|
Continental Glacier
In glaciology, an ice sheet, also known as a continental glacier, is a mass of glacial ice that covers surrounding terrain and is greater than . The only current ice sheets are in Antarctica and Greenland; during the Last Glacial Period at Last Glacial Maximum, the Laurentide Ice Sheet covered much of North America, the Weichselian ice sheet covered Northern Europe and the Patagonian Ice Sheet covered southern South America. Ice sheets are bigger than ice shelves or alpine glaciers. Masses of ice covering less than 50,000 km2 are termed an ice cap. An ice cap will typically feed a series of glaciers around its periphery. Although the surface is cold, the base of an ice sheet is generally warmer due to geothermal heat. In places, melting occurs and the melt-water lubricates the ice sheet so that it flows more rapidly. This process produces fast-flowing channels in the ice sheet — these are ice streams. The present-day polar ice sheets are relatively young in geolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica 6400px From Blue Marble
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Stream
An ice stream is a region of fast-moving ice within an ice sheet. It is a type of glacier, a body of ice that moves under its own weight. They can move upwards of a year, and can be up to in width, and hundreds of kilometers in length. They tend to be about deep at the thickest, and constitute the majority of the ice that leaves the sheet. In Antarctica, the ice streams account for approximately 90% of the sheet's mass loss per year, and approximately 50% of the mass loss in Greenland. The shear forces cause deformation and recrystallization that drive the movement, this movement then causes topographic lows and valleys to form after all of the material in the ice sheet has been discharged. Sediment also plays an important role in flow velocity, the softer and more easily deformed the sediment present, the easier it is for flow velocity to be higher. Most ice streams contain a layer of water at the bottom, which lubricates flow and acts to increase speed. Mechanics Ice str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
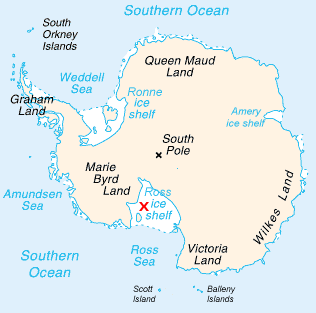
Ross Ice Shelf
The Ross Ice Shelf is the largest ice shelf of Antarctica (, an area of roughly and about across: about the size of France). It is several hundred metres thick. The nearly vertical ice front to the open sea is more than long, and between high above the water surface. Ninety percent of the floating ice, however, is below the water surface. Most of Ross Ice Shelf is in the Ross Dependency claimed by New Zealand. It floats in, and covers, a large southern portion of the Ross Sea and the entire Roosevelt Island located in the east of the Ross Sea. The ice shelf is named after Sir James Clark Ross, who discovered it on 28 January 1841. It was originally called "The Barrier", with various adjectives including "Great Ice Barrier", as it prevented sailing further south. Ross mapped the ice front eastward to 160° W. In 1947, the U.S. Board on Geographic Names applied the name "Ross Shelf Ice" to this feature and published it in the original U.S. Antarctic Gazetteer. In Januar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seabed
The seabed (also known as the seafloor, sea floor, ocean floor, and ocean bottom) is the bottom of the ocean. All floors of the ocean are known as 'seabeds'. The structure of the seabed of the global ocean is governed by plate tectonics. Most of the ocean is very deep, where the seabed is known as the abyssal plain. Seafloor spreading creates mid-ocean ridges along the center line of major ocean basins, where the seabed is slightly shallower than the surrounding abyssal plain. From the abyssal plain, the seabed slopes upward toward the continents and becomes, in order from deep to shallow, the continental rise, slope, and shelf. The depth within the seabed itself, such as the depth down through a sediment core, is known as the “depth below seafloor.” The ecological environment of the seabed and the deepest waters are collectively known, as a habitat for creatures, as the “benthos.” Most of the seabed throughout the world's oceans is covered in layers of marine sediments. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardised geodetic datumthat is used, for example, as a chart datum in cartography and marine navigation, or, in aviation, as the standard sea level at which atmospheric pressure is measured to calibrate altitude and, consequently, aircraft flight levels. A common and relatively straightforward mean sea-level standard is instead the midpoint between a mean low and mean high tide at a particular location. Sea levels can be affected by many factors and are known to have varied greatly over geological time scales. Current sea level rise is mainly caused by human-induced climate change. When temperatures rise, Glacier, mountain glaciers and the Ice sheet, polar ice caps melt, increasing the amount of water in water bodies. Because most of human settlem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Antarctic Ice Sheet
The Western Antarctic Ice Sheet (WAIS) is the segment of the Antarctic ice sheet, continental ice sheet that covers West Antarctica, the portion of Antarctica on the side of the Transantarctic Mountains that lies in the Western Hemisphere. The WAIS is classified as a marine-based ice sheet, meaning that its bed lies well below sea level and its edges flow into floating ice shelves. The WAIS is bounded by the Ross Ice Shelf, the Ronne Ice Shelf, and outlet glaciers that drain into the Amundsen Sea. Description It is estimated that the volume of the Antarctic ice sheet is about 25.4 million km3 (6.1 million cu mi), and the WAIS contains just under 10% of this, or 2.2 million km3 (530,000 cu mi). The weight of the ice has caused the underlying rock to sink by between in a process known as Isostasy, isostatic depression. Under the force of its own weight, the ice sheet deforms and flows. The interior ice flows slowly over rough bedrock. In some circumstances, ice ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Antarctic Ice Sheet
The East Antarctic Ice Sheet (EAIS) is one of two large ice sheets in Antarctica, and the largest on the entire planet. The EAIS lies between 45° west and 168° east longitudinally. The EAIS holds enough ice to raise global sea levels by and is considerably larger in area and mass than the West Antarctic Ice Sheet (WAIS). It is separated from the WAIS by the Transantarctic Mountains. The EAIS is the driest, windiest, and coldest place on Earth, with temperatures reported down to nearly -100°C. The EAIS holds the thickest ice on Earth, at . It is home to the geographic South Pole and the Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station. Temperature changes Cooling in East Antarctica during the decades of the 1980s and 1990s partially offset the impact of climate change on the West Antarctic Ice Sheet, which has warmed by more than 0.1 °C/decade in the last 50 years. The continent-wide average surface temperature trend of Antarctica is positive and statistically significant at >0.0 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transantarctic Mountains
The Transantarctic Mountains (abbreviated TAM) comprise a mountain range of uplifted (primarily sedimentary rock, sedimentary) rock in Antarctica which extend, with some interruptions, across the continent from Cape Adare in northern Victoria Land to Coats Land. These mountains divide East Antarctica and West Antarctica. They include a number of separately named mountain groups, which are often again subdivided into smaller ranges. The range was first sighted by James Clark Ross in 1841 at what was later named the Ross Ice Shelf in his honour. It was first crossed during the British National Antarctic Expedition of 1901-1904. Geography The mountain range stretches between the Ross Sea and the Weddell Sea, the entire width of Antarctica, hence the name. With a total length of about , the Transantarctic Mountains are one of the longest mountain ranges on Earth. The Antarctandes are even longer, having in common with the Transantarctic Mountains the ranges from Cape Adare to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature (journal)
''Nature'' is a British weekly scientific journal founded and based in London, England. As a multidisciplinary publication, ''Nature'' features peer-reviewed research from a variety of academic disciplines, mainly in science and technology. It has core editorial offices across the United States, continental Europe, and Asia under the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature. ''Nature'' was one of the world's most cited scientific journals by the Science Edition of the 2019 ''Journal Citation Reports'' (with an ascribed impact factor of 42.778), making it one of the world's most-read and most prestigious academic journals. , it claimed an online readership of about three million unique readers per month. Founded in autumn 1869, ''Nature'' was first circulated by Norman Lockyer and Alexander Macmillan as a public forum for scientific innovations. The mid-20th century facilitated an editorial expansion for the journal; ''Nature'' redoubled its efforts in exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surface is made up of the ocean, dwarfing Earth's polar ice, lakes, and rivers. The remaining 29% of Earth's surface is land, consisting of continents and islands. Earth's surface layer is formed of several slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's liquid outer core generates the magnetic field that shapes the magnetosphere of the Earth, deflecting destructive solar winds. The atmosphere of the Earth consists mostly of nitrogen and oxygen. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere like carbon dioxide (CO2) trap a part of the energy from the Sun close to the surface. Water vapor is widely present in the atmosphere and forms clouds that cover most of the planet. More solar e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclude the fungi and some algae, as well as the prokaryotes (the archaea and bacteria). By one definition, plants form the clade Viridiplantae (Latin name for "green plants") which is sister of the Glaucophyta, and consists of the green algae and Embryophyta (land plants). The latter includes the flowering plants, conifers and other gymnosperms, ferns and their allies, hornworts, liverworts, and mosses. Most plants are multicellular organisms. Green plants obtain most of their energy from sunlight via photosynthesis by primary chloroplasts that are derived from endosymbiosis with cyanobacteria. Their chloroplasts contain chlorophylls a and b, which gives them their green color. Some plants are parasitic or mycotrophic and have lost the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |