|
Common Asparagus Beetle
The common asparagus beetle (''Crioceris asparagi'') is an important pest of asparagus crops both in Europe and in North America. Asparagus is its only food plant. The beetle is 6.0 mm to 9.5 mm long and slightly elongated. It is metallic blue-black in color with cream or yellow spots on its red-bordered elytra. The larvae are fat gray grubs with dark heads. The adult beetles and the larvae strip the needle-like leaves off the asparagus fronds, depriving the plants of the ability to photosynthesize and store energy for future years. Additionally, they chew the spears and lay a lot of eggs on them, rendering the crop unusable. The larvae feed on the plants for a few weeks, then drop to the ground to pupate. One year may see two or three generations of the beetle. The adults overwinter in a dormant state underground or in nearby leaf litter. The parasitic wasp, '' Tetrastichus coeruleus'', occurring mainly in the United States and Europe, can cause up to 71% mortality in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was born in Råshult, the countryside of Småland, in southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he continued to collect an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
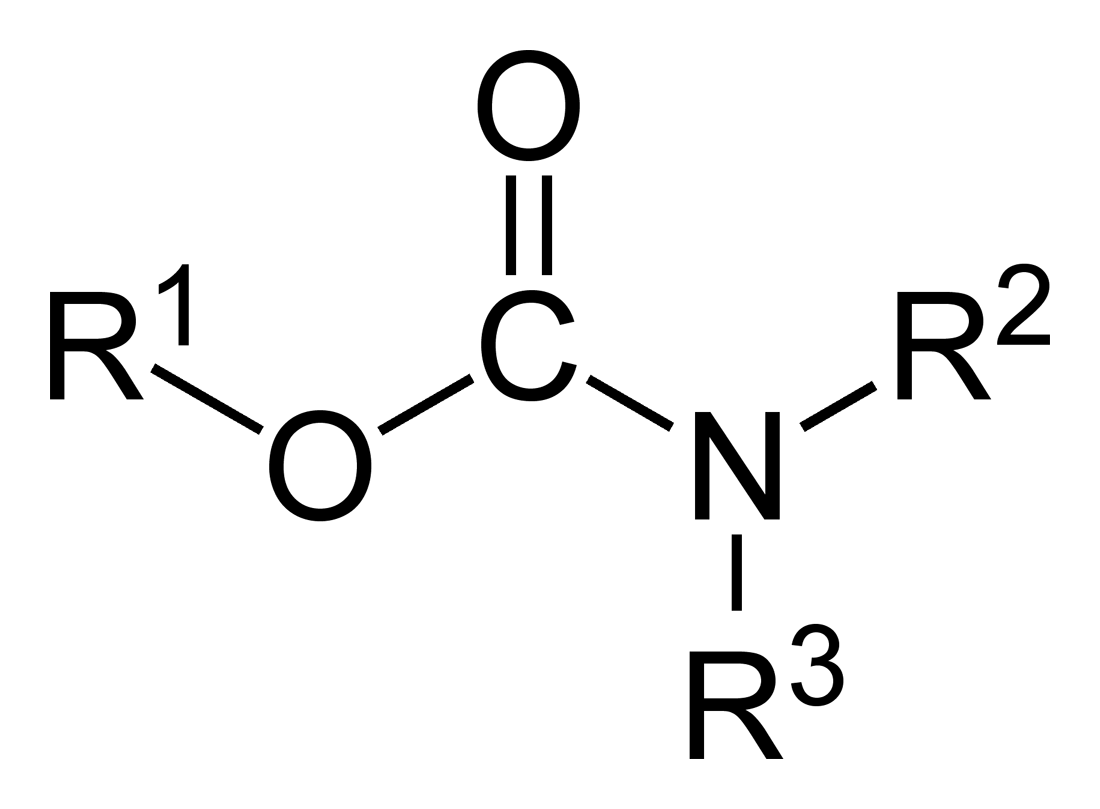
Carbamate
In organic chemistry, a carbamate is a category of organic compounds with the general formula and structure , which are formally derived from carbamic acid (). The term includes organic compounds (e.g., the ester ethyl carbamate), formally obtained by replacing one or more of the hydrogen atoms by other organic functional groups; as well as salts with the carbamate anion (e.g. ammonium carbamate). Polymers whose units are joined by carbamate groups are an important family of plastics, the polyurethanes. Properties While carbamic acids are unstable, many carbamate esters or ionic) are stable and well known. Equilibrium with carbonate and bicarbonate In water solutions, the carbamate anion slowly equilibrates with the ammonium cation and the carbonate or bicarbonate anions: : : Calcium carbamate is soluble in water, whereas calcium carbonate is not. Adding a calcium salt to an ammonium carbamate/carbonate solution will precipitate some calcium carbonate immediatel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beetles Described In 1758
Beetles are insects that form the order Coleoptera (), in the superorder Endopterygota. Their front pair of wings are hardened into wing-cases, elytra, distinguishing them from most other insects. The Coleoptera, with about 400,000 described species, is the largest of all orders, constituting almost 40% of described insects and 25% of all known animal life-forms; new species are discovered frequently, with estimates suggesting that there are between 0.9 and 2.1 million total species. Found in almost every habitat except the sea and the polar regions, they interact with their ecosystems in several ways: beetles often feed on plants and fungi, break down animal and plant debris, and eat other invertebrates. Some species are serious agricultural pests, such as the Colorado potato beetle, while others such as Coccinellidae (ladybirds or ladybugs) eat aphids, scale insects, thrips, and other plant-sucking insects that damage crops. Beetles typically have a particularly hard exosk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Criocerinae
The Criocerinae are a subfamily of the leaf beetles, or Chrysomelidae. Tribes and genera * Tribe Criocerini Latreille, 1804 ** '' Crioceris'' Geoffroy, 1762 ** ''Lilioceris'' Reitter, 1912 * Tribe Lemini Heinze, 1962 ** '' Lema'' Fabricius, 1798 ** ''Neolema'' Monrós, 1951 ** ''Oulema ''Oulema'' is a genus of leaf beetles in the family Chrysomelidae.Gomez-Zurita, Jesus. (2011). "A new species of Criocerinae (Chrysomelidae) from New Caledonia: ''Oulema (Oulema) taophiloides'' sp. nov." ''Zootaxa'' 2870: 63-68. Species These 3 ...'' Des Gozis, 1886 References Bibliography * Beetle subfamilies Taxa named by Pierre André Latreille {{Chrysomelidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spotted Asparagus Beetle
''Crioceris duodecimpunctata'' or the spotted asparagus beetle is a species of shining leaf beetle belonging to the family Chrysomelidae The insects of the beetle family Chrysomelidae are commonly known as leaf beetles, and include over 37,000 (and probably at least 50,000) species in more than 2,500 genera, making up one of the largest and most commonly encountered of all beetle ..., subfamily Criocerinae. The length of beetles varies from 5 to 6.5 millimeters. The colour of head, pronotum and elytra is reddish orange, while the scutellum is black. On the elytra there are twelve black dots. It feeds on Cucurbitaceae and asparagus species. The larvae feed only on the asparagus berries, being the second most important pest of this plant, while adults prefer tender shoots and leaves. They are found in the whole Palearctic realm, including the British Isles. References * Babilas V. F. Kagan, C. Piekarski - Handbook of plant protection - New York, Agricultural and Forestry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinosad
Spinosad is an insecticide based on chemical compounds found in the bacterial species ''Saccharopolyspora spinosa''. The genus ''Saccharopolyspora'' was discovered in 1985 in isolates from crushed sugarcane. The bacteria produce yellowish-pink aerial hyphae, with bead-like chains of spores enclosed in a characteristic hairy sheath. This genus is defined as aerobic, Gram-positive, nonacid-fast actinomycetes with fragmenting substrate mycelium. ''S. spinosa'' was isolated from soil collected inside a nonoperational sugar mill rum still in the Virgin Islands. Spinosad is a mixture of chemical compounds in the spinosyn family that has a generalized structure consisting of a unique tetracyclic ring system attached to an amino sugar (D-forosamine) and a neutral sugar (tri-''Ο''-methyl-L-rhamnose). Spinosad is relatively nonpolar and not easily dissolved in water. Spinosad is a novel mode-of-action insecticide derived from a family of natural products obtained by fermentation of ''S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinetoram
Spinetoram (marketed as Cheristin in its topical veterinary dosage-form) is an insecticidal mixture of two active neurotoxic constituents of ''Saccharopolyspora spinosa''. It is used to control pest insects in stored grain and on domestic cats. See also *Spinosad Spinosad is an insecticide based on chemical compounds found in the bacterial species ''Saccharopolyspora spinosa''. The genus ''Saccharopolyspora'' was discovered in 1985 in isolates from crushed sugarcane. The bacteria produce yellowish-pink ae ... References {{reflist Insecticides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrethroid
A pyrethroid is an organic compound similar to the natural pyrethrins, which are produced by the flowers of pyrethrums (''Chrysanthemum cinerariaefolium'' and ''Chrysanthemum coccineum, C. coccineum''). Pyrethroids are used as commercial and household insecticides. In household concentrations pyrethroids are generally harmless to humans. However, pyrethroids are toxic to insects such as bees, dragonflies, mayflies, Horse-fly, gadflies, and some other invertebrates, including those that constitute the base of aquatic and terrestrial food webs. Pyrethroids are toxic to aquatic organisms, especially fish.Pyrethroids fact sheet from the Illinois Department of Public Health. They have been shown to be an effective control measure for malaria outbreaks, through indoor applications. ...
|
Insecticide
Insecticides are substances used to kill insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against insect eggs and larvae, respectively. Insecticides are used in agriculture, medicine, industry and by consumers. Insecticides are claimed to be a major factor behind the increase in the 20th-century's agricultural productivity. Nearly all insecticides have the potential to significantly alter ecosystems; many are toxic to humans and/or animals; some become concentrated as they spread along the food chain. Insecticides can be classified into two major groups: systemic insecticides, which have residual or long term activity; and contact insecticides, which have no residual activity. The mode of action describes how the pesticide kills or inactivates a pest. It provides another way of classifying insecticides. Mode of action can be important in understanding whether an insecticide will be toxic to unrelated species, such as fish, birds and mammals. Insecticides may be repellent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10th Edition Of Systema Naturae
The 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae'' is a book written by Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus and published in two volumes in 1758 and 1759, which marks the starting point of zoological nomenclature. In it, Linnaeus introduced binomial nomenclature for animals, something he had already done for plants in his 1753 publication of '' Species Plantarum''. Starting point Before 1758, most biological catalogues had used polynomial names for the taxa included, including earlier editions of ''Systema Naturae''. The first work to consistently apply binomial nomenclature across the animal kingdom was the 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae''. The International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature therefore chose 1 January 1758 as the "starting point" for zoological nomenclature, and asserted that the 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae'' was to be treated as if published on that date. Names published before that date are unavailable, even if they would otherwise satisfy the rules. The only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Pest Control
Biological control or biocontrol is a method of controlling pests, such as insects, mites, weeds, and plant diseases, using other organisms. It relies on predation, parasitism, herbivory, or other natural mechanisms, but typically also involves an active human management role. It can be an important component of integrated pest management (IPM) programs. There are three basic strategies for biological pest control: classical (importation), where a natural enemy of a pest is introduced in the hope of achieving control; inductive (augmentation), in which a large population of natural enemies are administered for quick pest control; and inoculative (conservation), in which measures are taken to maintain natural enemies through regular reestablishment. Natural enemies of insect pests, also known as biological control agents, include predators, parasitoids, pathogens, and competitors. Biological control agents of plant diseases are most often referred to as antagonists. Biologic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrastichus Coeruleus
''Tetrastichus coeruleus'' is a gregarious koinobiont wasp which can be used as a biological control agent for the common asparagus beetle The common asparagus beetle (''Crioceris asparagi'') is an important pest of asparagus crops both in Europe and in North America. Asparagus is its only food plant. The beetle is 6.0 mm to 9.5 mm long and slightly elongated. It is metallic blue- .... It was originally named ''Tetrastichus asparagi'' Crawford, thus most of the literature about this species has been published under this other name. ''Tetrastichus coeruleus'' has populations which are infected with the parthenogenesis-inducing Wolbachia and populations which are not. On average, 4.75 ''T. coeruleus'' adults emerge per larva, though this ranges between 2 and 13 specimens per larva. References Eulophidae Insects used as insect pest control agents Insects described in 1834 Taxa named by Christian Gottfried Daniel Nees von Esenbeck {{eulophidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |