|
Condylarth
Condylarthra is an informal group – previously considered an order – of extinct placental mammals, known primarily from the Paleocene and Eocene epochs. They are considered early, primitive ungulates. It is now largely considered to be a wastebasket taxon, having served as a dumping ground for classifying ungulates which had not been clearly established as part of either Perissodactyla or Cetartiodactyla, being composed thus of several unrelated lineages. Taxonomic history Condylarthra always was a problematic group. When Condylarthra was first described by , Phenacodontidae was the type and only family therein. , however, raised Condylarthra to an order and included a wide range of diverse placentals with generalized dentitions and postcranial skeletons. More recent researchers (i.e. post-WW2) have been more restrictive; either including only a limited number of taxa, or proposing that the term should be abandoned altogether. Due to their primitive characteristics condyla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ungulates
Ungulates ( ) are members of the diverse clade Ungulata which primarily consists of large mammals with hooves. These include odd-toed ungulates such as horses, rhinoceroses, and tapirs; and even-toed ungulates such as cattle, pigs, giraffes, camels, sheep, deer, and hippopotamuses. Cetaceans such as whales, dolphins, and porpoises are also classified as even-toed ungulates, although they do not have hooves. Most terrestrial ungulates use the hoofed tips of their toes to support their body weight while standing or moving. The term means, roughly, "being hoofed" or "hoofed animal". As a descriptive term, "ungulate" normally excludes cetaceans as they do not possess most of the typical morphological characteristics of other ungulates, but recent discoveries indicate that they were also descended from early artiodactyls. Ungulates are typically herbivorous and many employ specialized gut bacteria to allow them to digest cellulose. Some modern species, such as pigs, are omnivorous, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Litopterna
Litopterna (from grc, λῑτή πτέρνα "smooth heel") is an extinct order of fossil hoofed mammals from the Cenozoic era. The order is one of the five great orders of South American ungulates that were endemic to the continent, until the Great American Biotic Interchange brought new ungulate species. Like other endemic South American mammals, their relationship to other mammal groups had long been unclear, but recent genetic and proteomic evidence indicates that their closest living relatives are Perissodactyls (odd-toed ungulates) including horses, rhinoceros, and tapirs, and that litopterns are closely related to notoungulates, another widespread group of South American ungulates. There were two major groups of litopterns: Proterotheriidae and Macraucheniidae. Proterotheriids were medium to large animals that evolved adaptations for fast running, and occupied a variety of niches that elsewhere were filled by animals such as goats and antelopes, mouse deer, and horses. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenacodontidae
Phenacodontidae is an extinct family of large herbivorous mammals traditionally placed in the “wastebasket taxon” Condylarthra, which may instead represent early-stage perissodactyls. They lived in the Paleocene and Eocene epochs (about 60–50 million years ago) and their fossil remains have been found in North America and Europe. Description These animals had a variety of body sizes, and could be as small as domestic cats ('' Tetraclaenodon'' and '' Ectocion'') and as large as sheep (''Phenacodus''). The skull of phenacodontids is long and narrow, and equipped with a small braincase. The skeleton of phenacodontids show several primitive characteristics (the long and heavy tail for example) but also a number of advanced, Perissodactyla-like adaptations: Their long legs, for example, had five fingers, but the first finger showed a clear reduction, and in some forms (like ''Phenacodus'') the fifth finger was reduced as well. Some species had tapir-like adaptations su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ectocion Ralstonensis
''Ectocion'' (sometimes ''Ectocyon'') is an extinct genus of placental mammals of the family Phenacodontidae. The genus was earlier classified as ''Gidleyina'' (Simpson 1935) and ''Prosthecion'' (Patterson and West 1973). Retrieved May 2013. Paleocene specimens of these hoofed, ground-dwelling herbivores have been found in Canada (Alberta, Saskatchewan) and the United States (Colorado, Montana, North Dakota, and Wyoming). Eocene specimens have been found in Mexico and the United States (Colorado, Mississippi, Wyoming). One of the dramatic effects of the Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum The Paleocene–Eocene thermal maximum (PETM), alternatively (ETM1), and formerly known as the "Initial Eocene" or "", was a time period with a more than 5–8 °C global average temperature rise across the event. This climate event o ... (PETM) was some animals evolving smaller bodies. Fossilized ''Ectocion'' jaw bones show that this genus was smaller during (''E. parvus'', 55. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order (biology)
Order ( la, ordo) is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between family and class. In biological classification, the order is a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and recognized by the nomenclature codes. An immediately higher rank, superorder, is sometimes added directly above order, with suborder directly beneath order. An order can also be defined as a group of related families. What does and does not belong to each order is determined by a taxonomist, as is whether a particular order should be recognized at all. Often there is no exact agreement, with different taxonomists each taking a different position. There are no hard rules that a taxonomist needs to follow in describing or recognizing an order. Some taxa are accepted almost universally, while others are recognized only rarely. The name of an order is usually written with a capital letter. For some groups of organisms, their orders may follo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talus Bone
The talus (; Latin for ankle or ankle bone), talus bone, astragalus (), or ankle bone is one of the group of foot bones known as the tarsus. The tarsus forms the lower part of the ankle joint. It transmits the entire weight of the body from the lower legs to the foot.Platzer (2004), p 216 The talus has joints with the two bones of the lower leg, the tibia and thinner fibula. These leg bones have two prominences (the lateral and medial malleoli) that articulate with the talus. At the foot end, within the tarsus, the talus articulates with the calcaneus (heel bone) below, and with the curved navicular bone in front; together, these foot articulations form the ball-and-socket-shaped talocalcaneonavicular joint. The talus is the second largest of the tarsal bones; it is also one of the bones in the human body with the highest percentage of its surface area covered by articular cartilage. It is also unusual in that it has a retrograde blood supply, i.e. arterial blood enters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
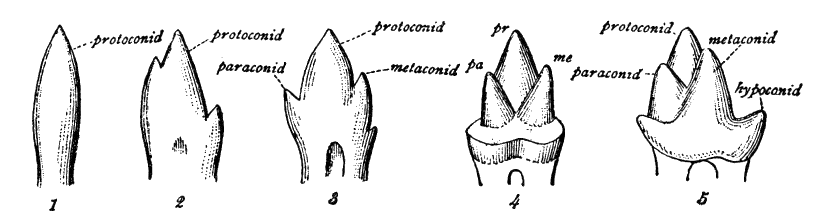
Trigonid
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone tooth", from ''mola'', millstone and ''dens'', tooth. Molars show a great deal of diversity in size and shape across mammal groups. The third molar of humans is sometimes vestigial. Human anatomy In humans, the molar teeth have either four or five cusps. Adult humans have 12 molars, in four groups of three at the back of the mouth. The third, rearmost molar in each group is called a wisdom tooth. It is the last tooth to appear, breaking through the front of the gum at about the age of 20, although this varies from individual to individual. Race can also affect the age at which this occurs, with statistical variations between groups. In some cases, it may not even erupt at all. The human mouth contains upper (maxillary) and lower (man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bunodont
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone tooth", from ''mola'', millstone and ''dens'', tooth. Molars show a great deal of diversity in size and shape across mammal groups. The third molar of humans is sometimes vestigial. Human anatomy In humans, the molar teeth have either four or five cusps. Adult humans have 12 molars, in four groups of three at the back of the mouth. The third, rearmost molar in each group is called a wisdom tooth. It is the last tooth to appear, breaking through the front of the gum at about the age of 20, although this varies from individual to individual. Race can also affect the age at which this occurs, with statistical variations between groups. In some cases, it may not even erupt at all. The human mouth contains upper (maxillary) and lower (mandibu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ectotympanic
The ectotympanic, or tympanicum, is a bony structure found in all mammals, located on the tympanic part of the temporal bone, which holds the tympanic membrane (eardrum) in place. In catarrhine primates (including humans), it takes a tube-shape. Its position and attachment to the skull vary between primates, and can be either inside or outside the auditory bulla. It is homologous with the angular bone of non-mammalian tetrapods Tetrapods (; ) are four-limb (anatomy), limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant taxon, extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids (reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (p .... References External links webref: Anthropology* * Skull Vertebrate anatomy {{Vertebrate anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auditory Bulla
The tympanic part of the temporal bone is a curved plate of bone lying below the squamous part of the temporal bone, in front of the mastoid process, and surrounding the external part of the ear canal. It originates as a separate bone (tympanic bone), which in some mammals stays separate through life. Evolutionarily, a portion of it is derived from the angular bone of the reptilian lower jaw. Surfaces Its postero-superior surface is concave, and forms the anterior wall, the floor, and part of the posterior wall of the bony ear canal. Medially, it presents a narrow furrow, the ''tympanic sulcus'', for the attachment of the tympanic membrane. Its antero-inferior surface is quadrilateral and slightly concave; it constitutes the posterior boundary of the mandibular fossa, and is in contact with the retromandibular part of the parotid gland. Borders Its lateral border is free and rough, and gives attachment to the cartilaginous part of the ear canal. Internally, the tymp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastoid Foramen
The mastoid foramen is a hole in the posterior border of the temporal bone. It transmits an emissary vein between the sigmoid sinus and the suboccipital venous plexus, and a small branch of the occipital artery, the posterior meningeal artery to the dura mater. Structure The mastoid foramen is a hole in the posterior border of the temporal bone of the skull. The opening of the mastoid foramen is an average of 18 mm from the asterion, and around 34 mm from the external auditory meatus. It is typically very narrow. This may be around 2 mm. Variation The position and size of this foramen are very variable. It is not always present. Sometimes, it is duplicated on one side or both sides. Sometimes, it is situated in the occipital bone, or in the suture between the temporal bone and the occipital bone. Function The mastoid foramen transmits: * an emissary vein between the sigmoid sinus and the suboccipital venous plexus or the posterior auricular vein. * a small branc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |