Medial temporal lobe structures that are critical for long-term memory include the hippocampus, along with the surrounding Hippocampal formation, hippocampal region consisting of the Perirhinal cortex, perirhinal, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontal Lobe
The frontal lobe is the largest of the four major lobes of the brain in mammals, and is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere (in front of the parietal lobe and the temporal lobe). It is parted from the parietal lobe by a groove between tissues called the central sulcus and from the temporal lobe by a deeper groove called the lateral sulcus (Sylvian fissure). The most anterior rounded part of the frontal lobe (though not well-defined) is known as the frontal pole, one of the three poles of the cerebrum. The frontal lobe is covered by the frontal cortex. The frontal cortex includes the premotor cortex, and the primary motor cortex – parts of the motor cortex. The front part of the frontal cortex is covered by the prefrontal cortex. There are four principal gyri in the frontal lobe. The precentral gyrus is directly anterior to the central sulcus, running parallel to it and contains the primary motor cortex, which controls voluntary movements of specific body parts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual System
The visual system comprises the sensory organ (the eye) and parts of the central nervous system (the retina containing photoreceptor cells, the optic nerve, the optic tract and the visual cortex) which gives organisms the sense of sight (the ability to perception, detect and process visible light) as well as enabling the formation of several non-image photo response functions. It detects and interprets information from the optical spectrum perceptible to that species to "build a representation" of the surrounding environment. The visual system carries out a number of complex tasks, including the reception of light and the formation of monocular neural representations, colour vision, the neural mechanisms underlying stereopsis and assessment of distances to and between objects, the identification of a particular object of interest, motion perception, the analysis and integration of visual information, pattern recognition, accurate motor coordination under visual guidance, and mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
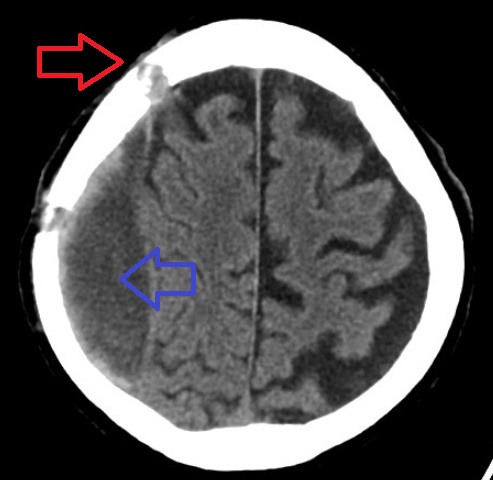
Subdural Hematoma
A subdural hematoma (SDH) is a type of bleeding in which a Hematoma, collection of blood—usually but not always associated with a traumatic brain injury—gathers between the inner layer of the dura mater and the arachnoid mater of the meninges surrounding the brain. It usually results from tears in bridging veins that cross the subdural space. Subdural hematomas may cause an increase in the intracranial pressure, pressure inside the skull, which in turn can cause compression of and damage to delicate brain tissue. Acute subdural hematomas are often life-threatening. Chronic subdural hematomas have a better prognosis if properly managed. In contrast, epidural hematomas are usually caused by tears in arteries, resulting in a build-up of blood between the dura mater and the skull. The third type of brain hemorrhage, known as a subarachnoid hemorrhage, causes bleeding into the subarachnoid space between the arachnoid mater and the pia mater. __TOC__ Signs and symptoms The sympt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemorrhage
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, vagina or anus, or through a puncture in the skin. Hypovolemia is a massive decrease in blood volume, and death by excessive loss of blood is referred to as exsanguination. Typically, a healthy person can endure a loss of 10–15% of the total blood volume without serious medical difficulties (by comparison, blood donation typically takes 8–10% of the donor's blood volume). The stopping or controlling of bleeding is called hemostasis and is an important part of both first aid and surgery. Types * Upper head ** Intracranial hemorrhage – bleeding in the skull. ** Cerebral hemorrhage – a type of intracranial hemorrhage, bleeding within the brain tissue itself. ** Intracerebral hemorrhage – bleeding in the brain caused by the ruptu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
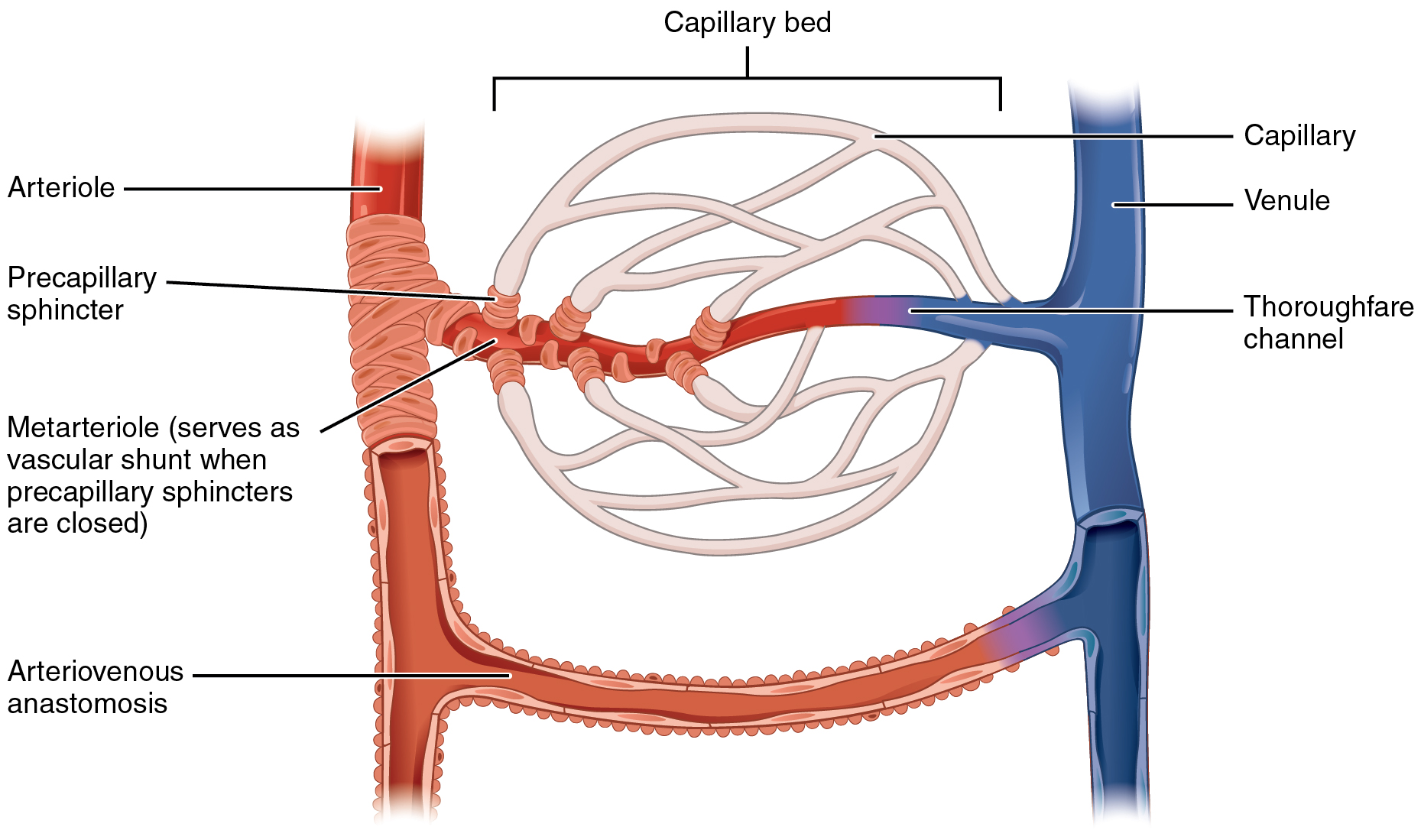
Microvessel
The microcirculation is the circulation of the blood in the smallest blood vessels, the microvessels of the microvasculature present within organ tissues. The microvessels include terminal arterioles, metarterioles, capillaries, and venules. Arterioles carry oxygenated blood to the capillaries, and blood flows out of the capillaries through venules into veins. In addition to these blood vessels, the microcirculation also includes lymphatic capillaries and collecting ducts. The main functions of the microcirculation are the delivery of oxygen and nutrients and the removal of carbon dioxide (CO2). It also serves to regulate blood flow and tissue perfusion thereby affecting blood pressure and responses to inflammation which can include edema (swelling). Most vessels of the microcirculation are lined by flattened cells of the endothelium and many of them are surrounded by contractile cells called pericytes. The endothelium provides a smooth surface for the flow of blood and regu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)