|
Color Superconductivity
Color superconductivity is a phenomenon where matter carries color charge without loss, similar to how conventional superconductors carry electric charge without loss. It is predicted to occur in quark matter if the baryon density is sufficiently high (well above nuclear density) and the temperature is not too high (well below 1012 kelvins). Color superconducting phases are to be contrasted with the normal phase of quark matter, which is just a weakly interacting Fermi liquid of quarks. In theoretical terms, a color superconducting phase is a state in which the quarks near the Fermi surface become correlated in Cooper pairs, which condense. In phenomenological terms, a color superconducting phase breaks some of the symmetries of the underlying theory, and has a very different spectrum of excitations and very different transport properties from the normal phase. Description Analogy with superconducting metals It is well known that at low temperature many metals become sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Charge
Color charge is a property of quarks and gluons that is related to the particles' strong interactions in the theory of quantum chromodynamics (QCD). The "color charge" of quarks and gluons is completely unrelated to the everyday meanings of color and charge (physics), charge. The term ''color'' and the labels red, green, and blue became popular simply because of the loose analogy to the primary colors. Some particles have corresponding antiparticles. A particle with red, green, or blue charge has a corresponding antiparticle in which the color charge must be the anticolor of red, green, and blue, respectively, for the color charge to be conserved in particle–antiparticle Particle creation, creation and annihilation. Particle physicists call these antired, antigreen, and antiblue. All three colors mixed together, or any one of these colors and its Complementary colors, complement (or negative), is "colorless" or "white" and has a net color charge of zero. Due to a property of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rivista Del Nuovo Cimento
''Nuovo Cimento'' is a series of peer-reviewed scientific journals of physics. The series was first established in 1855, when Carlo Matteucci and Raffaele Piria started publishing ''Il Nuovo Cimento'' as the continuation of ''Il Cimento'', which they established in 1844. In 1897, it became the official journal of the Italian Physical Society. Over time, the journal split into several sub-journals: * ''Nuovo Cimento A'' (1965–1999): Focused on particle physics. The journal ended when it was merged into the '' European Physical Journal'', in 1999. * ''Nuovo Cimento B'' (1965–2010): Focused on relativity, astronomy, and mathematical physics. As of 1 January 2011 it continues publication as the ''European Physical Journal Plus''. * ''Nuovo Cimento C'' (1978–present): Focuses on geophysics, astrophysics, and biophysics. * ''Nuovo Cimento D'' (1982–1998): Focuses on solid state physics, atomic physics, and molecular biology Molecular biology is the branch of biology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contemporary Physics
''Contemporary Physics'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal publishing introductory articles on important recent developments in physics. Editorial screening and peer review is carried out by members of the editorial board. Overview ''Contemporary Physics'' has been published by Taylor & Francis since 1959 and publishes four issues per year. The subjects covered by this journal are: astrophysics, atomic and nuclear physics, chemical physics, computational physics, condensed matter physics, environmental physics, experimental physics, general physics, particle & high energy physics, plasma physics, space science, and theoretical physics. Aims The journal publishes introductory review articles on a range of recent developments in physics and intends to be of particular use to undergraduates, teachers and lecturers, and those starting postgraduate studies. ''Contemporary Physics'' also contains a major section devoted to standard book reviews and essay reviews which review books ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontiers (PPARC Magazine)
Frontiers may refer to: * Frontier, areas near or beyond a boundary Arts and entertainment Music * ''Frontiers'' (Journey album), 1983 * ''Frontiers'' (Jermaine Jackson album), 1978 * ''Frontiers'' (Jesse Cook album), 2007 * ''Frontiers'' (Psycho le Cemu album), 2003 * "Frontiers", a song by Symphony X from ''The Odyssey'' * Frontiers Records, an Italian record label Other uses in arts and entertainment * ''Frontier(s)'', a 2007 horror film * ''Frontiers'' (magazine), a LGBT magazine * ''Frontiers'' (1989 TV series), a 1989 British documentary series that aired on the BBC * ''Frontiers'' (1996 TV series), a 1996 British crime drama that aired on ITV Science and academia ''Frontiers in...'' series of journals * Frontiers Media, publisher of the ''Frontiers in...'' series of 59 journals * ''Frontiers in Endocrinology'' * ''Frontiers in Plant Science'' * ''Frontiers in Psychology'' * ''Frontiers in Physics'' * ''Frontiers for Young Minds'', not part of the series proper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reviews Of Modern Physics
''Reviews of Modern Physics'' (abbreviated RMP) is a quarterly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the American Physical Society. It was established in 1929 and the current editor-in-chief is Michael Thoennessen. The journal publishes review articles, usually by established researchers, on all aspects of physics Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which ... and related fields. The reviews are usually accessible to non-specialists and serve as introductory material to graduate students, which survey recent work, discuss key problems to be solved and provide perspectives toward the end. References External links * Publications established in 1929 Physics review journals Quarterly journals English-language journals American Physical Society academic jour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annual Review Of Nuclear And Particle Science
Annual may refer to: *Annual publication, periodical publications appearing regularly once per year **Yearbook **Literary annual *Annual plant *Annual report *Annual giving *Annual, Morocco, a settlement in northeastern Morocco *Annuals (band), a musical group See also * Annual Review (other) Annual Review or Annual Reviews may refer to: * An annual performance appraisal or performance review of an employee * Annual Reviews (publisher), a publisher of academic journals * The ''Annual Reviews'' series of journals is published by Annual ... * Circannual cycle, in biology {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexaquark
In particle physics hexaquarks, alternatively known as sexaquarks, are a large family of hypothetical particles, each particle consisting of six quarks or antiquarks of any flavours. Six constituent quarks in any of several combinations could yield a colour charge of zero; for example a hexaquark might contain either six quarks, resembling two baryons bound together (a dibaryon), or three quarks and three antiquarks. Once formed, dibaryons are predicted to be fairly stable by the standards of particle physics. A number of experiments have been suggested to detect dibaryon decays and interactions. In the 1990s, several candidate dibaryon decays were observed but they were not confirmed. There is a theory that strange particles such as hyperons and dibaryons could form in the interior of a neutron star, changing its mass–radius ratio in ways that might be detectable. Accordingly, measurements of neutron stars could set constraints on possible dibaryon properties. A large fract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
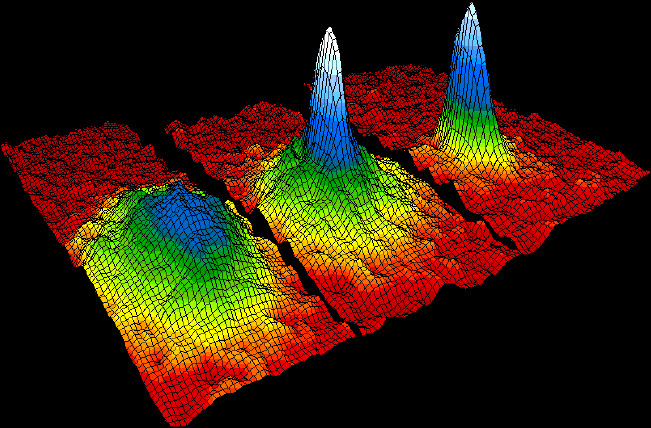
Bose–Einstein Condensate
In condensed matter physics, a Bose–Einstein condensate (BEC) is a state of matter that is typically formed when a gas of bosons at very low densities is cooled to temperatures very close to absolute zero (−273.15 °C or −459.67 °F). Under such conditions, a large fraction of bosons occupy the lowest quantum state, at which point microscopic quantum mechanical phenomena, particularly wavefunction interference, become apparent macroscopically. A BEC is formed by cooling a gas of extremely low density (about 100,000 times less dense than normal air) to ultra-low temperatures. This state was first predicted, generally, in 1924–1925 by Albert Einstein following and crediting a pioneering paper by Satyendra Nath Bose on the new field now known as quantum statistics. In 1995, the Bose-Einstein condensate was created by Eric Cornell and Carl Wieman of the University of Colorado at Boulder using rubidium atoms; later that year, Wolfgang Ketterle of MIT ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strange Matter
Strange matter (or strange quark matter) is quark matter containing strange quarks. In nature, strange matter is hypothesized to occur in the core of neutron stars, or, more speculatively, as isolated droplets that may vary in size from femtometers (strangelets) to kilometers, as in the hypothetical strange stars. At high enough density, strange matter is expected to be color superconducting. Ordinary matter, also referred to as atomic matter, is composed of atoms, with nearly all matter concentrated in the atomic nuclei. Nuclear matter is a liquid composed of neutrons and protons, and they are themselves composed of up and down quarks. Quark matter is a condensed form of matter composed entirely of quarks. When quark matter does not contain strange quarks, it is sometimes referred to as non-strange quark matter. Context In particle physics and astrophysics, the term 'strange matter' is used in two different contexts, one broader and the other more specific and hypothetic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutron Star
A neutron star is the collapsed core of a massive supergiant star, which had a total mass of between 10 and 25 solar masses, possibly more if the star was especially metal-rich. Except for black holes and some hypothetical objects (e.g. white holes, quark stars, and strange stars), neutron stars are the smallest and densest currently known class of stellar objects. Neutron stars have a radius on the order of and a mass of about 1.4 solar masses. They result from the supernova explosion of a massive star, combined with gravitational collapse, that compresses the core past white dwarf star density to that of atomic nuclei. Once formed, they no longer actively generate heat, and cool over time; however, they may still evolve further through collision or accretion. Most of the basic models for these objects imply that neutron stars are composed almost entirely of neutrons (subatomic particles with no net electrical charge and with slightly larger mass than protons); th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compact Star
In astronomy, the term compact star (or compact object) refers collectively to white dwarfs, neutron stars, and black holes. It would grow to include exotic stars if such hypothetical, dense bodies are confirmed to exist. All compact objects have a high mass relative to their radius, giving them a very high density, compared to ordinary atomic matter. Compact stars are often the endpoints of stellar evolution and, in this respect, are also called stellar remnants. The state and type of a stellar remnant depends primarily on the mass of the star that it formed from. The ambiguous term ''compact star'' is often used when the exact nature of the star is not known, but evidence suggests that it has a very small radius compared to ordinary stars. A compact star that is not a black hole may be called a degenerate star. In June 2020, astronomers reported narrowing down the source of Fast Radio Bursts (FRBs), which may now plausibly include "compact-object mergers and magnetars aris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |