|
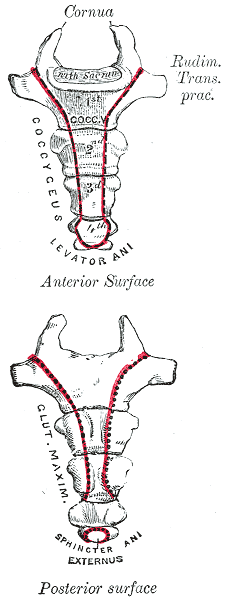
Coccyx
The coccyx ( : coccyges or coccyxes), commonly referred to as the tailbone, is the final segment of the vertebral column in all apes, and analogous structures in certain other mammals such as horses. In tailless primates (e.g. humans and other great apes) since ''Nacholapithecus'' (a Miocene hominoid),Nakatsukasa 2004, ''Acquisition of bipedalism'' (SeFig. 5entitled ''First coccygeal/caudal vertebra in short-tailed or tailless primates.''.) the coccyx is the remnant of a vestigial tail. In animals with bony tails, it is known as ''tailhead'' or ''dock'', in bird anatomy as ''tailfan''. It comprises three to five separate or fused coccygeal vertebrae below the sacrum, attached to the sacrum by a fibrocartilaginous joint, the sacrococcygeal symphysis, which permits limited movement between the sacrum and the coccyx. Structure The coccyx is formed of three, four or five rudimentary vertebrae. It articulates superiorly with the sacrum. In each of the first three segments may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
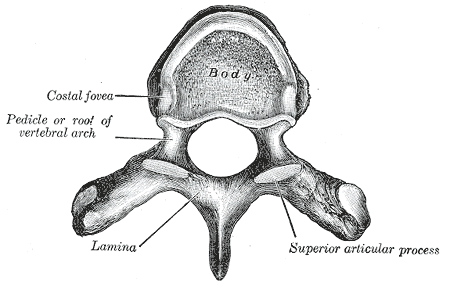
Lamina Of The Vertebral Arch
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates,Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristic irregular bone whose complex structure is composed primarily of bone, and secondarily of hyaline cartilage. They show variation in the proportion contributed by these two tissue types; such variations correlate on one hand with the cerebral/caudal rank (i.e., location within the backbone), and on the other with phylogenetic differences among the vertebrate taxa. The basic configuration of a vertebra varies, but the bone is its ''body'', with the central part of the body constituting the ''centrum''. The upper (closer to) and lower (further from), respectively, the cranium and its central nervous system surfaces of the vertebra body support attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch (i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinous Process
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates,Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristic irregular bone whose complex structure is composed primarily of bone, and secondarily of hyaline cartilage. They show variation in the proportion contributed by these two tissue types; such variations correlate on one hand with the cerebral/caudal rank (i.e., location within the backbone), and on the other with phylogenetic differences among the vertebrate taxa. The basic configuration of a vertebra varies, but the bone is its ''body'', with the central part of the body constituting the ''centrum''. The upper (closer to) and lower (further from), respectively, the cranium and its central nervous system surfaces of the vertebra body support attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch (i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedicle Of Vertebral Arch
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates,Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristic irregular bone whose complex structure is composed primarily of bone, and secondarily of hyaline cartilage. They show variation in the proportion contributed by these two tissue types; such variations correlate on one hand with the cerebral/caudal rank (i.e., location within the backbone), and on the other with phylogenetic differences among the vertebrate taxa. The basic configuration of a vertebra varies, but the bone is its ''body'', with the central part of the body constituting the ''centrum''. The upper (closer to) and lower (further from), respectively, the cranium and its central nervous system surfaces of the vertebra body support attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch (i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transverse Process
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates,Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristic irregular bone whose complex structure is composed primarily of bone, and secondarily of hyaline cartilage. They show variation in the proportion contributed by these two tissue types; such variations correlate on one hand with the cerebral/caudal rank (i.e., location within the vertebral column, backbone), and on the other with phylogenetic differences among the vertebrate taxon, taxa. The basic configuration of a vertebra varies, but the bone is its ''body'', with the central part of the body constituting the ''centrum''. The upper (closer to) and lower (further from), respectively, the cranium and its central nervous system surfaces of the vertebra body support attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebra
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates,Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristic irregular bone whose complex structure is composed primarily of bone, and secondarily of hyaline cartilage. They show variation in the proportion contributed by these two tissue types; such variations correlate on one hand with the cerebral/caudal rank (i.e., location within the backbone), and on the other with phylogenetic differences among the vertebrate taxa. The basic configuration of a vertebra varies, but the bone is its ''body'', with the central part of the body constituting the ''centrum''. The upper (closer to) and lower (further from), respectively, the cranium and its central nervous system surfaces of the vertebra body support attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebral Column
The vertebral column, also known as the backbone or spine, is part of the axial skeleton. The vertebral column is the defining characteristic of a vertebrate in which the notochord (a flexible rod of uniform composition) found in all chordata, chordates has been replaced by a segmented series of bone: vertebrae separated by intervertebral discs. Individual vertebrae are named according to their region and position, and can be used as anatomical landmarks in order to guide procedures such as Lumbar puncture, lumbar punctures. The vertebral column houses the spinal canal, a cavity that encloses and protects the spinal cord. There are about 50,000 species of animals that have a vertebral column. The human vertebral column is one of the most-studied examples. Many different diseases in humans can affect the spine, with spina bifida and scoliosis being recognisable examples. The general structure of human vertebrae is fairly typical of that found in mammals, reptiles, and birds. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Sacrococcygeal Ligament
The anterior sacrococcygeal ligament or ventral sacrococcygeal ligament consists of a few irregular fibers, which descend from the anterior surface of the sacrum to the front of the coccyx, blending with the periosteum.Morris (2005), p 59 This shortSinnatamby (2006), p 336 ligament forms the continuation of the anterior longitudinal ligament and stretches over the sacrococcygeal symphysis.OMD: DefinitionJinkins (2000), p 538Ebrall (2004), 243 See also * Posterior sacrococcygeal ligament * Coccydynia (coccyx pain, tailbone pain) * Ganglion impar The pelvic portion of each sympathetic trunk is situated in front of the sacrum, medial to the anterior sacral foramina. It consists of four or five small sacral ganglia, connected together by interganglionic cords, and continuous above with the ab ... Notes References * * * * Ligaments of the torso Bones of the vertebral column {{ligament-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rectum
The rectum is the final straight portion of the large intestine in humans and some other mammals, and the Gastrointestinal tract, gut in others. The adult human rectum is about long, and begins at the rectosigmoid junction (the end of the sigmoid colon) at the level of the third sacral vertebra or the sacral promontory depending upon what definition is used. Its diameter is similar to that of the sigmoid colon at its commencement, but it is dilated near its termination, forming the rectal ampulla. It terminates at the level of the anorectal ring (the level of the puborectalis sling) or the dentate line, again depending upon which definition is used. In humans, the rectum is followed by the anal canal which is about long, before the gastrointestinal tract terminates at the anal verge. The word rectum comes from the Latin ''Wikt:rectum, rectum Wikt:intestinum, intestinum'', meaning ''straight intestine''. Structure The rectum is a part of the lower gastrointestinal tract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levator Ani
The levator ani is a broad, thin muscle group, situated on either side of the pelvis. It is formed from three muscle components: the pubococcygeus, the iliococcygeus, and the puborectalis. It is attached to the inner surface of each side of the lesser pelvis, and these unite to form the greater part of the pelvic floor. The coccygeus muscle completes the pelvic floor, which is also called the ''pelvic diaphragm''. It supports the viscera in the pelvic cavity, and surrounds the various structures that pass through it. The levator ani is the main pelvic floor muscle and painfully contracts during vaginismus. It also contracts rhythmically during orgasm. Structure The levator ani is made up of 3 parts: * Iliococcygeus muscle * Pubococcygeus muscle * Puborectalis muscle The iliococcygeus arises from the inner side of the ischium (the lower and back part of the hip bone) and from the posterior part of the tendinous arch of the obturator fascia, and is attached to the coccyx and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether an organism is bipedal or quadrupedal. Additionally, for some animals such as invertebrates, some terms may not have any meaning at all; for example, an animal that is radially symmetrical will have no anterior surface, but can still have a description that a part is close to the middle ("proximal") or further from the middle ("distal"). International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standard vocabularies for subdisciplines of anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yonsei Medical Journal
The ''Yonsei Medical Journal'' is a general medical journal which has been published since 1960 by the Yonsei University Yonsei University (; ) is a private research university in Seoul, South Korea. As a member of the "SKY" universities, Yonsei University is deemed one of the three most prestigious institutions in the country. It is particularly respected in the ..., College of Medicine. It is published bimonthly. The journal covers in all areas related to medicine based on clinical or basic research. The editor in chief is In-Hong Choi. Internet and open access Since YMJ became the first Korean journal indexed in Index Medicus in 1962, YMJ has been indexed/tracked/covered by MEDLINE, PubMed, PubMed Central, Science Citation Index (SCI), BIOSIS Previews, SCOPUS, Embase, Chemical Abstracts Service (CAS), KoreaMed, Synapse, KoMCI, CrossRef and Google Scholar. Full text PDF files are available at YMJ Archive. References External links *WeCare Medical General medical journals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |