|
Constant Current Regulator
A current source is an electronic circuit that delivers or absorbs an electric current which is independent of the voltage across it. A current source is the duality (electrical circuits), dual of a voltage source. The term ''current sink'' is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply. Figure 1 shows the schematic symbol for an ideal current source driving a electrical load, resistive load. There are two types. An ''independent current source'' (or sink) delivers a constant current. A ''dependent current source'' delivers a current which is proportional to some other voltage or current in the circuit. Background , - align="center" , style="padding: 1em 2em 0;", , style="padding: 1em 2em 0;", , - align="center" , Voltage source , Current source , - align="center" , style="padding: 1em 2em 0;", , style="padding: 1em 2em 0;", , - align="center" , Controlled voltage source , Controlled current source , - align="center" , style="padding: 1em 2em 0;", ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ohms Law Current Source (white Background)
ohms (symbol Ω) usually refers to the plural for the unit of electrical resistance, named after Georg Ohm Ohms or OHMS may also refer to: * Ohm's law of electric currents, first proposed by Georg Ohm * O.H.M.S., On His Majesty's Service, On His/Her Majesty's Service * O.H.M.S. (film), ''O.H.M.S.'' (film), a 1937 British action comedy film * OHMS (1980 film), ''OHMS'' (1980 film), an American film starring Leslie Nielsen * Ohms (album), ''Ohms'' (album), a 2020 album by Deftones ** Ohms (song), "Ohms" (song), a song from the album * Office of Hazardous Materials Safety, federal safety authority within the United States Department of Transportation * Oral History Metadata Synchronizer, a web application for accessing oral history interviews See also * Ohm (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Power
Electric power is the rate at which electrical energy is transferred by an electric circuit. The SI unit of power is the watt, one joule per second. Standard prefixes apply to watts as with other SI units: thousands, millions and billions of watts are called kilowatts, megawatts and gigawatts respectively. A common misconception is that electric power is bought and sold, but actually electrical energy is bought and sold. For example, electricity is sold to consumers in kilowatt-hours (kilowatts multiplied by hours), because energy is power multiplied by time. Electric power is usually produced by electric generators, but can also be supplied by sources such as electric batteries. It is usually supplied to businesses and homes (as domestic mains electricity) by the electric power industry through an electrical grid. Electric power can be delivered over long distances by transmission lines and used for applications such as motion, light or heat with high efficiency. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Source
In electronics, a common-source amplifier is one of three basic single-stage field-effect transistor (FET) amplifier topologies, typically used as a voltage or transconductance amplifier. The easiest way to tell if a FET is common source, common drain, or common gate is to examine where the signal enters and leaves. The remaining terminal is what is known as "common". In this example, the signal enters the gate, and exits the drain. The only terminal remaining is the source. This is a common-source FET circuit. The analogous bipolar junction transistor circuit may be viewed as a transconductance amplifier or as a voltage amplifier. (See classification of amplifiers). As a transconductance amplifier, the input voltage is seen as modulating the current going to the load. As a voltage amplifier, input voltage modulates the current flowing through the FET, changing the voltage across the output resistance according to Ohm's law. However, the FET device's output resistance typicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Emitter
In electronics, a common-emitter amplifier is one of three basic single-stage bipolar-junction-transistor (BJT) amplifier topologies, typically used as a voltage amplifier. It offers high current gain (typically 200), medium input resistance and a high output resistance. The output of a common emitter amplifier is 180 degrees out of phase to the input signal. In this circuit the base terminal of the transistor serves as the input, the collector is the output, and the emitter is ''common'' to both (for example, it may be tied to ground reference or a power supply rail), hence its name. The analogous FET circuit is the common-source amplifier, and the analogous tube circuit is the common-cathode amplifier. Emitter degeneration Common-emitter amplifiers give the amplifier an inverted output and can have a very high gain that may vary widely from one transistor to the next. The gain is a strong function of both temperature and bias current, and so the actual gain is somewhat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Differential Amplifier
A differential amplifier is a type of electronic amplifier that amplifies the difference between two input voltages but suppresses any voltage common to the two inputs. It is an analog circuit with two inputs V_\text^- and V_\text^+ and one output V_\text, in which the output is ideally proportional to the difference between the two voltages: : V_\text = A(V_\text^+ - V_\text^-), where A is the gain of the amplifier. Single amplifiers are usually implemented by either adding the appropriate feedback resistors to a standard op-amp, or with a dedicated integrated circuit containing internal feedback resistors. It is also a common sub-component of larger integrated circuits handling analog signals. Theory The output of an ideal differential amplifier is given by : V_\text = A_\text(V_\text^+ - V_\text^-), where V_\text^+ and V_\text^- are the input voltages, and A_\text is the differential gain. In practice, however, the gain is not quite equal for the two inputs. This means ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny MOSFETs (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors) integrate into a small chip. This results in circuits that are orders of magnitude smaller, faster, and less expensive than those constructed of discrete electronic components. The IC's mass production capability, reliability, and building-block approach to integrated circuit design has ensured the rapid adoption of standardized ICs in place of designs using discrete transistors. ICs are now used in virtually all electronic equipment and have revolutionized the world of electronics. Computers, mobile phones and other home appliances are now inextricable parts of the structure of modern societies, made possible by the small size and low cost of ICs such as modern computer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
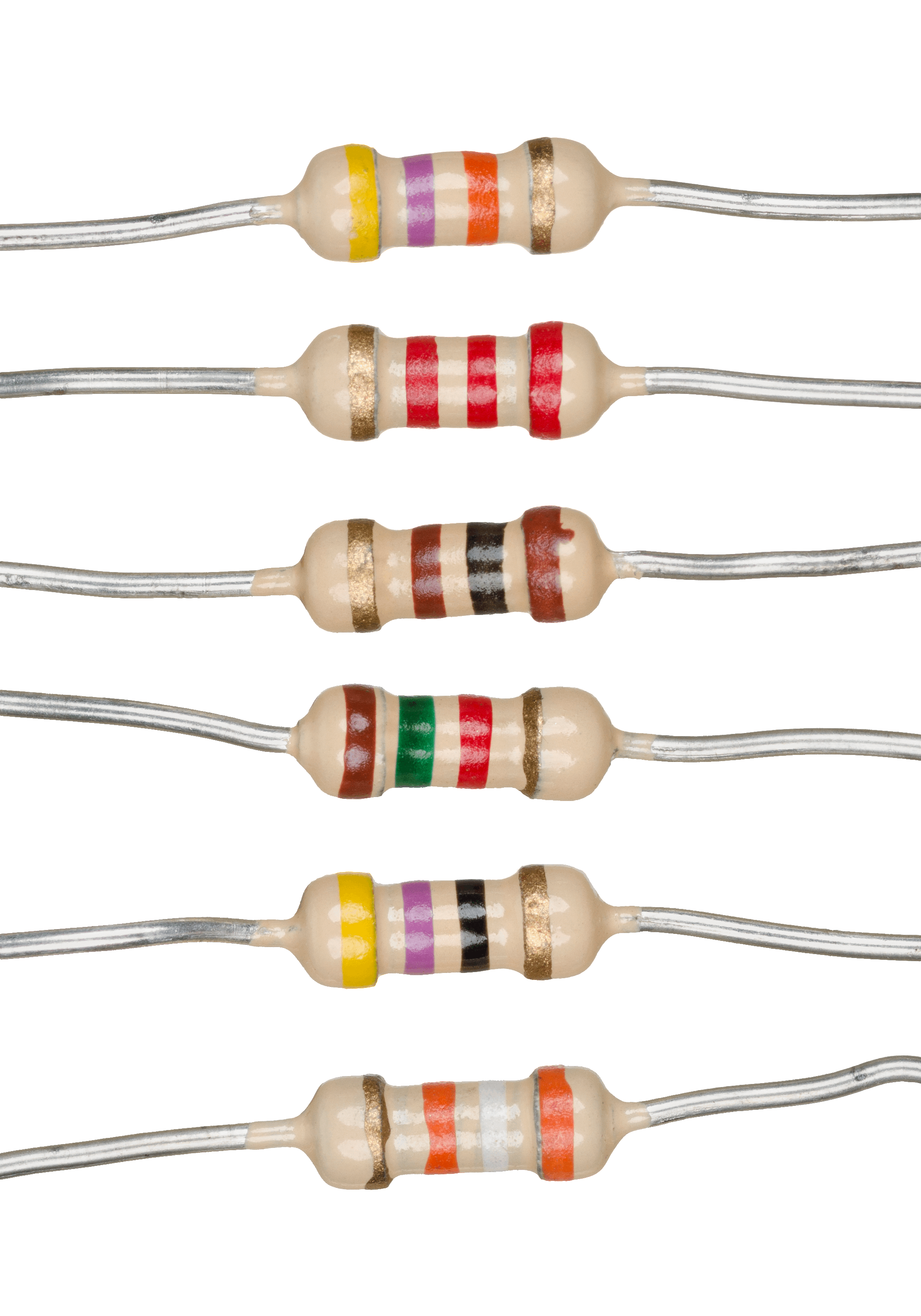
Resistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active elements, and terminate transmission lines, among other uses. High-power resistors that can dissipate many watts of electrical power as heat may be used as part of motor controls, in power distribution systems, or as test loads for generators. Fixed resistors have resistances that only change slightly with temperature, time or operating voltage. Variable resistors can be used to adjust circuit elements (such as a volume control or a lamp dimmer), or as sensing devices for heat, light, humidity, force, or chemical activity. Resistors are common elements of electrical networks and electronic circuits and are ubiquitous in electronic equipment. Practical resistors as discrete components can be composed of various compounds and forms. Resisto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vice Versa
References Additional references * * {{Latin phrases V ca:Locució llatina#V da:Latinske ord og vendinger#V fr:Liste de locutions latines#V id:Daftar frasa Latin#V it:Locuzioni latine#V nl:Lijst van Latijnse spreekwoorden en uitdrukkingen#V pt:Lista de provérbios e sentenças em latim#V ro:Listă de locuțiuni în limba latină#V sl:Seznam latinskih izrekov#V sv:Lista över latinska ordspråk och talesätt#V tl:Tala ng mga pariralang Latin#V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negative Feedback
Negative feedback (or balancing feedback) occurs when some function (Mathematics), function of the output of a system, process, or mechanism is feedback, fed back in a manner that tends to reduce the fluctuations in the output, whether caused by changes in the input or by other disturbances. Whereas positive feedback tends to lead to instability via exponential growth, oscillation or chaos theory, chaotic behavior, negative feedback generally promotes stability. Negative feedback tends to promote a settling to List of types of equilibrium, equilibrium, and reduces the effects of perturbations. Negative feedback loops in which just the right amount of correction is applied with optimum timing can be very stable, accurate, and responsive. Negative feedback is widely used in mechanical and electronic engineering, and also within living organisms, and can be seen in many other fields from chemistry and economics to physical systems such as the climate. General negative feedback ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megavolt (other) ''
{{Disambig ...
Megavolt may refer to: *One million volts in electronics and physics * Megavolt (Darkwing Duck), a fictional supervillain in the Disney animated series ''Darkwing Duck''. *Megavolt, a villain in the television series''Teenage Mutant Ninja Turtles ''Teenage Mutant Ninja Turtles'' is an American media franchise created by the comic book artists Kevin Eastman and Peter Laird. It follows Leonardo (Teenage Mutant Ninja Turtles), Leonardo, Michelangelo (Teenage Mutant Ninja Turtles), Miche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Van De Graaff Generator
A Van de Graaff generator is an electrostatic generator which uses a moving belt to accumulate electric charge on a hollow metal globe on the top of an insulated column, creating very high electric potentials. It produces very high voltage direct current (DC) electricity at low current levels. It was invented by American physicist Robert J. Van de Graaff in 1929. The potential difference achieved by modern Van de Graaff generators can be as much as 5 megavolts. A tabletop version can produce on the order of 100 kV and can store enough energy to produce visible electric sparks. Small Van de Graaff machines are produced for entertainment, and for physics education to teach electrostatics; larger ones are displayed in some science museums. The Van de Graaff generator was originally developed as a particle accelerator for physics research, as its high potential can be used to accelerate subatomic particles to great speeds in an evacuated tube. It was the most powerful type of accelera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltage Drop
Voltage drop is the decrease of electrical potential along the path of a current flowing in an electrical circuit. Voltage drops in the internal resistance of the source, across conductors, across contacts, and across connectors are undesirable because some of the energy supplied is dissipated. The voltage drop across the electrical load is proportional to the power available to be converted in that load to some other useful form of energy. For example, an electric space heater may have a resistance of ten ohms, and the wires that supply it may have a resistance of 0.2 ohms, about 2% of the total circuit resistance. This means that approximately 2% of the supplied voltage is lost in the wire itself. An excessive voltage drop may result in the unsatisfactory performance of a space heater and overheating of the wires and connections. National and local electrical codes may set guidelines for the maximum voltage drop allowed in electrical wiring to ensure efficiency of distributi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)