|
Co-processor
A coprocessor is a computer processor used to supplement the functions of the primary processor (the CPU). Operations performed by the coprocessor may be floating-point arithmetic, graphics, signal processing, string processing, cryptography or I/O interfacing with peripheral devices. By offloading processor-intensive tasks from the main processor, coprocessors can accelerate system performance. Coprocessors allow a line of computers to be customized, so that customers who do not need the extra performance do not need to pay for it. Functionality Coprocessors vary in their degree of autonomy. Some (such as FPUs) rely on direct control via coprocessor instructions, embedded in the CPU's instruction stream. Others are independent processors in their own right, capable of working asynchronously; they are still not optimized for general-purpose code, or they are incapable of it due to a limited instruction set focused on accelerating specific tasks. It is common for these to b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Floating-point Unit
A floating-point unit (FPU), numeric processing unit (NPU), colloquially math coprocessor, is a part of a computer system specially designed to carry out operations on floating-point numbers. Typical operations are addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and square root. Modern designs generally include a fused multiply-add instruction, which was found to be very common in real-world code. Some FPUs can also perform various transcendental functions such as exponential or trigonometric calculations, but the accuracy can be low, so some systems prefer to compute these functions in software. Floating-point operations were originally handled in software in early computers. Over time, manufacturers began to provide standardized floating-point libraries as part of their software collections. Some machines, those dedicated to scientific processing, would include specialized hardware to perform some of these tasks with much greater speed. The introduction of microcode in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
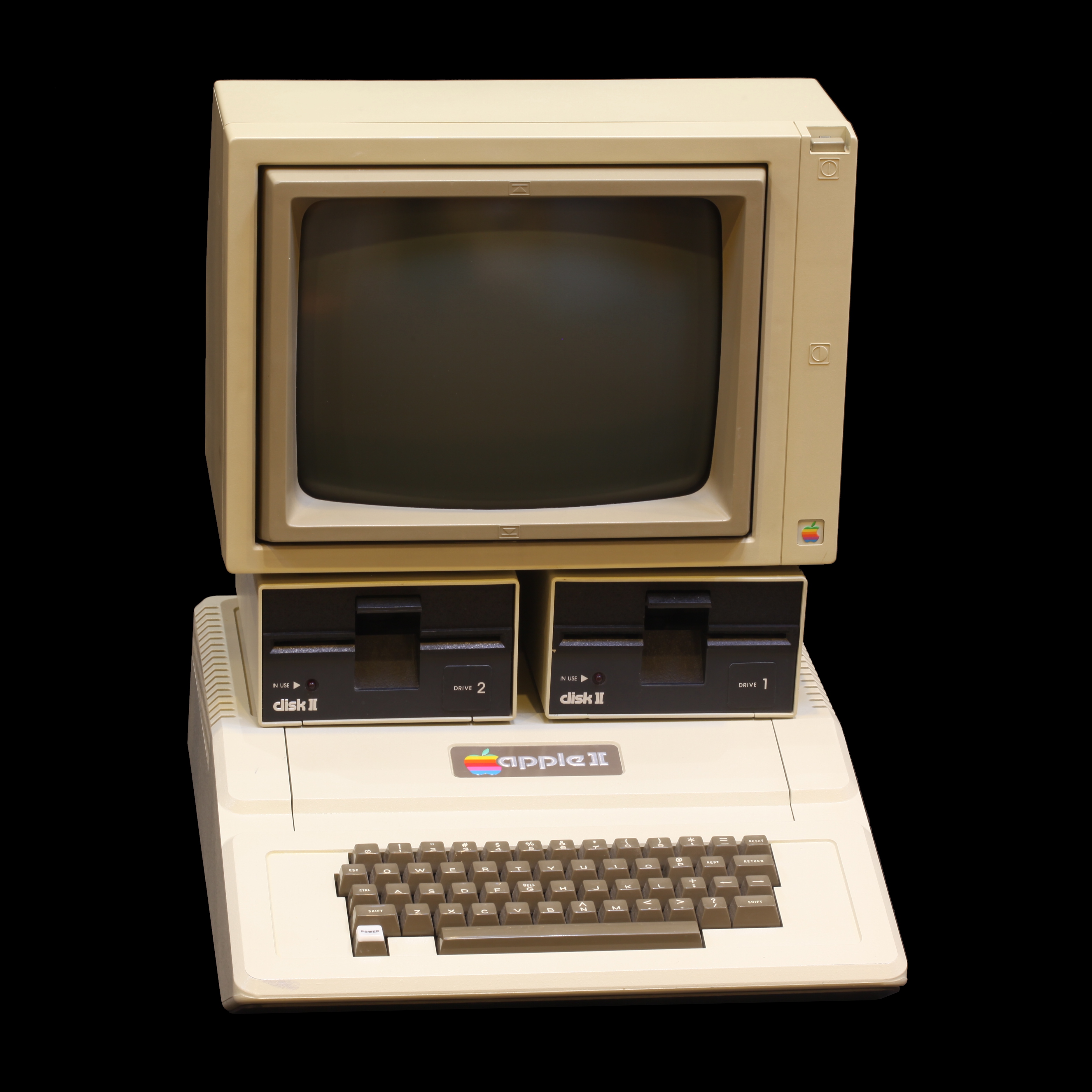
Desktop Computer
A desktop computer, often abbreviated as desktop, is a personal computer designed for regular use at a stationary location on or near a desk (as opposed to a portable computer) due to its size and power requirements. The most common configuration has a computer case, case that houses the power supply unit (computer), power supply, motherboard (a printed circuit board with a microprocessor as the central processing unit, computer memory, memory, bus (computing), bus, certain peripherals and other electronic components), disk storage (usually one or more hard disk drives, solid-state drives, optical disc drives, and in early models floppy disk drives); a computer keyboard, keyboard and computer mouse, mouse for input (computer science), input; and a computer monitor, monitor, computer speakers, speakers, and, often, a printer (computing), printer for output. The case may be oriented horizontally or vertically and placed either underneath, beside, or on top of a desk. Desktop Comput ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cryptographic Accelerator
In computing, a cryptographic accelerator is a co-processor designed specifically to perform computationally intensive cryptographic operations, doing so far more efficiently than the general-purpose CPU. Because many servers' system loads consist mostly of cryptographic operations, this can greatly increase performance. Intel's AES-NI is by far the most common cryptographic accelerator in commodity hardware. VIA PadLock is another recent example. Operating system support Several operating systems provide some support for cryptographic hardware. The BSD family of systems has the OpenBSD Cryptographic Framework (OCF), Linux systems have the Crypto API, Solaris OS has the Solaris Cryptographic Framework (SCF) and Microsoft Windows has the Microsoft CryptoAPI. Some cryptographic accelerators offer new machine instructions and can therefore be used directly by programs. Libraries such as OpenSSL and LibreSSL support some such cryptographic accelerators. Almost all Unix-like oper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Vector Processor
In computing, a vector processor or array processor is a central processing unit (CPU) that implements an instruction set where its instructions are designed to operate efficiently and effectively on large one-dimensional arrays of data called ''vectors''. This is in contrast to scalar processors, whose instructions operate on single data items only, and in contrast to some of those same scalar processors having additional single instruction, multiple data (SIMD) or SIMD within a register (SWAR) Arithmetic Units. Vector processors can greatly improve performance on certain workloads, notably numerical simulation, compression and similar tasks. Vector processing techniques also operate in video-game console hardware and in graphics accelerators. Vector machines appeared in the early 1970s and dominated supercomputer design through the 1970s into the 1990s, notably the various Cray platforms. The rapid fall in the price-to-performance ratio of conventional microprocessor de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
PlayStation 2
The PlayStation 2 (PS2) is a home video game console developed and marketed by Sony Interactive Entertainment, Sony Computer Entertainment. It was first released in Japan on 4 March 2000, in North America on 26 October, in Europe on 24 November, in Australia on 30 November, and other regions thereafter. It is the successor to the PlayStation (console), original PlayStation, as well as the second instalment in the PlayStation brand of consoles. As a sixth generation of video game consoles, sixth-generation console, it competed with Nintendo's GameCube, Sega's Dreamcast, and Microsoft's Xbox (console), Xbox. Announced in 1999, Sony began developing the console after the immense success of its predecessor. In addition to serving as a game console, it features a built-in DVD drive and was priced competitively with standalone DVD players of the time, enhancing its value. Full backward compatibility with original PlayStation games and accessories gave it access to a vast launch libra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Weitek
Weitek Corporation was an American Microprocessor, chip-design company that originally focused on floating-point units for a number of commercial Central processing unit, CPU designs. During the early to mid-1980s, Weitek designs could be found powering a number of high-end designs and Parallel computing, parallel-processing supercomputers. Weitek started in 1981, when several Intel engineers left to form their own company. Weitek developed math coprocessors for several systems, including those based on the Motorola Motorola 68000 series, 68000 family, the WTL 1064 and 1164, and for Intel-based i286 systems, the WTL 1067. The 1067 was physically implemented as three chips, the WTL 1163, 1164 and 1165. When Intel's own FPU design for the i386 fell far behind in development, Weitek delivered the 1167 for them in the form of a daughtercard. Improvements in chip manufacturing allowed this to be reduced to a single-chip version, the WTL 2167. The WTL 3167 of 1988, also known as the Ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
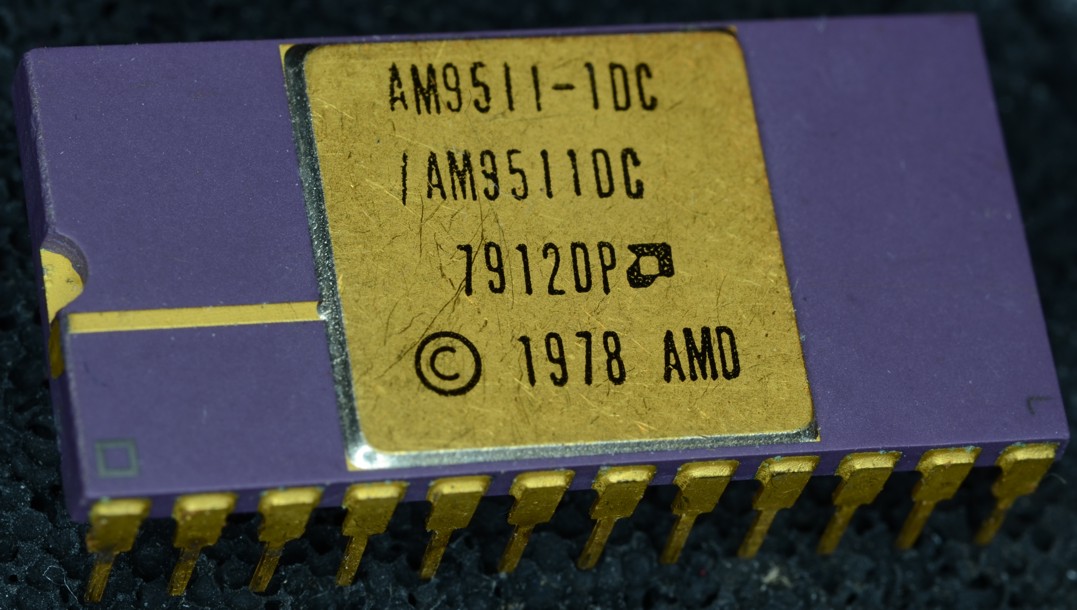
Intel 8231/8232
The Intel 8231 and 8232 were early designs of floating-point unit, floating-point maths coprocessors (FPUs), marketed for use with their Intel 8080, i8080 line of primary central processing unit, CPUs. They were licensed versions of AMD's Am9511 and Am9512 FPUs, from 1977 and 1979, themselves claimed by AMD as the world's first single-chip FPU solutions. Adoption Whilst the i8231/i8232 (and their AMD-branded cousins) were primarily intended to partner the i8080 (or the AMD clone Am9080), the multiple interface options in their design, from simple wait state insertion and Polling (computer science), status polling routines to interrupt and DMA controller driven methods suitable for a peripheral processor or add-in board, meant that – with a small amount of glue logic – it was usable in almost any microprocessor system that had a DMA subsystem or a spare interrupt input/interrupt vector available, and AMD's original documentation provided several different examples. This was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Computer-aided Design
Computer-aided design (CAD) is the use of computers (or ) to aid in the creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of a design. This software is used to increase the productivity of the designer, improve the quality of design, improve communications through documentation, and to create a database for manufacturing. Designs made through CAD software help protect products and inventions when used in patent applications. CAD output is often in the form of electronic files for print, machining, or other manufacturing operations. The terms computer-aided drafting (CAD) and computer-aided design and drafting (CADD) are also used. Its use in designing electronic systems is known as ''electronic design automation'' (''EDA''). In mechanical design it is known as ''mechanical design automation'' (''MDA''), which includes the process of creating a technical drawing with the use of computer software. CAD software for mechanical design uses either vector-based graphics to depict t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Floating-point
In computing, floating-point arithmetic (FP) is arithmetic on subsets of real numbers formed by a ''significand'' (a Sign (mathematics), signed sequence of a fixed number of digits in some Radix, base) multiplied by an integer power of that base. Numbers of this form are called floating-point numbers. For example, the number 2469/200 is a floating-point number in base ten with five digits: 2469/200 = 12.345 = \! \underbrace_\text \! \times \! \underbrace_\text\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\overbrace^ However, 7716/625 = 12.3456 is not a floating-point number in base ten with five digits—it needs six digits. The nearest floating-point number with only five digits is 12.346. And 1/3 = 0.3333… is not a floating-point number in base ten with any finite number of digits. In practice, most floating-point systems use Binary number, base two, though base ten (decimal floating point) is also common. Floating-point arithmetic operations, such as addition and division, approximate the correspond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Channel I/O
In computing, channel I/O is a high-performance input/output (I/O) architecture that is implemented in various forms on a number of computer architectures, especially on mainframe computers. In the past, channels were generally implemented with custom devices, variously named channel, I/O processor, I/O controller, I/O synchronizer, or '' DMA controller''. Overview Many I/O tasks can be complex and require logic to be applied to the data to convert formats and other similar duties. In these situations, the simplest solution is to ask the CPU to handle the logic, but because I/O devices are relatively slow, a CPU could waste time waiting for the data from the device. This situation is called 'I/O bound'. Channel architecture avoids this problem by processing some or all of the I/O task without the aid of the CPU by offloading the work to dedicated logic. Channels are logically self-contained, with sufficient logic and working storage to handle I/O tasks. Some are powerful or fle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |