|
Cloud Computing Security
Cloud computing security or, more simply, cloud security refers to a broad set of policies, technologies, applications, and controls utilized to protect virtualized IP, data, applications, services, and the associated infrastructure of cloud computing. It is a sub-domain of computer security, network security, and, more broadly, information security. Security issues associated with the cloud Cloud computing and storage provide users with capabilities to store and process their data in third-party data centers. Organizations use the cloud in a variety of different service models (with acronyms such as SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS) and deployment models ( private, public, hybrid, and community). Security concerns associated with cloud computing are typically categorized in two ways: as security issues faced by cloud providers (organizations providing software-, platform-, or infrastructure-as-a-service via the cloud) and security issues faced by their customers (companies or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is the on-demand availability of computer system resources, especially data storage ( cloud storage) and computing power, without direct active management by the user. Large clouds often have functions distributed over multiple locations, each of which is a data center. Cloud computing relies on sharing of resources to achieve coherence and typically uses a "pay as you go" model, which can help in reducing capital expenses but may also lead to unexpected operating expenses for users. Value proposition Advocates of public and hybrid clouds claim that cloud computing allows companies to avoid or minimize up-front IT infrastructure costs. Proponents also claim that cloud computing allows enterprises to get their applications up and running faster, with improved manageability and less maintenance, and that it enables IT teams to more rapidly adjust resources to meet fluctuating and unpredictable demand, providing burst computing capability: high computing p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypervisor
A hypervisor (also known as a virtual machine monitor, VMM, or virtualizer) is a type of computer software, firmware or hardware that creates and runs virtual machines. A computer on which a hypervisor runs one or more virtual machines is called a ''host machine'', and each virtual machine is called a ''guest machine''. The hypervisor presents the guest operating systems with a virtual operating platform and manages the execution of the guest operating systems. Unlike an emulator, the guest executes most instructions on the native hardware. Multiple instances of a variety of operating systems may share the virtualized hardware resources: for example, Linux, Windows, and macOS instances can all run on a single physical x86 machine. This contrasts with operating-system–level virtualization, where all instances (usually called ''containers'') must share a single kernel, though the guest operating systems can differ in user space, such as different Linux distributions with the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Sharing
Data sharing is the practice of making data used for scholarly research available to other investigators. Many funding agencies, institutions, and publication venues have policies regarding data sharing because transparency and openness are considered by many to be part of the scientific method. A number of funding agencies and science journals require authors of peer-reviewed papers to share any supplemental information (raw data, statistical methods or source code) necessary to understand, develop or reproduce published research. A great deal of scientific research is not subject to data sharing requirements, and many of these policies have liberal exceptions. In the absence of any binding requirement, data sharing is at the discretion of the scientists themselves. In addition, in certain situations governments and institutions prohibit or severely limit data sharing to protect proprietary interests, national security, and subject/patient/victim confidentiality. Data sharing may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network Eavesdropping
Network eavesdropping, also known as eavesdropping attack, sniffing attack, or snooping attack, is a method that retrieves user information through the internet. This attack happens on electronic devices like computers and smartphones. This network attack typically happens under the usage of unsecured networks, such as public wifi connections or shared electronic devices. Eavesdropping attacks through the network is considered one of the most urgent threats in industries that rely on collecting and storing data. Internet users use eavesdropping via the Internet to improve information security. A typical network eavesdropper may be called a Black-hat hacker and is considered a low-level hacker as it is simple to network eavesdrop successfully. The threat of network eavesdroppers is a growing concern. Research and discussions are brought up in the public's eye, for instance, types of eavesdropping, open-source tools, and commercial tools to prevent eavesdropping. Models against net ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Network
A computer network is a set of computers sharing resources located on or provided by network nodes. The computers use common communication protocols over digital interconnections to communicate with each other. These interconnections are made up of telecommunication network technologies, based on physically wired, optical, and wireless radio-frequency methods that may be arranged in a variety of network topologies. The nodes of a computer network can include personal computers, servers, networking hardware, or other specialised or general-purpose hosts. They are identified by network addresses, and may have hostnames. Hostnames serve as memorable labels for the nodes, rarely changed after initial assignment. Network addresses serve for locating and identifying the nodes by communication protocols such as the Internet Protocol. Computer networks may be classified by many criteria, including the transmission medium used to carry signals, bandwidth, communications pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penetration Test
A penetration test, colloquially known as a pen test or ethical hacking, is an authorized simulated cyberattack on a computer system, performed to evaluate the security of the system; this is not to be confused with a vulnerability assessment. The test is performed to identify weaknesses (also referred to as vulnerabilities), including the potential for unauthorized parties to gain access to the system's features and data, as well as strengths, enabling a full risk assessment to be completed. The process typically identifies the target systems and a particular goal, then reviews available information and undertakes various means to attain that goal. A penetration test target may be a white box (about which background and system information are provided in advance to the tester) or a black box (about which only basic information—if any—other than the company name is provided). A gray box penetration test is a combination of the two (where limited knowledge of the target is sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Masking
Data masking or data obfuscation is the process of modifying sensitive data in such a way that it is of no or little value to unauthorized intruders while still being usable by software or authorized personnel. Data masking can also be referred as anonymization, or tokenization, depending on different context. The main reason to mask data is to protect information that is classified as personally identifiable information, or mission critical data. However, the data must remain usable for the purposes of undertaking valid test cycles. It must also look real and appear consistent. It is more common to have masking applied to data that is represented outside of a corporate production system. In other words, where data is needed for the purpose of application development, building program extensions and conducting various test cycles. It is common practice in enterprise computing to take data from the production systems to fill the data component, required for these non-production en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Hardware
Computer hardware includes the physical parts of a computer, such as the computer case, case, central processing unit (CPU), Random-access memory, random access memory (RAM), Computer monitor, monitor, Computer mouse, mouse, Computer keyboard, keyboard, computer data storage, graphics card, sound card, Computer speakers, speakers and motherboard. By contrast, software is the set of instructions that can be stored and run by hardware. Hardware is so-termed because it is "Hardness, hard" or rigid with respect to changes, whereas software is "soft" because it is easy to change. Hardware is typically directed by the software to execute any command or Instruction (computing), instruction. A combination of hardware and software forms a usable computing system, although Digital electronics, other systems exist with only hardware. Von Neumann architecture The template for all modern computers is the Von Neumann architecture, detailed in a First Draft of a Report on the EDVAC, 1945 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single Sign-on
Single sign-on (SSO) is an authentication scheme that allows a user to log in with a single ID to any of several related, yet independent, software systems. True single sign-on allows the user to log in once and access services without re-entering authentication factors. It should not be confused with same-sign on (Directory Server Authentication), often accomplished by using the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) and stored LDAP databases on (directory) servers. A simple version of single sign-on can be achieved over IP networks using cookies but only if the sites share a common DNS parent domain. For clarity, a distinction is made between Directory Server Authentication (same-sign on) and single sign-on: Directory Server Authentication refers to systems requiring authentication for each application but using the same credentials from a directory server, whereas single sign-on refers to systems where a single authentication provides access to multiple applications by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federated Identity Management
A federated identity in information technology is the means of linking a person's electronic identity and attributes, stored across multiple distinct identity management systems. Federated identity is related to single sign-on (SSO), in which a user's single authentication ticket, or token, is trusted across multiple IT systems or even organizations. SSO is a subset of federated identity management, as it relates only to authentication and is understood on the level of technical interoperability and it would not be possible without some sort of federation. Retrieved 2017-07-03. Management In information technology (IT), federated identity management (FIdM) amounts to having a common set of policies, practices and protocols in place to manage the identity and trust into IT users and devices across organizations. Single sign-on (SSO) systems allow a single user authentication process across multiple IT systems or even organizations. SSO is a subset of federated identity manageme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
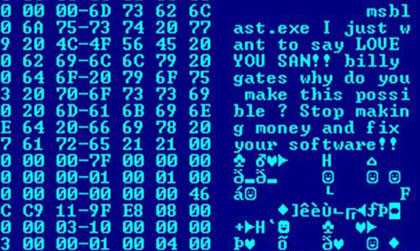
Malware
Malware (a portmanteau for ''malicious software'') is any software intentionally designed to cause disruption to a computer, server, client, or computer network, leak private information, gain unauthorized access to information or systems, deprive access to information, or which unknowingly interferes with the user's computer security and privacy. By contrast, software that causes harm due to some deficiency is typically described as a software bug. Malware poses serious problems to individuals and businesses on the Internet. According to Symantec's 2018 Internet Security Threat Report (ISTR), malware variants number has increased to 669,947,865 in 2017, which is twice as many malware variants as in 2016. Cybercrime, which includes malware attacks as well as other crimes committed by computer, was predicted to cost the world economy $6 trillion USD in 2021, and is increasing at a rate of 15% per year. Many types of malware exist, including computer viruses, worms, Trojan horses, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |