|
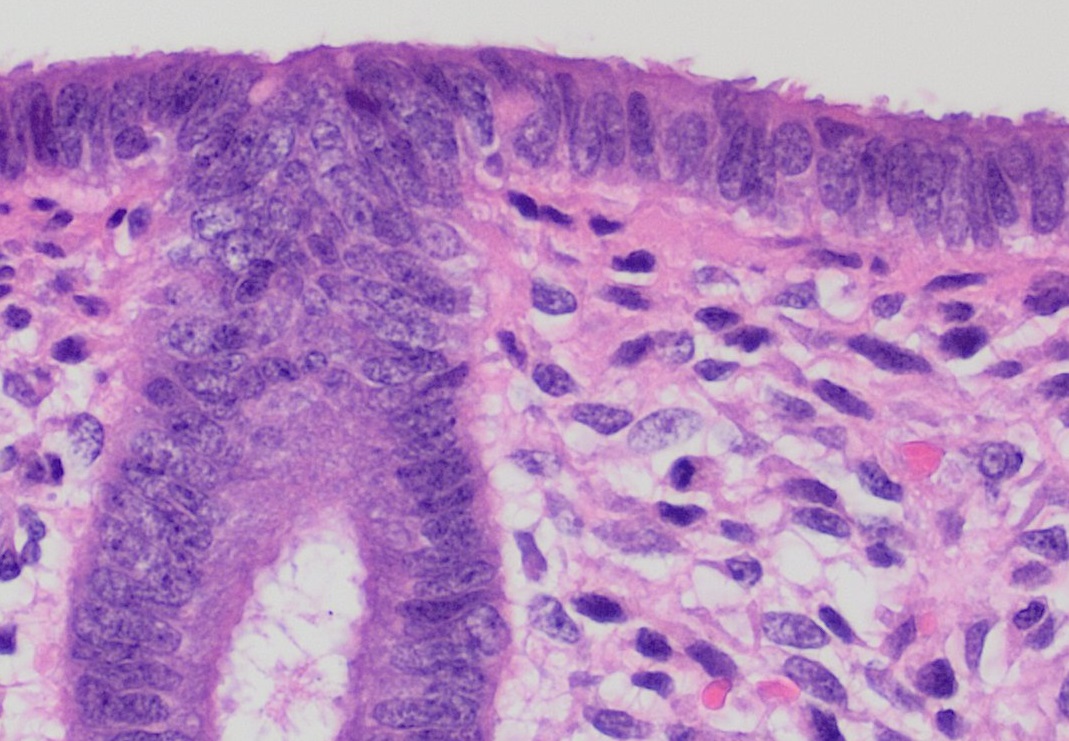
Chorion Frondosum
The chorion is the outermost fetal membrane around the embryo in mammals, birds and reptiles ( amniotes). It develops from an outer fold on the surface of the yolk sac, which lies outside the zona pellucida (in mammals), known as the vitelline membrane in other animals. In insects it is developed by the follicle cells while the egg is in the ovary.Chapman, R.F. (1998) "The insects: structure and function", Section ''The egg and embryology''. Previewed in Google Bookon 26 Sep 2009. Structure In humans and other mammals (excluding monotremes), the chorion is one of the fetal membranes that exist during pregnancy between the developing fetus and mother. The chorion and the amnion together form the amniotic sac. In humans it is formed by extraembryonic mesoderm and the two layers of trophoblast that surround the embryo and other membranes; the chorionic villi emerge from the chorion, invade the endometrium, and allow the transfer of nutrients from maternal blood to fetal bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fetal Membrane
The fetal membranes are the four extraembryonic membranes, associated with the developing embryo, and fetus in humans and other mammals.. They are the amnion, chorion, allantois, and yolk sac. The amnion and the chorion are the chorioamniotic membranes that make up the amniotic sac which surrounds and protects the embryo. The fetal membranes are four of six accessory organs developed by the conceptus that are not part of the embryo itself, the other two are the placenta, and the umbilical cord. Structure The fetal membranes surround the developing embryo and form the fetal-maternal interface. The fetal membranes are derived from the trophoblast layer (outer layer of cells) of the implanting blastocyst. The trophoblast layer differentiates into amnion and the chorion, which then comprise the fetal membranes. The amnion is the innermost layer and, therefore, contacts the amniotic fluid, the fetus and the umbilical cord. The internal pressure of the amniotic fluid causes th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amniotic Sac
The amniotic sac, also called the bag of waters or the membranes, is the sac in which the embryo and later fetus develops in amniotes. It is a thin but tough transparent pair of membranes that hold a developing embryo (and later fetus) until shortly before birth. The inner of these membranes, the amnion, encloses the amniotic cavity, containing the amniotic fluid and the embryo. The outer membrane, the chorion, contains the amnion and is part of the placenta. On the outer side, the amniotic sac is connected to the yolk sac, the allantois, and via the umbilical cord, the placenta. The yolk sac, amnion, chorion, and allantois are the four extraembryonic membranes that lie outside of the embryo and are involved in providing nutrients and protection to the developing embryo. They form from the inner cell mass; the first to form is the yolk sac followed by the amnion which grows over the developing embryo. The amnion remains an important extraembryonic membrane throughout prenatal dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chorionic Arteries
Chorionic (plate) vessels, also fetal surface vessels are blood vessels, including both arteries and veins, that carry blood through the chorion in the fetoplacental circulation. Chorionic arteries branch off the umbilical artery, and supply the capillaries of the chorionic villi. Increased vasocontractility of chorionic arteries may contribute to preeclampsia Pre-eclampsia is a disorder of pregnancy characterized by the onset of high blood pressure and often a significant amount of protein in the urine. When it arises, the condition begins after 20 weeks of pregnancy. In severe cases of the disease .... References Embryology of cardiovascular system {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umbilical Arteries
The umbilical artery is a paired artery (with one for each half of the body) that is found in the abdominal and pelvic regions. In the fetus, it extends into the umbilical cord. Structure Development The umbilical arteries supply deoxygenated blood from the fetus to the placenta. Although this blood is typically referred to as deoxygenated, this blood is fetal systemic arterial blood and will have the same amount of oxygen and nutrients as blood distributed to the other fetal tissues. There are usually two umbilical arteries present together with one umbilical vein in the umbilical cord. The umbilical arteries surround the urinary bladder and then carry all the deoxygenated blood out of the fetus through the umbilical cord. Inside the placenta, the umbilical arteries connect with each other at a distance of approximately 5 mm from the cord insertion in what is called the ''Hyrtl anastomosis''. Subsequently, they branch into chorionic arteries or ''intraplacental fetal arteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vascularized
Angiogenesis is the physiological process through which new blood vessels form from pre-existing vessels, formed in the earlier stage of vasculogenesis. Angiogenesis continues the growth of the vasculature by processes of sprouting and splitting. Vasculogenesis is the embryonic formation of endothelial cells from mesoderm cell precursors, and from neovascularization, although discussions are not always precise (especially in older texts). The first vessels in the developing embryo form through vasculogenesis, after which angiogenesis is responsible for most, if not all, blood vessel growth during development and in disease. Angiogenesis is a normal and vital process in growth and development, as well as in wound healing and in the formation of granulation tissue. However, it is also a fundamental step in the transition of tumors from a benign state to a malignant one, leading to the use of angiogenesis inhibitors in the treatment of cancer. The essential role of angiogenesis in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uterine Decidua
The decidua is the modified mucosal lining of the uterus (that is, modified endometrium) that forms every month, in preparation for pregnancy. It is shed off each month when there is no fertilised egg to support. The decidua is under the influence of progesterone. Endometrial cells become highly characteristic. The decidua forms the maternal part of the placenta and remains for the duration of the pregnancy. After birth the decidua is shed together with the placenta. Structure The part of the decidua that interacts with the trophoblast is the ''decidua basalis'' (also called ''decidua placentalis''), while the ''decidua capsularis'' grows over the embryo on the luminal side, enclosing it into the endometrium. The remainder of the decidua is termed the ''decidua parietalis'' or ''decidua vera'', and it will fuse with the decidua capsularis by the fourth month of gestation. Three morphologically distinct layers of the decidua basalis can then be described: * Compact outer layer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Process (anatomy)
In anatomy, a process ( la, processus) is a projection or outgrowth of tissue from a larger body. For instance, in a vertebra, a process may serve for muscle attachment and leverage (as in the case of the transverse and spinous processes), or to fit (forming a synovial joint), with another vertebra (as in the case of the articular processes).Moore, Keith L. et al. (2010) ''Clinically Oriented Anatomy'', 6th Ed, p.442 fig. 4.2 The word is used even at the microanatomic level, where cells can have processes such as cilia or pedicels. Depending on the tissue, processes may also be called by other terms, such as ''apophysis'', ''tubercle'', or ''protuberance''. Examples Examples of processes include: *The many processes of the human skull: ** The mastoid and styloid processes of the temporal bone ** The zygomatic process of the temporal bone ** The zygomatic process of the frontal bone ** The orbital, temporal, lateral, frontal, and maxillary processes of the zygomatic bone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syncytiotrophoblast
Syncytiotrophoblast (from the Greek 'syn'- "together"; 'cytio'- "of cells"; 'tropho'- "nutrition"; 'blast'- "bud") is the epithelial covering of the highly vascular embryonic placental villi, which invades the wall of the uterus to establish nutrient circulation between the embryo and the mother. It is a multi-nucleate, terminally differentiated syncytium, extending to 13cm. Function It is the outer layer of the trophoblasts and actively invades the uterine wall, during implantation, rupturing maternal capillaries and thus establishing an interface between maternal blood and embryonic extracellular fluid, facilitating passive exchange of material between the mother and the embryo. The syncytial property is important since the mother's immune system includes white blood cells that are able to migrate into tissues by "squeezing" in between cells. If they were to reach the fetal side of the placenta many foreign proteins would be recognised, triggering an immune reaction. Howeve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multinucleate
Multinucleate cells (also known as multinucleated or polynuclear cells) are eukaryotic cells that have more than one nucleus per cell, i.e., multiple nuclei share one common cytoplasm. Mitosis in multinucleate cells can occur either in a coordinated, synchronous manner where all nuclei divide simultaneously or asynchronously where individual nuclei divide independently in time and space. Certain organisms may have a multinuclear stage of their life cycle. For example, slime molds have a vegetative, multinucleate life stage called a plasmodium. Although not normally viewed as a case of multinucleation, plant cells share a common cytoplasm by plasmodesmata, and most cells in animal tissues are in communication with their neighbors via gap junctions. Multinucleate cells, depending on the mechanism by which they are formed, can be divided into "syncytia" (formed by cell fusion) or "coenocytes" (formed by nuclear division not being followed by cytokinesis). A number of dinoflagellat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytotrophoblast
"Cytotrophoblast" is the name given to both the inner layer of the trophoblast (also called layer of Langhans) or the cells that live there. It is interior to the syncytiotrophoblast and external to the wall of the blastocyst in a developing embryo. The cytotrophoblast is considered to be the trophoblastic stem cell because the layer surrounding the blastocyst remains while daughter cells differentiate and proliferate to function in multiple roles. There are two lineages that cytotrophoblastic cells may differentiate through: fusion and invasive. The fusion lineage yields syncytiotrophoblast and the invasive lineage yields interstitial cytotrophoblast cells. Cytotrophoblastic cells play an important role in the implantation of an embryo in the uterus. Fusion lineage The formation of all syncytiotrophoblast is from the fusion of two or more cytotrophoblasts via this fusion pathway. This pathway is important because the syncytiotrophoblast plays an important role in fetal-maternal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endometrium
The endometrium is the inner epithelial layer, along with its mucous membrane, of the mammalian uterus. It has a basal layer and a functional layer: the basal layer contains stem cells which regenerate the functional layer. The functional layer thickens and then is shed during menstruation in humans and some other mammals, including apes, Old World monkeys, some species of bat, the elephant shrew and the Cairo spiny mouse. In most other mammals, the endometrium is reabsorbed in the estrous cycle. During pregnancy, the glands and blood vessels in the endometrium further increase in size and number. Vascular spaces fuse and become interconnected, forming the placenta, which supplies oxygen and nutrition to the embryo and fetus.Blue Histology - Female Reproductive System . School ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |