|
Cipher Text
In cryptography, ciphertext or cyphertext is the result of encryption performed on plaintext using an algorithm, called a cipher. Ciphertext is also known as encrypted or encoded information because it contains a form of the original plaintext that is unreadable by a human or computer without the proper cipher to decrypt it. This process prevents the loss of sensitive information via hacking. Decryption, the inverse of encryption, is the process of turning ciphertext into readable plaintext. Ciphertext is not to be confused with codetext because the latter is a result of a code, not a cipher. Conceptual underpinnings Let m\! be the plaintext message that Alice wants to secretly transmit to Bob and let E_k\! be the encryption cipher, where _k\! is a cryptographic key. Alice must first transform the plaintext into ciphertext, c\!, in order to securely send the message to Bob, as follows: : c = E_k(m). \! In a symmetric-key system, Bob knows Alice's encryption key. Once the mes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Vigenère Cipher
The Vigenère cipher () is a method of encryption, encrypting alphabetic text where each letter of the plaintext is encoded with a different Caesar cipher, whose increment is determined by the corresponding letter of another text, the key (cryptography), key. For example, if the plaintext is attacking tonight and the key is oculorhinolaryngology, then *the first letter of the plaintext, a, is shifted by 14 positions in the alphabet (because the first letter of the key, o, is the 14th letter of the alphabet, counting from zero), yielding o; *the second letter, t, is shifted by 2 (because the second letter of the key, c, is the 2nd letter of the alphabet, counting from zero) yielding v; *the third letter, t, is shifted by 20 (u), yielding n, with wrap-around; and so on. It is important to note that traditionally spaces and punctuation are removed prior to encryption and reintroduced afterwards. * In this example the tenth letter of the plaintext t is shifted by 14 position ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Advanced Encryption Standard
The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), also known by its original name Rijndael (), is a specification for the encryption of electronic data established by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in 2001. AES is a variant of the Rijndael block cipher developed by two Belgium, Belgian cryptographers, Joan Daemen and Vincent Rijmen, who submitted a proposal to NIST during the Advanced Encryption Standard process, AES selection process. Rijndael is a family of ciphers with different key size, key and Block size (cryptography), block sizes. For AES, NIST selected three members of the Rijndael family, each with a block size of 128 bits, but three different key lengths: 128, 192 and 256 bits. AES has been adopted by the Federal government of the United States, U.S. government. It supersedes the Data Encryption Standard (DES), which was published in 1977. The algorithm described by AES is a symmetric-key algorithm, meaning the same key is used for both encrypting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
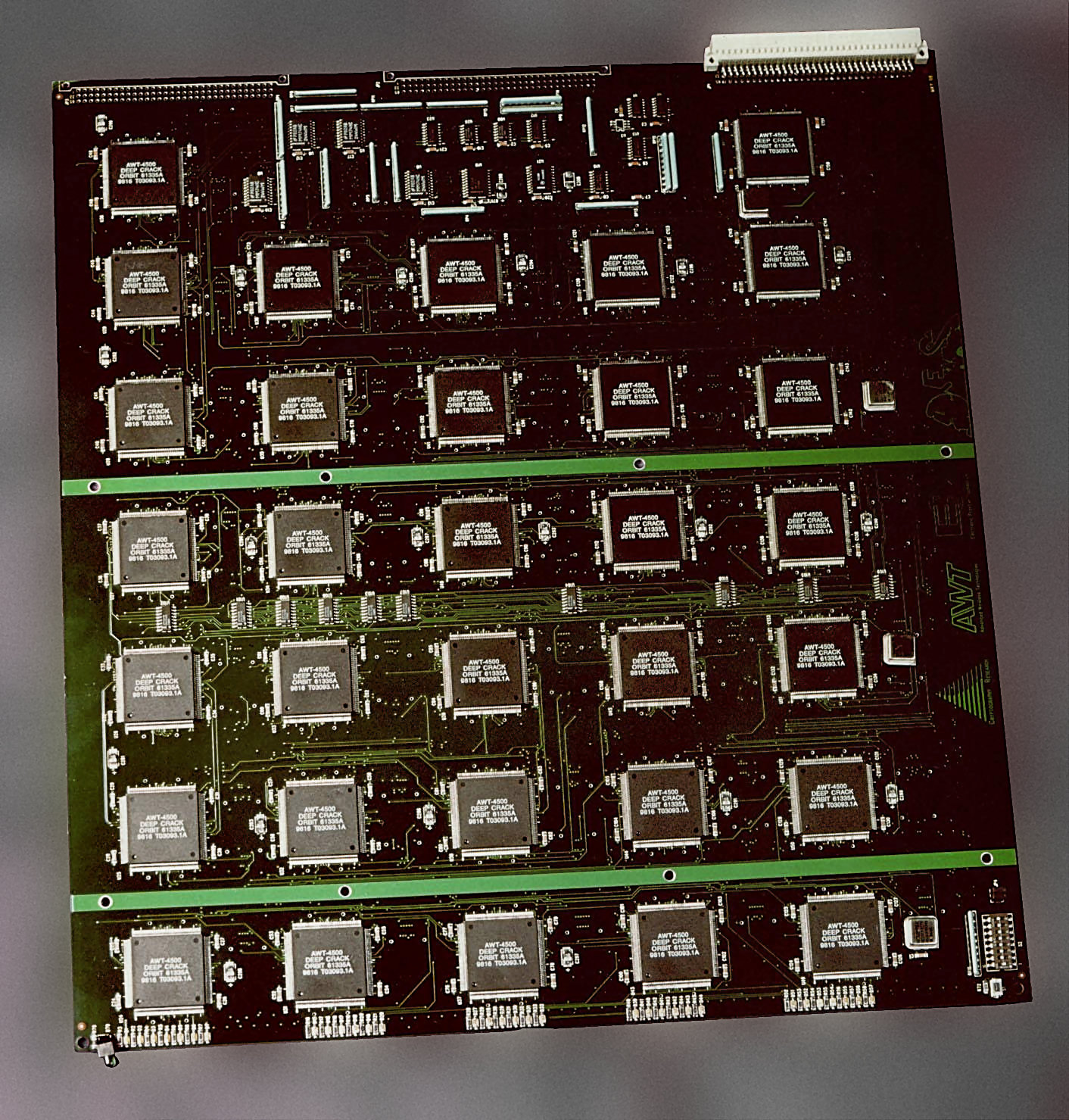
Data Encryption Standard
The Data Encryption Standard (DES ) is a symmetric-key algorithm for the encryption of digital data. Although its short key length of 56 bits makes it too insecure for modern applications, it has been highly influential in the advancement of cryptography. Developed in the early 1970s at IBM and based on an earlier design by Horst Feistel, the algorithm was submitted to the National Bureau of Standards (NBS) following the agency's invitation to propose a candidate for the protection of sensitive, unclassified electronic government data. In 1976, after consultation with the National Security Agency (NSA), the NBS selected a slightly modified version (strengthened against differential cryptanalysis, but weakened against brute-force attacks), which was published as an official Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) for the United States in 1977. The publication of an NSA-approved encryption standard led to its quick international adoption and widespread academic scrutiny. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Asymmetric Key Algorithm
Public-key cryptography, or asymmetric cryptography, is the field of cryptographic systems that use pairs of related keys. Each key pair consists of a public key and a corresponding private key. Key pairs are generated with cryptographic algorithms based on mathematical problems termed one-way functions. Security of public-key cryptography depends on keeping the private key secret; the public key can be openly distributed without compromising security. There are many kinds of public-key cryptosystems, with different security goals, including digital signature, Diffie–Hellman key exchange, public-key key encapsulation, and public-key encryption. Public key algorithms are fundamental security primitives in modern cryptosystems, including applications and protocols that offer assurance of the confidentiality and authenticity of electronic communications and data storage. They underpin numerous Internet standards, such as Transport Layer Security (TLS), SSH, S/MIME, and PG ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Symmetric Key Algorithm
Symmetric-key algorithms are algorithms for cryptography that use the same cryptographic keys for both the encryption of plaintext and the decryption of ciphertext. The keys may be identical, or there may be a simple transformation to go between the two keys. The keys, in practice, represent a shared secret between two or more parties that can be used to maintain a private information link. The requirement that both parties have access to the secret key is one of the main drawbacks of symmetric-key encryption, in comparison to public-key encryption (also known as asymmetric-key encryption). However, symmetric-key encryption algorithms are usually better for bulk encryption. With exception of the one-time pad they have a smaller key size, which means less storage space and faster transmission. Due to this, asymmetric-key encryption is often used to exchange the secret key for symmetric-key encryption. Types Symmetric-key encryption can use either stream ciphers or block ciphers. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Brute Force Attack
In cryptography, a brute-force attack or exhaustive key search is a cryptanalytic attack that consists of an attacker submitting many possible Key (cryptography), keys or passwords with the hope of eventually guessing correctly. This strategy can theoretically be used to break any form of encryption that is not information-theoretically secure. However, in a properly designed cryptosystem the chance of successfully guessing the key is negligible. When Password cracking, cracking passwords, this method is very fast when used to check all short passwords, but for longer passwords other methods such as the dictionary attack are used because a brute-force search takes too long. Longer passwords, passphrases and keys have more possible values, making them exponentially more difficult to crack than shorter ones due to diversity of characters. Brute-force attacks can be made less effective by Obfuscation (software), obfuscating the data to be encoded making it more difficult for an att ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rail Fence
The rail fence cipher (also called a zigzag cipher) is a classical type of transposition cipher. It derives its name from the manner in which encryption is performed, in analogy to a fence built with horizontal rails. Encryption In the rail fence cipher, the plaintext is written downwards diagonally on successive "rails" of an imaginary fence, then moving up when the bottom rail is reached, down again when the top rail is reached, and so on until the whole plaintext is written out. The ciphertext is then read off in rows. For example, to encrypt the message 'WE ARE DISCOVERED. RUN AT ONCE.' with 3 "rails", write the text as: W . . . E . . . C . . . R . . . U . . . O . . . . E . R . D . S . O . E . E . R . N . T . N . E . . A . . . I . . . V . . . D . . . A . . . C . (Spaces and punctuation are omitted.) Then read off the text horizontally to get the ciphertext: WECRUO ERDSOEERNTNE AIVDAC Decryption Let N be the number of rails used during encryption. Observe that as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Permutation
In mathematics, a permutation of a set can mean one of two different things: * an arrangement of its members in a sequence or linear order, or * the act or process of changing the linear order of an ordered set. An example of the first meaning is the six permutations (orderings) of the set : written as tuples, they are (1, 2, 3), (1, 3, 2), (2, 1, 3), (2, 3, 1), (3, 1, 2), and (3, 2, 1). Anagrams of a word whose letters are all different are also permutations: the letters are already ordered in the original word, and the anagram reorders them. The study of permutations of finite sets is an important topic in combinatorics and group theory. Permutations are used in almost every branch of mathematics and in many other fields of science. In computer science, they are used for analyzing sorting algorithms; in quantum physics, for describing states of particles; and in biology, for describing RNA sequences. The number of permutations of distinct objects is factorial, us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Transposition Cipher
In cryptography, a transposition cipher (also known as a permutation cipher) is a method of encryption which scrambles the positions of characters (''transposition'') without changing the characters themselves. Transposition ciphers reorder units of plaintext (typically characters or groups of characters) according to a regular system to produce a ciphertext which is a permutation of the plaintext. They differ from Substitution cipher, substitution ciphers, which do not change the position of units of plaintext but instead change the units themselves. Despite the difference between transposition and substitution operations, they are often combined, as in historical ciphers like the ADFGVX cipher or complex high-quality encryption methods like the modern Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). General principle Plaintexts can be rearranged into a ciphertext using a Key (cryptography), key, scrambling the order of characters like the shuffled pieces of a jigsaw puzzle. The resulting m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |