|
Closed System (control Theory)
The terms closed system and '' open system'' have long been defined in the widely (and long before any sort of amplifier was invented) established subject of thermodynamics, in terms that have nothing to do with the concepts of feedback and feedforward. The terms 'feedforward' and 'feedback' arose first in the 1920s in the theory of amplifier design, more recently than the thermodynamic terms. Negative feedback was eventually patented by H.S Black in 1934. In thermodynamics, an open system is one that can take in and give out ponderable matter. In thermodynamics, a closed system is one that cannot take in or give out ponderable matter, but may be able to take in or give out radiation and heat and work or any form of energy. In thermodynamics, a closed system can be further restricted, by being 'isolated': an isolated system cannot take in nor give out either ponderable matter or any form of energy. It does not make sense to try to use these well established terms to try to disti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open System (systems Theory)
An open system is a system that has external interactions. Such interactions can take the form of information, energy, or material transfers into or out of the system boundary, depending on the discipline which defines the concept. An open system is contrasted with the concept of an isolated system which exchanges neither energy, matter, nor information with its environment. An open system is also known as a flow system. The concept of an open system was formalized within a framework that enabled one to interrelate the theory of the organism, thermodynamics, and evolutionary theory. This concept was expanded upon with the advent of information theory and subsequently systems theory. Today the concept has its applications in the natural and social sciences. In the natural sciences an open system is one whose border is permeable to both energy and mass. By contrast, a closed system is permeable to energy but not to matter. The definition of an open system assumes that there are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that can increase the magnitude of a signal (a time-varying voltage or current). It may increase the power significantly, or its main effect may be to boost the voltage or current (power, voltage or current amplifier). It is a two-port electronic circuit that uses electric power from a power supply to increase the amplitude of a signal applied to its input terminals, producing a greater amplitude signal at its output. The ratio of output to input voltage, current, or power is termed gain (voltage, current, or power gain). An amplifier, by definition has gain greater than unity (if the gain is less than unity, the device is an attenuator). An amplifier can either be a separate piece of equipment or an electrical circuit contained within another device. Amplification is fundamental to modern electronics, and amplifiers are widely used in almost all electronic equipment. Amplifiers can be categorize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a branch of physics that deals with heat, work, and temperature, and their relation to energy, entropy, and the physical properties of matter and radiation. The behavior of these quantities is governed by the four laws of thermodynamics which convey a quantitative description using measurable macroscopic physical quantities, but may be explained in terms of microscopic constituents by statistical mechanics. Thermodynamics applies to a wide variety of topics in science and engineering, especially physical chemistry, biochemistry, chemical engineering and mechanical engineering, but also in other complex fields such as meteorology. Historically, thermodynamics developed out of a desire to increase the efficiency of early steam engines, particularly through the work of French physicist Sadi Carnot (1824) who believed that engine efficiency was the key that could help France win the Napoleonic Wars. Scots-Irish physicist Lord Kelvin was the first to formulate a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feed Forward (control)
A feed forward (sometimes written feedforward) is an element or pathway within a control system that passes a controlling signal from a source in its external environment to a load elsewhere in its external environment. This is often a command signal from an external operator. A control system which has only feed-forward behavior responds to its control signal in a pre-defined way without responding to the way the load reacts; it is in contrast with a system that also has feedback, which adjusts the input to take account of how it affects the load, and how the load itself may vary unpredictably; the load is considered to belong to the external environment of the system. In a feed-forward system, the control variable adjustment is not error-based. Instead it is based on knowledge about the process in the form of a mathematical model of the process and knowledge about, or measurements of, the process disturbances. Some prerequisites are needed for control scheme to be reliable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negative Feedback
Negative feedback (or balancing feedback) occurs when some function (Mathematics), function of the output of a system, process, or mechanism is feedback, fed back in a manner that tends to reduce the fluctuations in the output, whether caused by changes in the input or by other disturbances. Whereas positive feedback tends to lead to instability via exponential growth, oscillation or chaos theory, chaotic behavior, negative feedback generally promotes stability. Negative feedback tends to promote a settling to List of types of equilibrium, equilibrium, and reduces the effects of perturbations. Negative feedback loops in which just the right amount of correction is applied with optimum timing can be very stable, accurate, and responsive. Negative feedback is widely used in mechanical and electronic engineering, and also within living organisms, and can be seen in many other fields from chemistry and economics to physical systems such as the climate. General negative feedback ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ponderable Matter
Imponderable fluids are features of several superseded scientific theories, such as archaic atomic and electromotive theories. Description The term has been used in natural philosophy and physics to explain certain phenomena as the result of invisible and practically weightless (Latin: ''imponderabilis'') fluids. Historically proposed imponderable fluids include phlogiston and caloric; additionally some physicists considered electricity imponderable. Fluids theories In an article published in 1868, English inventor and polymath Fleeming Jenkin described myriad hypotheses of physics that had been put forth involving imponderable fluids: Leibniz mentions with great disapproval a certain Hartsoeker who supposed that atoms moved in an ambient fluid, though the idea is not unlike his own. It is difficult to trace the origin of the hypothesis, but Galileo and Hobbes both speak of a subtle ether. The conception of an all-pervading imponderable fluid of this kind has formed part of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Closed System
A closed system is a natural physical system that does not allow transfer of matter in or out of the system, although — in contexts such as physics, chemistry or engineering — the transfer of energy (''e.g.'' as work or heat) is allowed. In physics In classical mechanics In nonrelativistic classical mechanics, a closed system is a physical system that doesn't exchange any matter with its surroundings, and isn't subject to any net force whose source is external to the system. A closed system in classical mechanics would be equivalent to an isolated system in thermodynamics. Closed systems are often used to limit the factors that can affect the results of a specific problem or experiment. In thermodynamics In thermodynamics, a closed system can exchange energy (as heat or work) but not matter, with its surroundings. An isolated system cannot exchange any heat, work, or matter with the surroundings, while an open system can exchange energy and matter. (This scheme of definit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isolated System
In physical science, an isolated system is either of the following: # a physical system so far removed from other systems that it does not interact with them. # a thermodynamic system enclosed by rigid immovable walls through which neither mass nor energy can pass. Though subject internally to its own gravity, an isolated system is usually taken to be outside the reach of external gravitational and other long-range forces. This can be contrasted with what (in the more common terminology used in thermodynamics) is called a closed system, being enclosed by selective walls through which energy can pass as heat or work, but not matter; and with an open system, which both matter and energy can enter or exit, though it may have variously impermeable walls in parts of its boundaries. An isolated system obeys the conservation law that its total energy–mass stays constant. Most often, in thermodynamics, mass and energy are treated as separately conserved. Because of the require ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
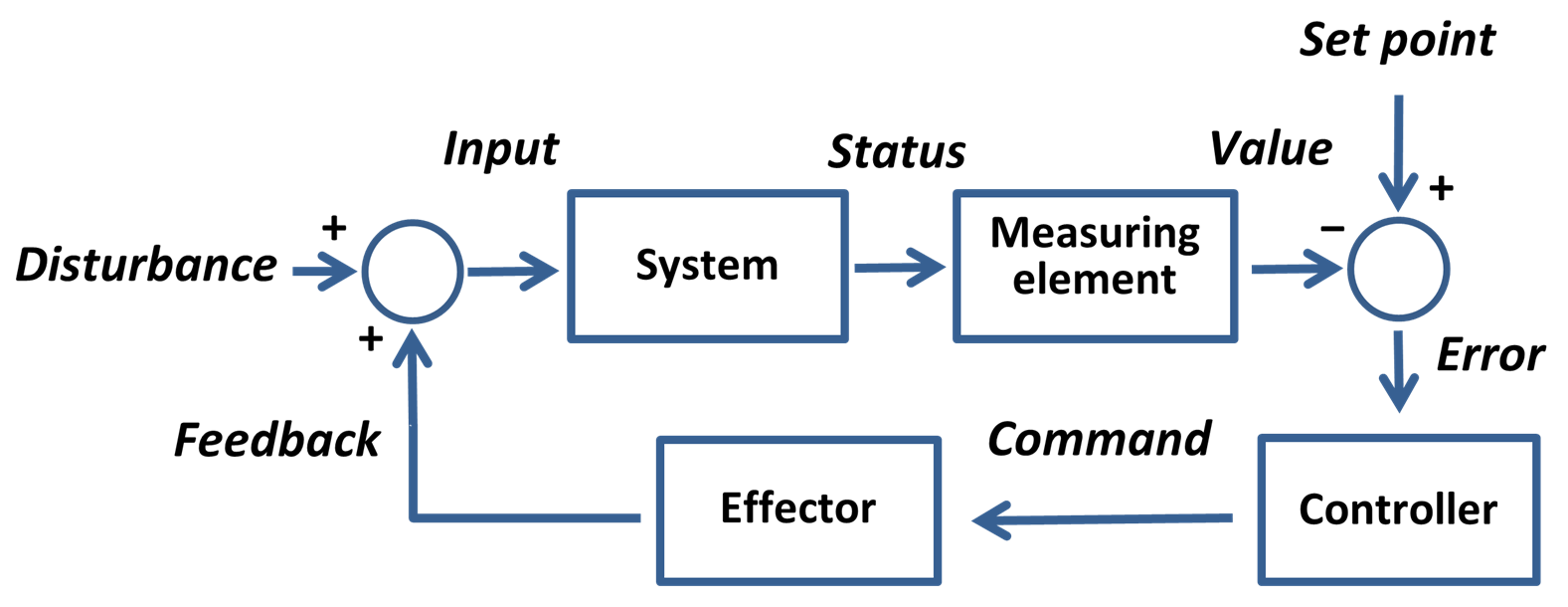
Control System
A control system manages, commands, directs, or regulates the behavior of other devices or systems using control loops. It can range from a single home heating controller using a thermostat controlling a domestic boiler to large industrial control systems which are used for controlling processes or machines. The control systems are designed via control engineering process. For continuously modulated control, a feedback controller is used to automatically control a process or operation. The control system compares the value or status of the process variable (PV) being controlled with the desired value or setpoint (SP), and applies the difference as a control signal to bring the process variable output of the plant to the same value as the setpoint. For sequential and combinational logic, software logic, such as in a programmable logic controller, is used. Open-loop and closed-loop control There are two common classes of control action: open loop and closed loop. In an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feedback Loop
Feedback occurs when outputs of a system are routed back as inputs as part of a chain of cause-and-effect that forms a circuit or loop. The system can then be said to ''feed back'' into itself. The notion of cause-and-effect has to be handled carefully when applied to feedback systems: History Self-regulating mechanisms have existed since antiquity, and the idea of feedback had started to enter economic theory in Britain by the 18th century, but it was not at that time recognized as a universal abstraction and so did not have a name. The first ever known artificial feedback device was a float valve, for maintaining water at a constant level, invented in 270 BC in Alexandria, Egypt. This device illustrated the principle of feedback: a low water level opens the valve, the rising water then provides feedback into the system, closing the valve when the required level is reached. This then reoccurs in a circular fashion as the water level fluctuates. Centrifugal governors were u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feedback
Feedback occurs when outputs of a system are routed back as inputs as part of a chain of cause-and-effect that forms a circuit or loop. The system can then be said to ''feed back'' into itself. The notion of cause-and-effect has to be handled carefully when applied to feedback systems: History Self-regulating mechanisms have existed since antiquity, and the idea of feedback had started to enter economic theory in Britain by the 18th century, but it was not at that time recognized as a universal abstraction and so did not have a name. The first ever known artificial feedback device was a float valve, for maintaining water at a constant level, invented in 270 BC in Alexandria, Egypt. This device illustrated the principle of feedback: a low water level opens the valve, the rising water then provides feedback into the system, closing the valve when the required level is reached. This then reoccurs in a circular fashion as the water level fluctuates. Centrifugal governors were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Gain
The power gain of an electrical network is the ratio of an output power to an input power. Unlike other signal gains, such as voltage and current gain, "power gain" may be ambiguous as the meaning of terms "input power" and "output power" is not always clear. Three important power gains are operating power gain, transducer power gain and available power gain. Note that all these definitions of power gains employ the use of average (as opposed to instantaneous) power quantities and therefore the term "average" is often suppressed, which can be confusing at occasions. Operating power gain The operating power gain of a two-port network, GP, is defined as: :G_P = \frac where *Pload is the maximum time averaged power delivered to the load, where the maximization is over the load impedance, i.e., we desire the load impedance which maximizes the time averaged power delivered to the load. *Pinput is the time averaged power entering the network. If the time averaged input power depends on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)