|
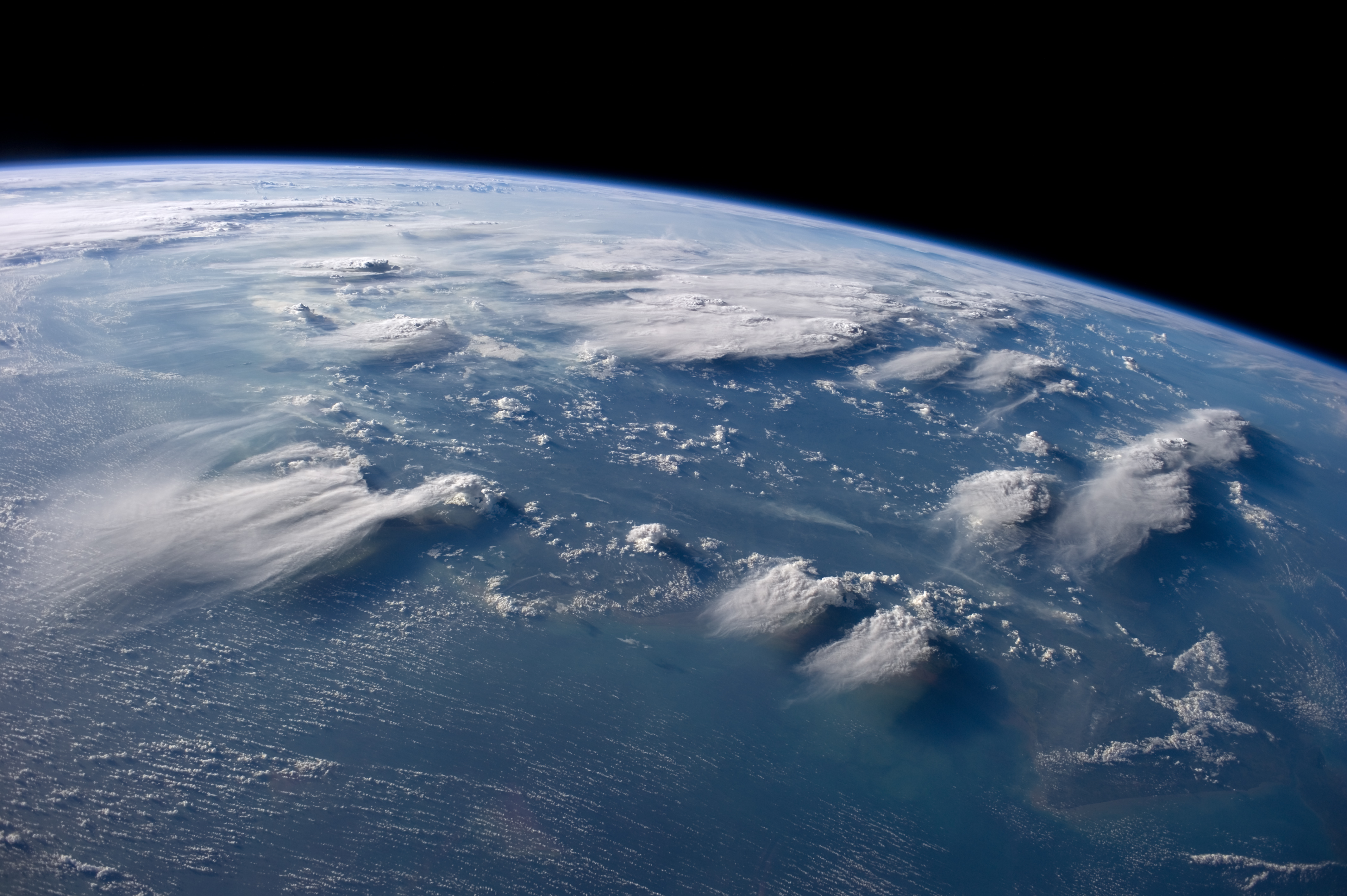
Cirrostratus
Cirrostratus is a high-level, very thin, generally uniform ''stratiform'' genus-type of cloud. It is made out of ice-crystals, which are pieces of frozen water. It is difficult to detect and it can make halos. These are made when the cloud takes the form of thin cirrostratus nebulosus. The cloud has a fibrous texture with no halos if it is thicker cirrostratus fibratus. On the approach of a frontal system, the cirrostratus often begins as nebulous and turns to fibratus. If the cirrostratus begins as fragmented of clouds in the sky it often means the front is weak. Cirrostratus is usually located above 5.5 km (18,000 ft). Its presence indicates a large amount of moisture in the upper troposphere. Clouds resembling cirrostratus occasionally form in polar regions of the lower stratosphere. Polar stratospheric clouds can take on this appearance when composed of tiny supercooled droplets of water or nitric acid. Cirrostratus clouds sometimes signal the approach of a warm fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloud
In meteorology, a cloud is an aerosol consisting of a visible mass of miniature liquid droplets, frozen crystals, or other particles suspended in the atmosphere of a planetary body or similar space. Water or various other chemicals may compose the droplets and crystals. On Earth, clouds are formed as a result of saturation of the air when it is cooled to its dew point, or when it gains sufficient moisture (usually in the form of water vapor) from an adjacent source to raise the dew point to the ambient temperature. They are seen in the Earth's homosphere, which includes the troposphere, stratosphere, and mesosphere. Nephology is the science of clouds, which is undertaken in the cloud physics branch of meteorology. There are two methods of naming clouds in their respective layers of the homosphere, Latin and common name. Genus types in the troposphere, the atmospheric layer closest to Earth's surface, have Latin names because of the universal adoption of Luke Howard's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cirrostratus Nebulosus
Cirrostratus nebulosus is a type of high-level cirrostratus cloud. The name ''cirrostratus nebulosus'' is derived from Latin, the adjective ''nebulosus'' meaning "full of vapor, foggy, cloudy, dark". Cirrostratus nebulosus is one of the two most common forms that cirrostratus often takes, with the other being cirrostratus fibratus. The nebulosus species is featureless and uniform, while the fibratus species has a fibrous appearance. Cirrostratus nebulosus are formed by gently rising air. The cloud is often hard to see unless the sun shines through it at the correct angle, forming a halo. While usually very light, the cloud may also be very dense, and the exact appearance of the cloud can vary from one formation to another. In the winter, precipitation often follows behind these clouds; however, they are not a precipitation-producing cloud. See also *List of cloud types The list of cloud types groups all genera as ''high'' (cirro-, cirrus), ''middle'' (alto-), ''multi-level'' (nimb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cirrostratus Fibratus
Cirrostratus fibratus or also called Cirrostratus filosus is a type of cirrostratus cloud. The name ''cirrostratus fibratus'' is derived from Latin, meaning "fibrous". Cirrostratus fibratus is one of the two most common forms that cirrostratus often takes, with the other being cirrostratus nebulosus. They are formed from strong, continuous winds blowing at high altitudes, and they often cover a large portion of the sky. Cirrostratus fibratus may often develop from either cirrus fibratus or cirrus spissatus cloud. Precipitation is often imminent behind these clouds; however, they are not a precipitation-producing cloud. See also *List of cloud types The list of cloud types groups all genera as ''high'' (cirro-, cirrus), ''middle'' (alto-), ''multi-level'' (nimbo-, cumulo-, cumulus), and ''low'' (strato-, stratus). These groupings are determined by the altitude level or levels in the troposphe ... References External linksInternational Cloud Atlas – Cirrostratus fibratus Ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cirrostratus Nebulosus
Cirrostratus nebulosus is a type of high-level cirrostratus cloud. The name ''cirrostratus nebulosus'' is derived from Latin, the adjective ''nebulosus'' meaning "full of vapor, foggy, cloudy, dark". Cirrostratus nebulosus is one of the two most common forms that cirrostratus often takes, with the other being cirrostratus fibratus. The nebulosus species is featureless and uniform, while the fibratus species has a fibrous appearance. Cirrostratus nebulosus are formed by gently rising air. The cloud is often hard to see unless the sun shines through it at the correct angle, forming a halo. While usually very light, the cloud may also be very dense, and the exact appearance of the cloud can vary from one formation to another. In the winter, precipitation often follows behind these clouds; however, they are not a precipitation-producing cloud. See also *List of cloud types The list of cloud types groups all genera as ''high'' (cirro-, cirrus), ''middle'' (alto-), ''multi-level'' (nimb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altostratus Cloud
Altostratus is a middle-altitude cloud genus made up of water droplets, ice crystals, or a mixture of the two. Altostratus clouds are formed when large masses of warm, moist air rise, causing water vapor to condense. Altostratus clouds are usually gray or blueish featureless sheets, although some variants have wavy or banded bases. The sun can be seen through thinner altostratus clouds, but thicker layers can be quite opaque. Altostratus clouds usually predict the arrival of warm fronts. Once altostratus clouds associated with a warm front arrive, continuous rain or snow will usually follow in the next 12 to 24 hours. Although altostratus clouds predict the arrival of warmer, wetter weather, they themselves do not produce significant precipitation. Thunderstorms can be embedded in altostratus clouds; however, bringing showers. Because altostratus clouds can contain ice crystals, they can produce some optical phenomena like iridescence and coronas. Description Altostratus clo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratus Cloud
Stratus clouds are low-level clouds characterized by horizontal layering with a uniform base, as opposed to convective or cumuliform clouds that are formed by rising thermals. More specifically, the term ''stratus'' is used to describe flat, hazy, featureless clouds at low altitudes varying in color from dark gray to nearly white. The word ''stratus'' comes from the Latin prefix ''strato-'', meaning "layer". Stratus clouds may produce a light drizzle or a small amount of snow. These clouds are essentially above-ground fog formed either through the lifting of morning fog or through cold air moving at low altitudes over a region. Some call these clouds "high fog" for their fog-like form. While light rain may fall, this cloud does not indicate much meteorological precipitation. Formation Stratus clouds form when weak vertical currents lift a layer of air off the ground and it depressurizes, following the lapse rate. This causes the relative humidity to increase due to the adiabati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warm Front
A warm front is a density discontinuity located at the leading edge of a homogeneous warm air mass, and is typically located on the equator-facing edge of an isotherm gradient. Warm fronts lie within broader troughs of low pressure than cold fronts, and move more slowly than the cold fronts which usually follow because cold air is denser and less easy to remove from the Earth's surface. This also forces temperature differences across warm fronts to be broader in scale. Clouds ahead of the warm front are mostly stratiform, and rainfall defiantly increases as the front approaches. Fog can also occur preceding a warm frontal passage. Clearing and warming is usually rapid after frontal passage. If the warm air mass is unstable, thunderstorms may be embedded among the stratiform clouds ahead of the front, and after frontal passage thundershowers may continue. On weather maps, the surface location of a warm front is marked with a red line of semicircles pointing in the direction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contrails
Contrails (; short for "condensation trails") or vapor trails are line-shaped clouds produced by aircraft engine exhaust or changes in air pressure, typically at aircraft cruising altitudes several miles above the Earth's surface. Contrails are composed primarily of water, in the form of ice crystals. The combination of water vapor in aircraft engine exhaust and the low ambient temperatures that exist at high altitudes allows the formation of the trails. Impurities in the engine exhaust from the fuel, including sulfur compounds (0.05% by weight in jet fuel) provide some of the particles that can serve as nucleation sites for water droplet growth in the exhaust. If water droplets form, they might freeze to form ice particles that compose a contrail. Their formation can also be triggered by changes in air pressure in wingtip vortices or in the air over the entire wing surface. Contrails, and other clouds directly resulting from human activity, are collectively named homogenitus. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halo (optical Phenomenon)
A halo is an optical phenomenon produced by light (typically from the Sun or Moon) interacting with ice crystals suspended in the atmosphere. Halos can have many forms, ranging from colored or white rings to arcs and spots in the sky. Many of these appear near the Sun or Moon, but others occur elsewhere or even in the opposite part of the sky. Among the best known halo types are the circular halo (properly called the 22° halo), light pillars, and sun dogs, but many others occur; some are fairly common while others are extremely rare. The ice crystals responsible for halos are typically suspended in cirrus or cirrostratus clouds in the upper troposphere (), but in cold weather they can also float near the ground, in which case they are referred to as diamond dust. The particular shape and orientation of the crystals are responsible for the type of halo observed. Light is reflected and refracted by the ice crystals and may split into colors because of dispersion. The crystals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nimbostratus Cloud
A nimbostratus cloud is a multi-level, amorphous, nearly uniform and often dark grey cloud that usually produces continuous rain, snow or sleet but no lightning or thunder. in the Oxford Dictionaries Online Although it is usually a low-based cloud, it actually forms most commonly in the middle level of the troposphere and then spreads vertically into the low and high levels. Nimbostratus usually produces precipitation over a wide area. ''Nimbo-'' is from the Latin word ''nimbus'', which denotes cloud or halo. Downward-growing nimbostratus can have the same vertical extent as most large upward-growing cumulus, but its horizontal extent tends to be even greater. Appearance Nimbostratus has a diffuse |
Polar Stratospheric Cloud
Polar stratospheric clouds (PSCs) are clouds in the winter polar stratosphere at altitudes of . They are best observed during civil twilight, when the Sun is between 1 and 6 degrees below the horizon, as well as in winter and in more northerly latitudes. One main type of PSC is made up mostly of supercooled droplets of water and nitric acid and is implicated in the formation of ozone holes. The other main type consists only of ice crystals which are not harmful. This type of PSC is also referred to as nacreous (, from ''nacre'', or mother of pearl, due to its iridescence). Formation The stratosphere is very dry; unlike the troposphere, it rarely allows clouds to form. In the extreme cold of the polar winter, however, stratospheric clouds of different types may form, which are classified according to their physical state (super-cooled liquid or ice) and chemical composition. Due to their high altitude and the curvature of the surface of the Earth, these clouds will receive sunlig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precipitation (meteorology)
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. Precipitation occurs when a portion of the atmosphere becomes saturated with water vapor (reaching 100% relative humidity), so that the water condenses and "precipitates" or falls. Thus, fog and mist are not precipitation but colloids, because the water vapor does not condense sufficiently to precipitate. Two processes, possibly acting together, can lead to air becoming saturated: cooling the air or adding water vapor to the air. Precipitation forms as smaller droplets coalesce via collision with other rain drops or ice crystals within a cloud. Short, intense periods of rain in scattered locations are called showers. Moisture that is lifted or otherwise forced to rise over a layer of sub-freezing air at the surface may be condense ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |