|
Commodity Swap
A commodity swap is a type of swap agreement whereby a floating (or market or spot) price based on an underlying commodity is traded for a fixed price over a specified period. The vast majority of commodity swaps involve oil. Many airline and rail companies enter oil commodity swap deals in order to secure lower oil costs in the long term. Concept A commodity swap is similar to a fixed-floating interest rate swap. The difference is that in an interest rate swap, the floating leg is based on standard interest rates such as LIBOR and EURIBOR. However, in a commodity swap, the floating leg is based on the price of underlying commodity like oil, sugar, and precious metals. No commodities are exchanged during the trade. In this swap, the user of a commodity would secure a maximum price and agree to pay a financial institution Financial institutions, sometimes called banking institutions, are business entities that provide services as intermediaries for different types of financial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swap (finance)
In finance, a swap is an agreement between two counterparties to exchange financial instruments, cashflows, or payments for a certain time. The instruments can be almost anything but most swaps involve cash based on a notional principal amount.Financial Industry Business Ontology Version 2 Annex D: Derivatives, EDM Council, Inc., Object Management Group, Inc., 2019 The general swap can also be seen as a series of forward contracts through which two parties exchange financial instruments, resulting in a common series of exchange dates and two streams of instruments, the ''legs'' of the swap. The legs can be almost anything but usually one leg involves cash flows based on a |
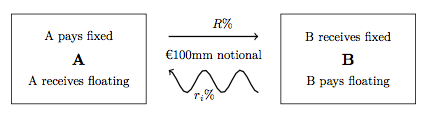
Interest Rate Swap
In finance, an interest rate swap (IRS) is an interest rate derivative (IRD). It involves exchange of interest rates between two parties. In particular it is a "linear" IRD and one of the most liquid, benchmark products. It has associations with forward rate agreements (FRAs), and with zero coupon swaps (ZCSs). In its December 2014 statistics release, the Bank for International Settlements reported that interest rate swaps were the largest component of the global OTC derivative market, representing 60%, with the notional amount outstanding in OTC interest rate swaps of $381 trillion, and the gross market value of $14 trillion. Interest rate swaps can be traded as an index through the FTSE MTIRS Index. Interest rate swaps General description An interest rate swap's (IRS's) effective description is a derivative contract, agreed between two counterparties, which specifies the nature of an exchange of payments benchmarked against an interest rate index. The most common IRS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LIBOR
The London Inter-Bank Offered Rate is an interest-rate average calculated from estimates submitted by the leading banks in London. Each bank estimates what it would be charged were it to borrow from other banks. The resulting average rate is usually abbreviated to Libor () or LIBOR, or more officially to ICE LIBOR (for Intercontinental Exchange LIBOR). It was formerly known as BBA Libor (for British Bankers' Association Libor or the trademark bba libor) before the responsibility for the administration was transferred to Intercontinental Exchange. It is the primary benchmark, along with the Euribor, for short-term interest rates around the world. Libor was phased out at the end of 2021, and market participants are being encouraged to transition to risk-free interest rates. As of late 2022, parts of it have been discontinued, and the rest is scheduled to end within 2023; the Secured Overnight Financing Rate (SOFR) is its replacement. Libor rates are calculated for five currenci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EURIBOR
The Euro Interbank Offered Rate (Euribor) is a daily reference rate, published by the European Money Markets Institute, based on the averaged interest rates at which Eurozone banks offer to lend unsecured funds to other banks in the euro wholesale money market (or interbank market). Prior to 2015, the rate was published by the European Banking Federation. Scope Euribors are used as a reference rate for euro-denominated forward rate agreements, short-term interest rate futures contracts and interest rate swaps, in very much the same way as LIBORs are commonly used for Sterling and US dollar-denominated instruments. They thus provide the basis for some of the world's most liquid and active interest rate markets. Domestic reference rates, like Paris' PIBOR, Frankfurt's FIBOR, and Helsinki's Helibor merged into Euribor on EMU day on 1 January 1999. Euribor should be distinguished from the less commonly used "Euro LIBOR" rates set in London by 16 major banks. Technical feature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commodity
In economics, a commodity is an economic good, usually a resource, that has full or substantial fungibility: that is, the market treats instances of the good as equivalent or nearly so with no regard to who produced them. The price of a commodity good is typically determined as a function of its market as a whole: well-established physical commodities have actively traded spot and derivative markets. The wide availability of commodities typically leads to smaller profit margins and diminishes the importance of factors (such as brand name) other than price. Most commodities are raw materials, basic resources, agricultural, or mining products, such as iron ore, sugar, or grains like rice and wheat. Commodities can also be mass-produced unspecialized products such as chemical substance, chemicals and computer memory. Popular commodities include Petroleum, crude oil, Maize, corn, and gold. Other definitions of commodity include something useful or valued and an alternative ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Institution
Financial institutions, sometimes called banking institutions, are business entities that provide services as intermediaries for different types of financial monetary transactions. Broadly speaking, there are three major types of financial institutions: # Depository institutions – deposit-taking institutions that accept and manage deposits and make loans, including banks, building societies, credit unions, trust companies, and mortgage loan companies; # Contractual institutions – insurance companies and pension funds # Investment institutions – investment banks, underwriters, and other different types of financial entities managing investments. Financial institutions can be distinguished broadly into two categories according to ownership structure: * Commercial banks * Cooperative banks Some experts see a trend toward homogenisation of financial institutions, meaning a tendency to invest in similar areas and have similar business strategies. A consequence of this might ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swaps (finance)
In finance, a swap is an agreement between two counterparties to exchange financial instruments, cashflows, or payments for a certain time. The instruments can be almost anything but most swaps involve cash based on a notional principal amount.Financial Industry Business Ontology Version 2 Annex D: Derivatives, EDM Council, Inc., Object Management Group, Inc., 2019 The general swap can also be seen as a series of forward contracts through which two parties exchange financial instruments, resulting in a common series of exchange dates and two streams of instruments, the ''legs'' of the swap. The legs can be almost anything but usually one leg involves cash flows based on a |