|
Ciliates
The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to flagellum, eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a different wikt:undulating, undulating pattern than flagella. Cilia occur in all members of the group (although the peculiar Suctoria only have them for part of their biological life cycle, life cycle) and are variously used in swimming, crawling, attachment, feeding, and sensation. Ciliates are an important group of protists, common almost anywhere there is water—in lakes, ponds, oceans, rivers, and soils. About 4,500 unique free-living species have been described, and the potential number of extant species is estimated at 27,000–40,000. Included in this number are many Ectosymbiosis, ectosymbiotic and endosymbiotic species, as well as some Obligate parasite, obligate and Facultative parasite, opportunistic parasites. Ciliate species r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alveolate
The alveolates (meaning "pitted like a honeycomb") are a group of protists, considered a major clade and Biological classification, superphylum within Eukarya. They are currently grouped with the stramenopiles and Rhizaria among the protists with tubulocristate mitochondria, the group being referred to as SAR supergroup, SAR. Characteristics The most notable shared characteristic is the presence of cortical (near the surface) alveoli (sacs). These are flattened vesicle (biology), vesicles (sacs) arranged as a layer just under the cell membrane, membrane and supporting it, typically contributing to a flexible pellicle (thin skin). In armored dinoflagellates they may contain stiff plates. Alveolates have mitochondrion, mitochondria with tubular cristae (invaginations), and cells often have pore-like intrusions through the cell surface. The group contains free-living and parasitic organisms, predatory flagellates, and photosynthetic organisms. Almost all sequenced mitochondrial g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protist
A protist () is any eukaryotic organism (that is, an organism whose cells contain a cell nucleus) that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. While it is likely that protists share a common ancestor (the last eukaryotic common ancestor), the exclusion of other eukaryotes means that protists do not form a natural group, or clade. Therefore, some protists may be more closely related to animals, plants, or fungi than they are to other protists. However, like the groups ''algae'', ''invertebrates'', and '' protozoans'', the biological category ''protist'' is used for convenience. Others classify any unicellular eukaryotic microorganism as a protist. The study of protists is termed protistology. History The classification of a third kingdom separate from animals and plants was first proposed by John Hogg in 1860 as the kingdom Protoctista; in 1866 Ernst Haeckel also proposed a third kingdom Protista as "the kingdom of primitive forms". Originally these also included prokaryotes, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
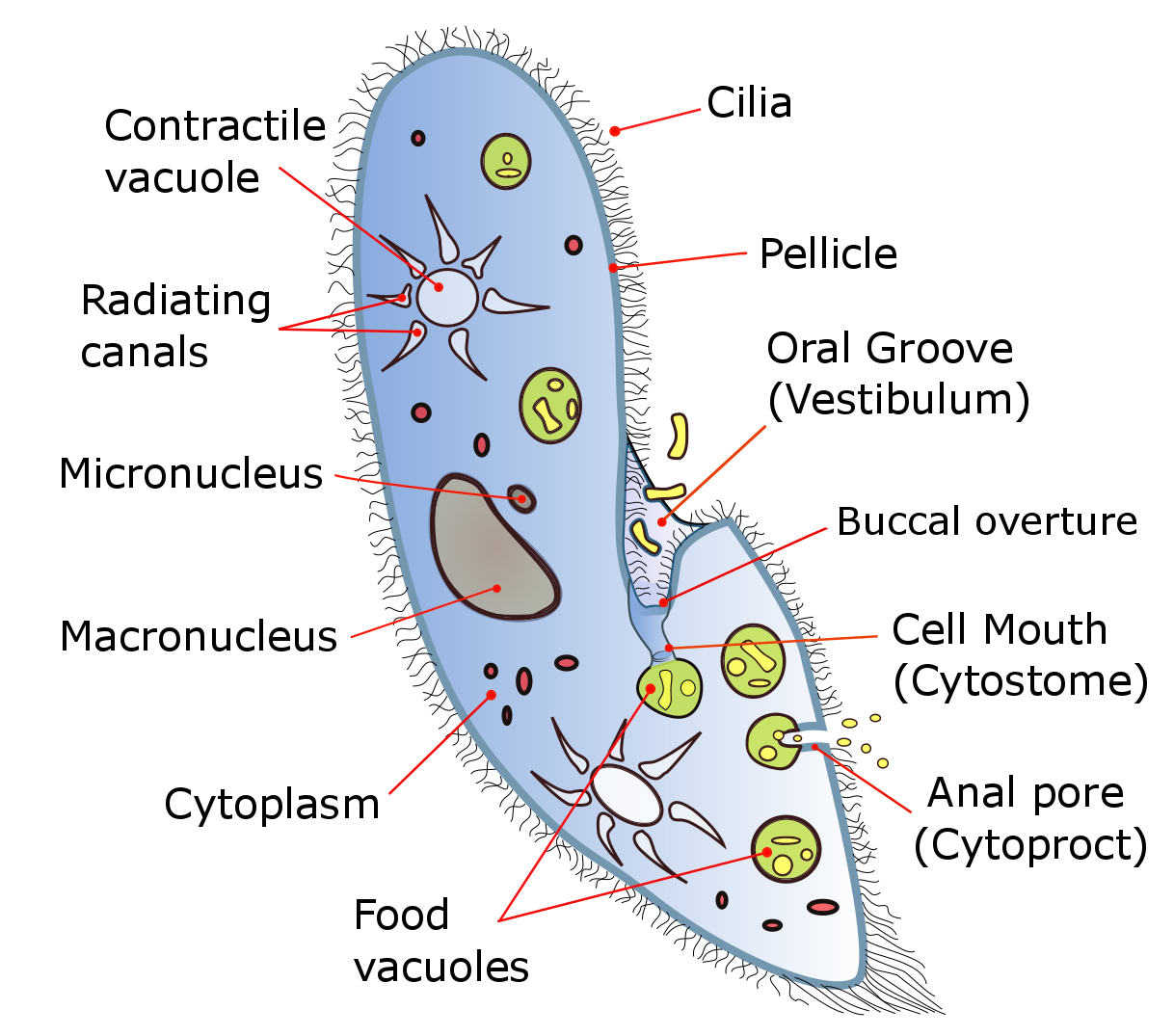
Paramecium
'' ''Paramecium'' ( , ; also spelled ''Paramoecium'') is a genus of eukaryotic, unicellular ciliates, commonly studied as a representative of the ciliate group. ''Paramecia'' are widespread in freshwater, brackish, and marine environments and are often very abundant in stagnant basins and ponds. Because some species are readily cultivated and easily induced to conjugate and divide, it has been widely used in classrooms and laboratories to study biological processes. Its usefulness as a model organism has caused one ciliate researcher to characterize it as the " white rat" of the phylum Ciliophora. Historical background ''Paramecia'' were among the first ciliates to be seen by microscopists, in the late 17th century. They were probably known to the Dutch pioneer of protozoology, Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, and were clearly described by his contemporary Christiaan Huygens in a letter of 1678. The earliest known illustration of a Paramecium was published anonymously in Philosophi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armophorea
Armophorea is a class of ciliates in the subphylum Intramacronucleata. . It was first resolved in 2004 and comprises three orders: Metopida, Clevelandellida, and Armophorida. Previously members of this class were thought to be heterotrichs because of similarities in morphology, most notably a characteristic dense arrangement of cilia surrounding their oral structures. However, the development of genetic tools and subsequent incorporation of DNA sequence information has led to major revisions in the evolutionary relationships of many protists, including ciliates. Metopids, clevelandellids, and armophorids were grouped into this class based on similarities in their small subunit rRNA sequences, making them one of two so-called "riboclasses" of ciliates, however, recent analyses suggest that Armophorida may not be related to the other two orders. Etymology The name Armophorea is thought to be derived from the Latin word ''arma,'' meaning weapons, or ''armus'', meaning shoulder. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterotrich
The heterotrichs are a class of ciliates. They typically have a prominent adoral zone of membranelles circling the mouth, used in locomotion and feeding, and shorter cilia on the rest of the body. Many species are highly contractile, and are typically compressed or conical in form. These include some of the largest protozoa, such as ''Stentor'' and ''Spirostomum'', as well as many brightly pigmented forms, such as certain ''Blepharisma''. Etymology The term ''heterotrich'' derives from the ancient Greek (), meaning "another, different", and , (), meaning 'hair', because of the contrast between the regular somatic ciliation and the one of the oral zone. Ultrastructure A number of ultrastructural details characterize the group. The cilia on the body are in dikinetids, in which either the anterior one or both kinetosomes may be ciliated, and which are associated with fibers composed of overlapping postciliary microtubules, called ''postciliodesmata'' and found only in this g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dileptus
''Dileptus'' is a genus of unicellular ciliates in the class Litostomatea. Species of ''Dileptus'' occur in fresh and salt water, as well as mosses and soils. Most are aggressive predators equipped with long, mobile proboscides lined with toxic extrusomes, with which they stun smaller organisms before consuming them. 13 species and subspecies of ''Dileptus'' are currently recognized.Vďačný, Peter, and Wilhelm Foissner. Monograph of the dileptids (Protista, Ciliophora, Rhynchostomatia). Land Oberösterreich, Biologiezentrum/Oberösterreichische Landesmuseen, 2012 ''Dileptus'' species have served as model organisms, used in the study of ciliary patterns, ontogenesis, conjugation and food acquisition. Appearance and characteristics ''Dileptus'' bodies are typically narrow or cylindrical, and have a macronucleus made up of more than a hundred scattered nodules. During cell division, these nodules divide individually. At the front end of the cell is a mobile proboscis. The cyto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stentor (ciliate)
''Stentor'', sometimes called trumpet animalcules, are a genus of filter-feeding, heterotrophic ciliates, representative of the heterotrichs. They are usually horn-shaped, and reach lengths of two millimeters; as such, they are among the largest known extant unicellular organisms. They reproduce asexually through Fission (biology), binary fission. Description The body, or Cortex (anatomy), cortex, is generally horn-shaped, hence the association with the Stentor, Greek herald, and the former name "trumpet animalcule". A ring of prominent cilia around the anterior "bell" sweep in food and aid in swimming. Some reach several millimeters in length, making them among the largest single-celled organisms. ''Stentor'' can come in different colors: for example, ''S. coeruleus'' can appear blue due to the presence of stentorin, a natural pigment. As in many freshwater protozoans, ''Stentor'' has a contractile vacuole. Because the concentration of salt inside the cell and in the surroundi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coleps
''Coleps'' is a genus of ciliates in the class Prostomatea with barrel-shaped bodies surrounded by regularly arranged plates composed of calcium carbonate. Description Species of ''Coleps'' can grow up to 250 µm in length, but are usually under 100 µm in their longest axis. ''Coleps'' can be taxonomically distinguished by the ornamentation of the ectoplasmic plates which make up their test. These plates are located outside alveolar vesicles of the cell cortex, and contain both organic and inorganic components, the latter of which is mostly amorphous calcium carbonate. Predatory behavior ''Coleps'' feeds on bacteria, algae, flagellate A flagellate is a cell or organism with one or more whip-like appendages called flagella. The word ''flagellate'' also describes a particular construction (or level of organization) characteristic of many prokaryotes and eukaryotes and their ...s, living and dead ciliates, animal and plant tissues. ''Coleps'' uses toxicysts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suctoria
Suctoria are ciliates that become sessile in their developed stage and then lose their redundant cilia. They feed by extracellular digestion. They were originally thought to feed by suction – hence their name. In fact, they use specialized microtubules to ensnare and manipulate their prey. They live in both freshwater and marine environments, including some that live on the surface of aquatic animals, and typically feed on other ciliates. Instead of a single cytostome, each cell feeds by means of several specialized tentacles. These are supported by microtubules and phyllae, and have toxic extrusomes called haptocysts at the tip, which they attach to prey. They then suck the prey's cytoplasm directly into a food vacuole inside the cell, where they digest and absorb its contents. Most suctoria are around 15-30 μm in size, with a non-contractile stalk and often a lorica or shell. Suctoria reproduce primarily by budding, producing swarmers that lack both tentacles and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protocruziea
Protocruziea is a class of ciliates in the subphylum Intramacronucleata Intramacronucleata is a subphylum of ciliates. The group is characterized by the manner in which division of the macronucleus is accomplished during binary fission of the cell. In ciliates of this subphylum, division of the macronucleus is achiev .... References * Intramacronucleata Monotypic SAR supergroup taxa Ciliate classes {{Ciliate-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagellum
A flagellum (; ) is a hairlike appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many protists with flagella are termed as flagellates. A microorganism may have from one to many flagella. A gram-negative bacterium ''Helicobacter pylori'' for example uses its multiple flagella to propel itself through the mucus lining to reach the stomach epithelium, where it may cause a gastric ulcer to develop. In some bacteria the flagellum can also function as a sensory organelle, being sensitive to wetness outside the cell. Across the three domains of Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukaryota the flagellum has a different structure, protein composition, and mechanism of propulsion but shares the same function of providing motility. The Latin word means " whip" to describe its lash-like swimming motion. The flagellum in archaea is called the archaellum to note its difference from the bacterial flagellum. Eukaryotic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






_-_160x_(13895748593).jpg)