|
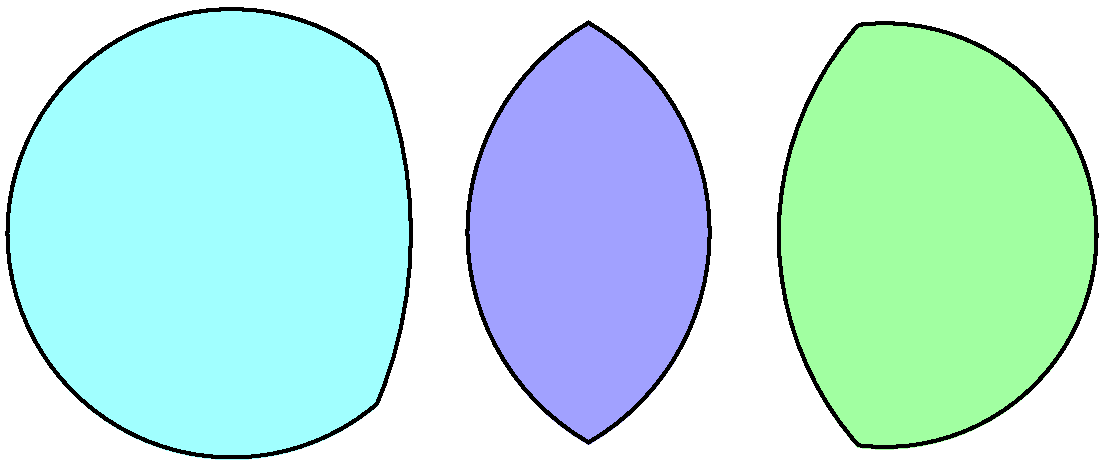
Circular Triangle
In geometry, a circular triangle is a triangle with circular arc edges. Construction A convex circular triangle may be constructed by three circles intersecting each other and represents the area of intersection. Its edges are all curved outwards. The sum of the internal angles of a circular triangle is greater than 180°. A Reuleaux triangle is a special case based on an equilateral triangle where the center of each arc is on the opposite vertex. A circular horn triangle is a similar concept, but represents the area interior to 3 mutually tangent circles so all of the internal angles are zero. The arbelos is a special case with three collinear vertices and three semicircular edges.. Other circular triangles can have a mixture of convex and concave circular arc edges. : Long arcs can produce concave figures regardless of whether individual edges are curved inwards or outwards. Inward curved arcs can create self-intersecting forms, such as the a triquetra figure: : Tessel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circular Triangle Example
{{disambiguation ...
Circular may refer to: * The shape of a circle * ''Circular'' (album), a 2006 album by Spanish singer Vega * Circular letter (other) ** Flyer (pamphlet), a form of advertisement * Circular reasoning, a type of logical fallacy * Circular reference * Government circular, a written statement of government policy See also * Circular DNA (other) * Circular Line (other) * Circularity (other) Circularity may refer to: *Circular definition *Circular economy *Circular reasoning, also known as circular logic **Begging the question *Circularity of an object or roundness *A circularity ratio as a compactness measure of a shape *An assumptio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semicircle
In mathematics (and more specifically geometry), a semicircle is a one-dimensional locus of points that forms half of a circle. The full arc of a semicircle always measures 180° (equivalently, radians, or a half-turn). It has only one line of symmetry (reflection symmetry). In non-technical usage, the term "semicircle" is sometimes used to refer to a half-disk, which is a two-dimensional geometric shape that also includes the diameter segment from one end of the arc to the other as well as all the interior points. By Thales' theorem, any triangle inscribed in a semicircle with a vertex at each of the endpoints of the semicircle and the third vertex elsewhere on the semicircle is a right triangle, with a right angle at the third vertex. All lines intersecting the semicircle perpendicularly are concurrent at the center of the circle containing the given semicircle. Uses A semicircle can be used to construct the arithmetic and geometric means of two lengths using straight-e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digon
In geometry, a digon is a polygon with two sides (edges) and two vertices. Its construction is degenerate in a Euclidean plane because either the two sides would coincide or one or both would have to be curved; however, it can be easily visualised in elliptic space. A regular digon has both angles equal and both sides equal and is represented by Schläfli symbol . It may be constructed on a sphere as a pair of 180 degree arcs connecting antipodal points, when it forms a lune. The digon is the simplest abstract polytope of rank 2. A truncated ''digon'', t is a square, . An alternated digon, h is a monogon, . In Euclidean geometry The digon can have one of two visual representations if placed in Euclidean space. One representation is degenerate, and visually appears as a double-covering of a line segment. Appearing when the minimum distance between the two edges is 0, this form arises in several situations. This double-covering form is sometimes used for defining degener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lens (geometry)
In 2-dimensional geometry, a lens is a convex region bounded by two circular arcs joined to each other at their endpoints. In order for this shape to be convex, both arcs must bow outwards (convex-convex). This shape can be formed as the intersection of two circular disks. It can also be formed as the union of two circular segments (regions between the chord of a circle and the circle itself), joined along a common chord. Types If the two arcs of a lens have equal radius, it is called a symmetric lens, otherwise is an asymmetric lens. The vesica piscis is one form of a symmetric lens, formed by arcs of two circles whose centers each lie on the opposite arc. The arcs meet at angles of 120° at their endpoints. Area ;Symmetric The area of a symmetric lens can be expressed in terms of the radius ''R'' and arc lengths ''θ'' in radians: :A = R^2\left(\theta - \sin \theta \right). ;Asymmetric The area of an asymmetric lens formed from circles of radii ''R'' and ''r'' with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lune (mathematics)
In plane geometry, a lune () is the concave-convex region bounded by two circular arcs. It has one boundary portion for which the connecting segment of any two nearby points moves outside the region and another boundary portion for which the connecting segment of any two nearby points lies entirely inside the region. A convex-convex region is termed a lens. Formally, a lune is the relative complement of one disk in another (where they intersect but neither is a subset of the other). Alternatively, if A and B are disks, then A \smallsetminus A \cap B is a lune. Squaring the lune In the 5th century BC, Hippocrates of Chios showed that the Lune of Hippocrates and two other lunes could be exactly squared (converted into a square having the same area) by straightedge and compass. In 1766 the Finnish mathematician Daniel Wijnquist, quoting Daniel Bernoulli, listed all five geometrical squareable lunes, adding to those known by Hippocrates. In 1771 Leonard Euler gave a general a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperbolic Triangle
In hyperbolic geometry, a hyperbolic triangle is a triangle in the hyperbolic plane. It consists of three line segments called ''sides'' or ''edges'' and three points called ''angles'' or ''vertices''. Just as in the Euclidean case, three points of a hyperbolic space of an arbitrary dimension always lie on the same plane. Hence planar hyperbolic triangles also describe triangles possible in any higher dimension of hyperbolic spaces. Definition A hyperbolic triangle consists of three non-collinear points and the three segments between them. Properties Hyperbolic triangles have some properties that are analogous to those of triangles in Euclidean geometry: *Each hyperbolic triangle has an inscribed circle but not every hyperbolic triangle has a circumscribed circle (see below). Its vertices can lie on a horocycle or hypercycle. Hyperbolic triangles have some properties that are analogous to those of triangles in spherical or elliptic geometry: *Two triangles with the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tessellation
A tessellation or tiling is the covering of a surface, often a plane (mathematics), plane, using one or more geometric shapes, called ''tiles'', with no overlaps and no gaps. In mathematics, tessellation can be generalized to high-dimensional spaces, higher dimensions and a variety of geometries. A periodic tiling has a repeating pattern. Some special kinds include ''regular tilings'' with regular polygonal tiles all of the same shape, and ''semiregular tilings'' with regular tiles of more than one shape and with every corner identically arranged. The patterns formed by periodic tilings can be categorized into 17 wallpaper groups. A tiling that lacks a repeating pattern is called "non-periodic". An ''aperiodic tiling'' uses a small set of tile shapes that cannot form a repeating pattern. A ''tessellation of space'', also known as a space filling or honeycomb, can be defined in the geometry of higher dimensions. A real physical tessellation is a tiling made of materials such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seven Overlapping Circles Grid
An overlapping circles grid is a geometric pattern of repeating, overlapping circles of an equal radius in two-dimensional space. Commonly, designs are based on circles centered on triangles (with the simple, two circle form named ''vesica piscis'') or on the square lattice pattern of points. Patterns of seven overlapping circles appear in historical artefacts from the 7th century BC onwards; they become a frequently used ornament in the Roman Empire period, and survive into medieval artistic traditions both in Islamic art (girih decorations) and in Gothic art. The name "Flower of Life" is given to the overlapping circles pattern in New Age publications. Of special interest is the six petal rosette derived from the "seven overlapping circles" pattern, also known as "Sun of the Alps" from its frequent use in alpine folk art in the 17th and 18th century. Triangular grid of overlapping circles The triangular lattice form, with circle radii equal to their separation is called a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Circular Triangles Convex Concave
Long may refer to: Measurement * Long, characteristic of something of great duration * Long, characteristic of something of great length * Longitude (abbreviation: long.), a geographic coordinate * Longa (music), note value in early music mensural notation Places Asia * Long District, Laos * Long District, Phrae, Thailand * Longjiang (other) or River Long (lit. "dragon river"), one of several rivers in China * Yangtze River or Changjiang (lit. "Long River"), China Elsewhere * Long, Somme, France * Long, Washington, United States People * Long (surname) * Long (surname 龍) (Chinese surname) Fictional characters * Long (''Bloody Roar''), in the video game series Sports * Long, a fielding term in cricket * Long, in tennis and similar games, beyond the service line during a serve and beyond the baseline during play Other uses * , a U.S. Navy ship name * Long (finance), a position in finance, especially stock markets * Lòng, name for a laneway in Shanghai * Long in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triquetra
The triquetra ( ; from the Latin adjective ''triquetrus'' "three-cornered") is a triangular figure composed of three interlaced arcs, or (equivalently) three overlapping '' vesicae piscis'' lens shapes. It is used as an ornamental design in architecture, and in medieval manuscript illumination (particularly in the Insular tradition). Its depiction as interlaced is common in Insular ornaments from about the 7th century. In this interpretation, the triquetra represents the topologically simplest possible knot. History Iron Age The term ''triquetra'' in archaeology is used of any figure consisting of three arcs, including a pinwheel design of the type of the triskeles. Such symbols become frequent from about the 4th century BC ornamented ceramics of Anatolia and Persia, and it appears on early Lycian coins. The triquetra is found on runestones in Northern Europe, such as the Funbo Runestones, and on early Germanic coins. It bears a resemblance to the ''valknut'', a design of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circular Triangles Convex Concave
{{disambiguation ...
Circular may refer to: * The shape of a circle * ''Circular'' (album), a 2006 album by Spanish singer Vega * Circular letter (other) ** Flyer (pamphlet), a form of advertisement * Circular reasoning, a type of logical fallacy * Circular reference * Government circular, a written statement of government policy See also * Circular DNA (other) * Circular Line (other) * Circularity (other) Circularity may refer to: *Circular definition *Circular economy *Circular reasoning, also known as circular logic **Begging the question *Circularity of an object or roundness *A circularity ratio as a compactness measure of a shape *An assumptio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Mathematical Monthly
''The American Mathematical Monthly'' is a mathematical journal founded by Benjamin Finkel in 1894. It is published ten times each year by Taylor & Francis for the Mathematical Association of America. The ''American Mathematical Monthly'' is an expository journal intended for a wide audience of mathematicians, from undergraduate students to research professionals. Articles are chosen on the basis of their broad interest and reviewed and edited for quality of exposition as well as content. In this the ''American Mathematical Monthly'' fulfills a different role from that of typical mathematical research journals. The ''American Mathematical Monthly'' is the most widely read mathematics journal in the world according to records on JSTOR. Tables of contents with article abstracts from 1997–2010 are availablonline The MAA gives the Lester R. Ford Awards annually to "authors of articles of expository excellence" published in the ''American Mathematical Monthly''. Editors *2022– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |