|
Conductance Quantum
The conductance quantum, denoted by the symbol , is the quantized unit of electrical conductance. It is defined by the elementary charge ''e'' and Planck constant ''h'' as: :G_0 = \frac = It appears when measuring the conductance of a quantum point contact, and, more generally, is a key component of the Landauer formula, which relates the electrical conductance of a quantum conductor to its quantum properties. It is twice the reciprocal of the von Klitzing constant (2/''R''K). Note that the conductance quantum does not mean that the conductance of any system must be an integer multiple of ''G''0. Instead, it describes the conductance of two quantum channels (one channel for spin up and one channel for spin down) if the probability for transmitting an electron that enters the channel is unity, i.e. if transport through the channel is ballistic. If the transmission probability is less than unity, then the conductance of the channel is less than ''G''0. The total conductance of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Conductance
The electrical resistance of an object is a measure of its opposition to the flow of electric current. Its reciprocal quantity is , measuring the ease with which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with mechanical friction. The SI unit of electrical resistance is the ohm (), while electrical conductance is measured in siemens (S) (formerly called the 'mho' and then represented by ). The resistance of an object depends in large part on the material it is made of. Objects made of electrical insulators like rubber tend to have very high resistance and low conductance, while objects made of electrical conductors like metals tend to have very low resistance and high conductance. This relationship is quantified by resistivity or conductivity. The nature of a material is not the only factor in resistance and conductance, however; it also depends on the size and shape of an object because these properties are extensive rather than inten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Hall Effect
The quantum Hall effect (or integer quantum Hall effect) is a quantized version of the Hall effect which is observed in two-dimensional electron systems subjected to low temperatures and strong magnetic fields, in which the Hall resistance exhibits steps that take on the quantized values : R_ = \frac = \frac , where is the Hall voltage, is the channel current, is the elementary charge and is Planck's constant. The divisor can take on either integer () or fractional () values. Here, is roughly but not exactly equal to the filling factor of Landau levels. The quantum Hall effect is referred to as the integer or fractional quantum Hall effect depending on whether is an integer or fraction, respectively. The striking feature of the integer quantum Hall effect is the persistence of the quantization (i.e. the Hall plateau) as the electron density is varied. Since the electron density remains constant when the Fermi level is in a clean spectral gap, this situation corresp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanoelectronics
Nanoelectronics refers to the use of nanotechnology in electronic components. The term covers a diverse set of devices and materials, with the common characteristic that they are so small that inter-atomic interactions and quantum mechanical properties need to be studied extensively. Some of these candidates include: hybrid molecular/semiconductor electronics, one-dimensional nanotubes/nanowires (e.g. silicon nanowires or carbon nanotubes) or advanced molecular electronics. Nanoelectronic devices have critical dimensions with a size range between 1 nm and 100 nm. Recent silicon MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor, or MOS transistor) technology generations are already within this regime, including 22 nanometers CMOS (complementary MOS) nodes and succeeding 14 nm, 10 nm and 7 nm FinFET (fin field-effect transistor) generations. Nanoelectronics is sometimes considered as disruptive technology because present candidates are significantly different f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Electronics
Quantum optics is a branch of atomic, molecular, and optical physics dealing with how individual quanta of light, known as photons, interact with atoms and molecules. It includes the study of the particle-like properties of photons. Photons have been used to test many of the counter-intuitive predictions of quantum mechanics, such as entanglement and teleportation, and are a useful resource for quantum information processing. History Light propagating in a restricted volume of space has its energy and momentum quantized according to an integer number of particles known as photons. Quantum optics studies the nature and effects of light as quantized photons. The first major development leading to that understanding was the correct modeling of the blackbody radiation spectrum by Max Planck in 1899 under the hypothesis of light being emitted in discrete units of energy. The photoelectric effect was further evidence of this quantization as explained by Albert Einstein in a 1905 paper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Conductance Quantum
In physics, the thermal conductance quantum g_0 describes the rate at which heat is transported through a single ballistic phonon channel with temperature T. It is given by :g_ = \frac \approx (9.464\times10^ ^)\;T. The thermal conductance of any electrically insulating structure that exhibits ballistic phonon transport is a positive integer multiple of g_0. The thermal conductance quantum was first measured in 2000. These measurements employed suspended silicon nitride () nanostructures that exhibited a constant thermal conductance of 16 g_0 at temperatures below approximately 0.6 kelvin. Relation to the quantum of electrical conductance For ballistic electrical conductors, the electron contribution to the thermal conductance is also quantized as a result of the electrical conductance quantum and the Wiedemann–Franz law In physics, the Wiedemann–Franz law states that the ratio of the electronic contribution of the thermal conductivity (''κ'') to the electrical con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
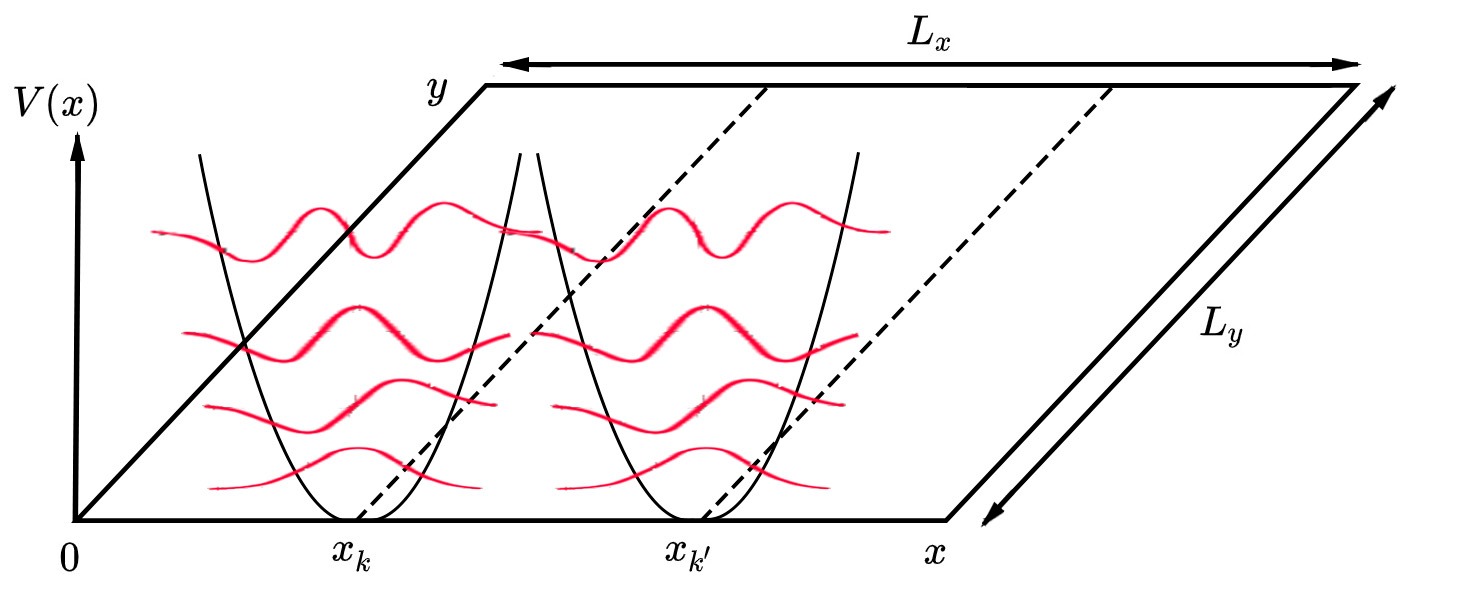
Quantum Wire
In mesoscopic physics, a quantum wire is an electrically conducting wire in which quantum effects influence the transport properties. Usually such effects appear in the dimension of nanometers, so they are also referred to as nanowires. Quantum effects If the diameter of a wire is sufficiently small, electrons will experience quantum confinement in the transverse direction. As a result, their transverse energy will be limited to a series of discrete values. One consequence of this quantization is that the classical formula for calculating the electrical resistance of a wire, : R = \rho \frac, is not valid for quantum wires (where \rho is the material's resistivity, l is the length, and A is the cross-sectional area of the wire). Instead, an exact calculation of the transverse energies of the confined electrons has to be performed to calculate a wire's resistance. Following from the quantization of electron energy, the electrical conductance (the inverse of the resistance) is fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
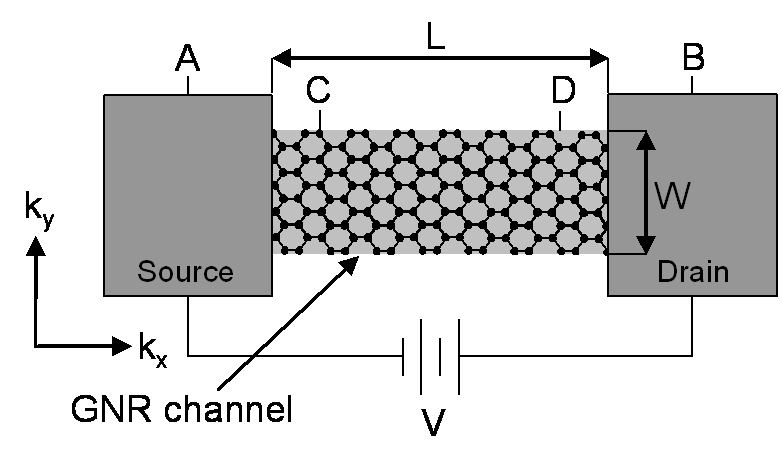
Quantum Point Contact
A quantum point contact (QPC) is a narrow constriction between two wide electrically conducting regions, of a width comparable to the electronic wavelength (nano- to micrometer). The importance of QPC lies in the fact that they prove quantisation of ballistic conductance in mesoscopic systems. The conductance of a QPC is quantized in units of 2e^2/h, the so-called conductance quantum. Quantum point contacts were first reported in 1988 by a Dutch team from Delft University of Technology and Philips Research and, independently, by a British team from the Cavendish Laboratory. They are based on earlier work by the British group which showed how split gates could be used to convert a two-dimensional electron gas into one-dimension, first in silicon and then in gallium arsenide. This quantisation is reminiscent of the quantisation of the Hall conductance, but is measured in the absence of a magnetic field. The zero-field conductance quantisation and the smooth transition to the quantum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoscopic Physics
Mesoscopic physics is a subdiscipline of condensed matter physics that deals with materials of an intermediate size. These materials range in size between the nanoscale for a quantity of atoms (such as a molecule) and of materials measuring micrometres. The lower limit can also be defined as being the size of individual atoms. At the micrometre level are bulk materials. Both mesoscopic and macroscopic objects contain many atoms. Whereas average properties derived from constituent materials describe macroscopic objects, as they usually obey the laws of classical mechanics, a mesoscopic object, by contrast, is affected by thermal fluctuations around the average, and its electronic behavior may require modeling at the level of quantum mechanics.Sci-Tech Dictionary. McGraw-Hill Dictionary of Scientific and Technical Terms. 2003. McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc A macroscopic electronic device, when scaled down to a meso-size, starts revealing quantum mechanical properties. For example, at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elementary Charge
The elementary charge, usually denoted by is the electric charge carried by a single proton or, equivalently, the magnitude of the negative electric charge carried by a single electron, which has charge −1 . This elementary charge is a fundamental physical constant. In the SI system of units, the value of the elementary charge is exactly defined as e = coulombs, or 160.2176634 zeptocoulombs (zC). Since the 2019 redefinition of SI base units, the seven SI base units are defined by seven fundamental physical constants, of which the elementary charge is one. In the centimetre–gram–second system of units (CGS), the corresponding quantity is . Robert A. Millikan and Harvey Fletcher's oil drop experiment first directly measured the magnitude of the elementary charge in 1909, differing from the modern accepted value by just 0.6%. Under assumptions of the then-disputed atomic theory, the elementary charge had also been indirectly inferred to ~3% accuracy from bla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballistic Transport
In mesoscopic physics, ballistic conduction (ballistic transport) is the unimpeded flow (or transport) of charge carriers (usually electrons), or energy-carrying particles, over relatively long distances in a material. In general, the resistivity of a material exists because an electron, while moving inside a medium, is scattered by impurities, defects, thermal fluctuations of ions in a crystalline solid, or, generally, by any freely-moving atom/molecule composing a gas or liquid. Without scattering, electrons simply obey Newton's second law of motion at non-relativistic speeds. The mean free path of a particle can be described as the average length that the particle can travel freely, i.e., before a collision, which could change its momentum. The mean free path can be increased by reducing the number of impurities in a crystal or by lowering its temperature. Ballistic transport is observed when the mean free path of the particle is (much) longer than the dimension of the medium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Von Klitzing Constant
The quantum Hall effect (or integer quantum Hall effect) is a quantized version of the Hall effect which is observed in two-dimensional electron systems subjected to low temperatures and strong magnetic fields, in which the Hall resistance exhibits steps that take on the quantized values : R_ = \frac = \frac , where is the Hall voltage, is the channel current, is the elementary charge and is Planck's constant. The divisor can take on either integer () or fractional () values. Here, is roughly but not exactly equal to the filling factor of Landau levels. The quantum Hall effect is referred to as the integer or fractional quantum Hall effect depending on whether is an integer or fraction, respectively. The striking feature of the integer quantum Hall effect is the persistence of the quantization (i.e. the Hall plateau) as the electron density is varied. Since the electron density remains constant when the Fermi level is in a clean spectral gap, this situation correspond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |