|
Cold Nodule
A cold nodule is a thyroid nodule that does not produce thyroid hormone. On a radioactive iodine uptake test a cold nodule takes up less radioactive material than the surrounding thyroid tissue. A cold nodule may be malignant or benign. On scintigraphy cold nodules do not show but are easily shown on ultrasound. Figure 1 illustrates the basic anatomy of the thyroid gland. The case shown in Figure 4 shows a cold nodule quite emphasized representation of the thyroid. The investigation was carried out due to a goiter rating of 3. Striking was the discrepancy between the magnification sonographically depicted the thyroid lobe and the findings in the scintigraphy; the lower part of the right lobe and the lateral part of the left missing in the bone scan, although demonstrably thyroid tissue is present there sonographically. This imperfective representation for thyroid tissue is the characteristic of "cold node". "Cold nodule" in older women usually benign and 15-20% Malignant. And in Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroid Nodule
Thyroid nodules are nodules (raised areas of tissue or fluid) which commonly arise within an otherwise normal thyroid gland. They may be hyperplastic or tumorous, but only a small percentage of thyroid tumors are malignant. Small, asymptomatic nodules are common, and often go unnoticed. Nodules that grow larger or produce symptoms may eventually need medical care. A goitre may have one nodule – uninodular, multiple nodules – multinodular, or be diffuse. Signs and symptoms Often these abnormal growths of thyroid tissue are located at the edge of the thyroid gland and can be felt as a lump in the throat. When they are large, they can sometimes be seen as a lump in the front of the neck. Sometimes a thyroid nodule presents as a fluid-filled cavity called a thyroid cyst. Often, solid components are mixed with the fluid. Thyroid cysts most commonly result from degenerating thyroid adenomas, which are benign, but they occasionally contain malignant solid components. Diagnosis A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroid Hormone
File:Thyroid_system.svg, upright=1.5, The thyroid system of the thyroid hormones T3 and T4 rect 376 268 820 433 Thyroid-stimulating hormone rect 411 200 849 266 Thyrotropin-releasing hormone rect 297 168 502 200 Hypothalamus rect 66 216 386 256 Anterior pituitary gland rect 66 332 342 374 Negative feedback rect 308 436 510 475 Thyroid gland rect 256 539 563 635 Thyroid hormones rect 357 827 569 856 Catecholamine rect 399 716 591 750 Metabolism desc bottom-left Thyroid hormones are any hormones produced and released by the thyroid gland, namely triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). They are tyrosine-based hormones that are primarily responsible for regulation of metabolism. T3 and T4 are partially composed of iodine. A deficiency of iodine leads to decreased production of T3 and T4, enlarges the thyroid tissue and will cause the disease known as simple goitre. The major form of thyroid hormone in the blood is thyroxine (T4), whose half-life of around one week is longer th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radioactive Iodine Uptake Test
The radioactive iodine uptake test is a type of scan used in the diagnosis of thyroid problems, particularly hyperthyroidism. It is entirely different from radioactive iodine therapy (RAI therapy), which uses much higher doses to destroy cancerous cells. The RAIU test is also used as a follow up to RAI therapy to verify that no thyroid cells survived, which could still be cancerous. ThyCa: Thyroid Cancer Survivors' Association, Inc., Radioactive Iodine (RAI). The patient swallows Isotopes of iodine#Notable radioisotopes, a radioisotope of in the form of capsule or fluid, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scintigraphy
Scintigraphy (from Latin ''scintilla'', "spark"), also known as a gamma scan, is a diagnostic test in nuclear medicine, where radioisotopes attached to drugs that travel to a specific organ or tissue (radiopharmaceuticals) are taken internally and the emitted gamma radiation is captured by external detectors (gamma cameras) to form two-dimensional images in a similar process to the capture of x-ray images. In contrast, SPECT and ''positron emission tomography'' (PET) form 3-dimensional images and are therefore classified as separate techniques from scintigraphy, although they also use gamma cameras to detect internal radiation. Scintigraphy is unlike a diagnostic X-ray where external radiation is passed through the body to form an image. Process Scintillography is an imaging method of nuclear events provoked by collisions or charged current interactions among nuclear particles or ionizing radiation and atoms which result in a brief, localised pulse of electromagnetic radiation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequency, frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing range, hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies from person to person and is approximately 20 Hertz, kilohertz (20,000 hertz) in healthy young adults. Ultrasound devices operate with frequencies from 20 kHz up to several gigahertz. Ultrasound is used in many different fields. Ultrasonic devices are used to detect objects and measure distances. Ultrasound imaging or sonography is often used in medicine. In the nondestructive testing of products and structures, ultrasound is used to detect invisible flaws. Industrially, ultrasound is used for cleaning, mixing, and accelerating chemical processes. Animals such as bats and porpoises use ultrasound for locating Predation, prey and obstacles. History Acoustics, the science of sound, starts as far back as Pyth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
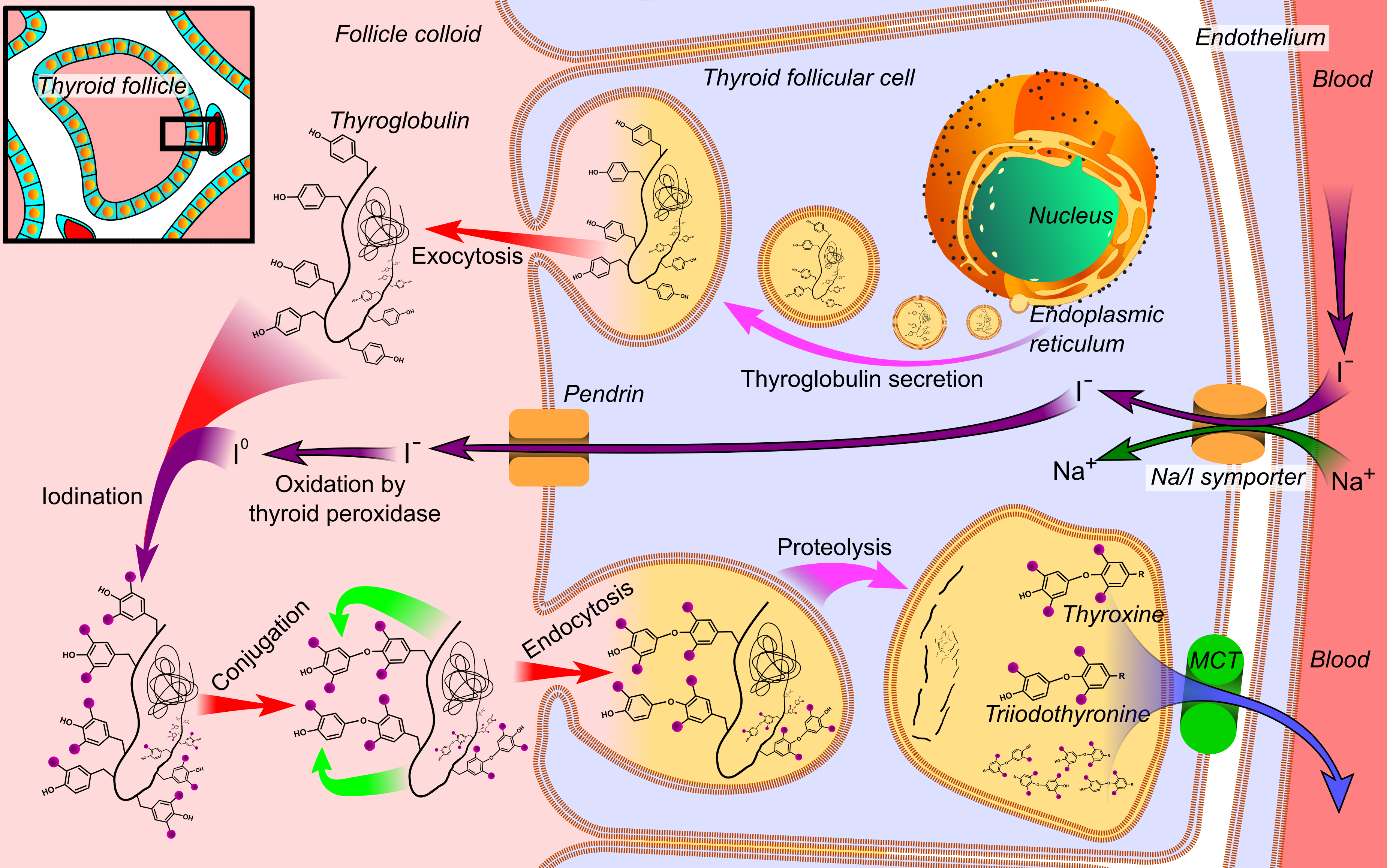
Thyroid Gland
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans it is in the neck and consists of two connected lobe (anatomy), lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of Connective tissue, tissue called the thyroid isthmus. The thyroid is located at the front of the neck, below the Adam's apple. Microscopically, the functional unit of the thyroid gland is the spherical Thyroid follicular cell#Location, thyroid follicle, lined with thyroid follicular cell, follicular cells (thyrocytes), and occasional parafollicular cells that surround a follicular lumen, lumen containing colloid. The thyroid gland secretes three hormones: the two thyroid hormonestriiodothyronine, triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroid hormone, thyroxine (T4)and a peptide hormone, calcitonin. The thyroid hormones influence the basal metabolic rate, metabolic rate and protein biosynthesis, protein synthesis, and in children, growth and development. Calcitonin plays a role in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sonography
Medical ultrasound includes diagnostic techniques (mainly medical imaging, imaging techniques) using ultrasound, as well as therapeutic ultrasound, therapeutic applications of ultrasound. In diagnosis, it is used to create an image of internal body structures such as tendons, muscles, joints, blood vessels, and internal organs, to measure some characteristics (e.g. distances and velocities) or to generate an informative audible sound. Its aim is usually to find a source of disease or to exclude pathology. The usage of ultrasound to produce visual images for medicine is called medical ultrasonography or simply sonography. The practice of examining pregnant women using ultrasound is called obstetric ultrasonography, and was an early development of clinical ultrasonography. Ultrasound is composed of sound waves with frequency, frequencies which are significantly higher than the range of human hearing (>20,000 Hz). Ultrasonic images, also known as sonograms, are created by se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bone Scan
A bone scan or bone scintigraphy is a nuclear medicine imaging technique of the bone. It can help diagnose a number of bone conditions, including cancer of the bone or metastasis, location of bone inflammation and fractures (that may not be visible in traditional X-ray images), and bone infection (osteomyelitis). Nuclear medicine provides functional imaging and allows visualisation of bone metabolism or bone remodeling, which most other imaging techniques (such as X-ray computed tomography, CT) cannot. Bone scintigraphy competes with positron emission tomography (PET) for imaging of abnormal metabolism in bones, but is considerably less expensive. Bone scintigraphy has higher sensitivity but lower specificity than CT or MRI for diagnosis of scaphoid fractures following negative plain radiography. History Some of the earliest investigations into skeletal metabolism were carried out by George de Hevesy in the 1930s, using phosphorus-32 and by Charles Pecher in the 1940s. In t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroid Nodule
Thyroid nodules are nodules (raised areas of tissue or fluid) which commonly arise within an otherwise normal thyroid gland. They may be hyperplastic or tumorous, but only a small percentage of thyroid tumors are malignant. Small, asymptomatic nodules are common, and often go unnoticed. Nodules that grow larger or produce symptoms may eventually need medical care. A goitre may have one nodule – uninodular, multiple nodules – multinodular, or be diffuse. Signs and symptoms Often these abnormal growths of thyroid tissue are located at the edge of the thyroid gland and can be felt as a lump in the throat. When they are large, they can sometimes be seen as a lump in the front of the neck. Sometimes a thyroid nodule presents as a fluid-filled cavity called a thyroid cyst. Often, solid components are mixed with the fluid. Thyroid cysts most commonly result from degenerating thyroid adenomas, which are benign, but they occasionally contain malignant solid components. Diagnosis A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
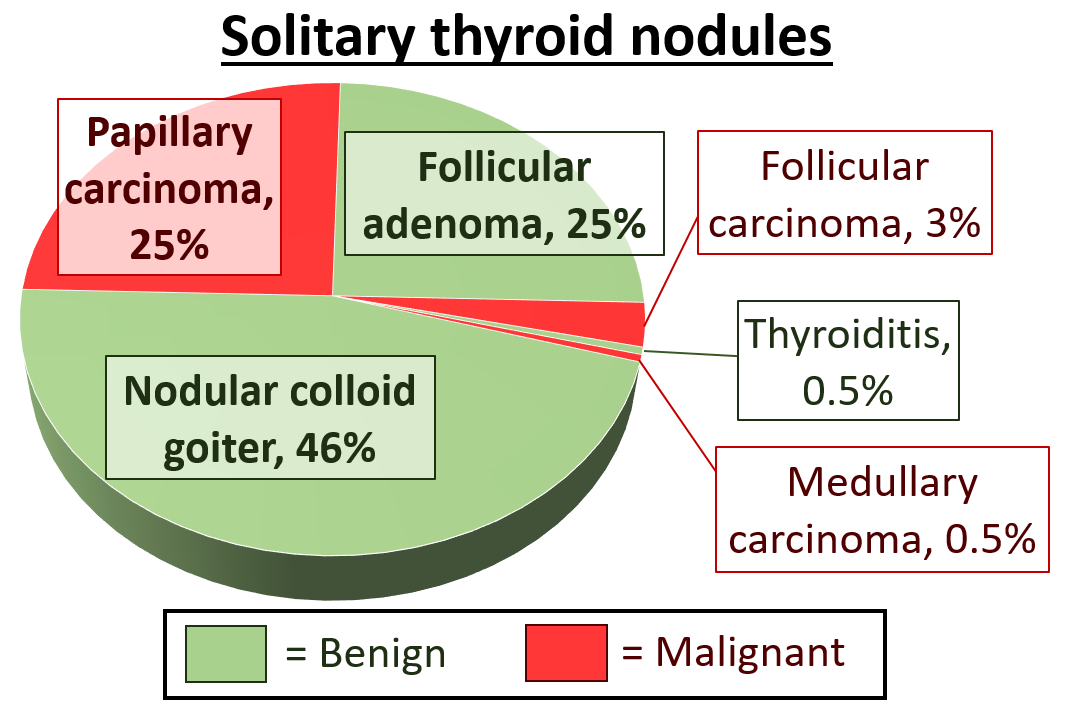
Colloid Nodule
Colloid nodules, also known as adenomatous nodules or colloid nodular goiter are benign, noncancerous enlargement of thyroid tissue. Although they may grow large, and there may be more than one, they are not malignant and they will not spread beyond the thyroid gland. Colloid nodules are the most common kind of thyroid nodule. Presentation Colloid nodules are usually small enough to be undetectable without an ultrasound or other imaging techniques. They usually produce no symptoms, so patients are unlikely to notice them until their size makes them easier to detect. Like other thyroid nodules, they are usually first noticed in a routine physical examination. Diagnosis Colloid nodules may be initially identified as an unspecified kind of thyroid nodule. Follow-up examinations typically include an ultrasound if it is unclear whether or not there really is a nodule present. Once the presence of a nodule has been confirmed, the determination of the kind of thyroid nodule is done by fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroid
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans it is in the neck and consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the thyroid isthmus. The thyroid is located at the front of the neck, below the Adam's apple. Microscopically, the functional unit of the thyroid gland is the spherical thyroid follicle, lined with follicular cells (thyrocytes), and occasional parafollicular cells that surround a lumen containing colloid. The thyroid gland secretes three hormones: the two thyroid hormones triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4)and a peptide hormone, calcitonin. The thyroid hormones influence the metabolic rate and protein synthesis, and in children, growth and development. Calcitonin plays a role in calcium homeostasis. Secretion of the two thyroid hormones is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is secreted from the anterior pituitary gland. TSH is regula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |