|
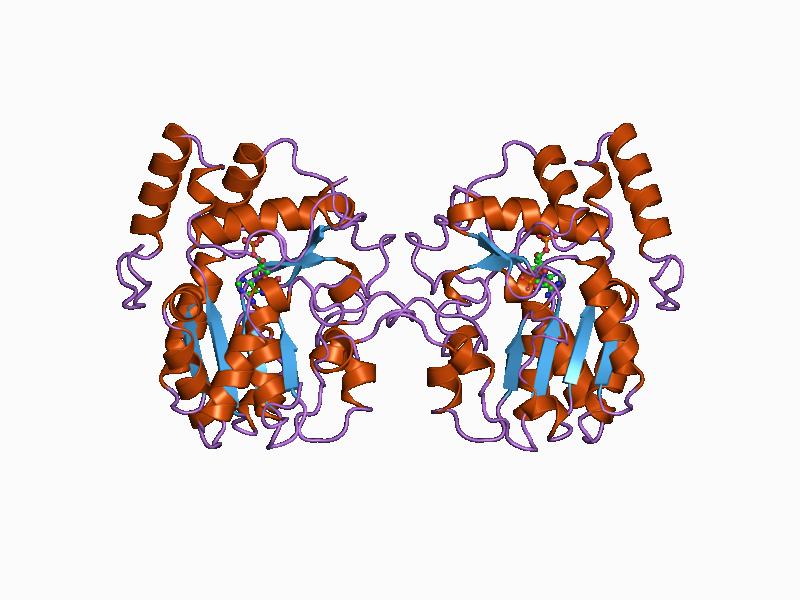
Choline O-acetyltransferase
Choline acetyltransferase (commonly abbreviated as ChAT, but sometimes CAT) is a transferase enzyme responsible for the synthesis of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. ChAT catalyzes the transfer of an acetyl group from the coenzyme acetyl-CoA to choline, yielding acetylcholine (ACh). ChAT is found in high concentration in cholinergic neurons, both in the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS). As with most nerve terminal proteins, ChAT is produced in the body of the neuron and is transported to the nerve terminal, where its concentration is highest. Presence of ChAT in a nerve cell classifies this cell as a "cholinergic" neuron. In humans, the choline acetyltransferase enzyme is encoded by the ''CHAT'' gene. History Choline acetyltransferase was first described by David Nachmansohn and A. L. Machado in 1943. A German biochemist, Nachmansohn had been studying the process of nerve impulse conduction and utilization of energy-yielding chemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transferase
A transferase is any one of a class of enzymes that catalyse the transfer of specific functional groups (e.g. a methyl or glycosyl group) from one molecule (called the donor) to another (called the acceptor). They are involved in hundreds of different biochemical pathways throughout biology, and are integral to some of life's most important processes. Transferases are involved in myriad reactions in the cell. Three examples of these reactions are the activity of coenzyme A (CoA) transferase, which transfers thiol esters, the action of N-acetyltransferase, which is part of the pathway that metabolizes tryptophan, and the regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH), which converts pyruvate to acetyl CoA. Transferases are also utilized during translation. In this case, an amino acid chain is the functional group transferred by a peptidyl transferase. The transfer involves the removal of the growing amino acid chain from the tRNA molecule in the A-site of the ribosome and its subse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto Meyerhof
Otto Fritz Meyerhof (; April 12, 1884 – October 6, 1951) was a German physician and biochemist who won the 1922 Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine. Biography Otto Fritz Meyerhof was born in Hannover, at Theaterplatz 16A (now:Rathenaustrasse 16A), the son of wealthy Jewish parents. In 1888, his family moved to Berlin, where Otto spent most of his childhood, and where he started his study of medicine. He continued these studies in Strasbourg and Heidelberg, from which he graduated in 1909, with a work titled "Contributions to the Psychological Theory of Mental Illness". In Heidelberg, he met Hedwig Schallenberg. They married in 1914 and became parents of a daughter, Bettina, and two sons, Gottfried (who referred, after emigration, to himself as Geoffrey) as well as Walter. In 1912, Otto Meyerhof moved to the University of Kiel, where he received a professorship in 1918. In 1922, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine, with Archibald Vivian Hill, for his work on muscle met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid Sequence
Protein primary structure is the linear sequence of amino acids in a peptide or protein. By convention, the primary structure of a protein is reported starting from the amino-terminal (N) end to the carboxyl-terminal (C) end. Protein biosynthesis is most commonly performed by ribosomes in cells. Peptides can also be synthesized in the laboratory. Protein primary structures can be directly sequenced, or inferred from DNA sequences. Formation Biological Amino acids are polymerised via peptide bonds to form a long backbone, with the different amino acid side chains protruding along it. In biological systems, proteins are produced during translation by a cell's ribosomes. Some organisms can also make short peptides by non-ribosomal peptide synthesis, which often use amino acids other than the standard 20, and may be cyclised, modified and cross-linked. Chemical Peptides can be synthesised chemically via a range of laboratory methods. Chemical methods typically synthe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-transcriptional Modification
Transcriptional modification or co-transcriptional modification is a set of biological processes common to most eukaryotic cells by which an RNA primary transcript is chemically altered following transcription from a gene to produce a mature, functional RNA molecule that can then leave the nucleus and perform any of a variety of different functions in the cell. There are many types of post-transcriptional modifications achieved through a diverse class of molecular mechanisms. One example is the conversion of precursor messenger RNA transcripts into mature messenger RNA that is subsequently capable of being translated into protein. This process includes three major steps that significantly modify the chemical structure of the RNA molecule: the addition of a 5' cap, the addition of a 3' polyadenylated tail, and RNA splicing. Such processing is vital for the correct translation of eukaryotic genomes because the initial precursor mRNA produced by transcription often contains both exo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exon Skipping
In molecular biology, exon skipping is a form of RNA splicing used to cause cells to “skip” over faulty or misaligned sections (exons) of genetic code, leading to a truncated but still functional protein despite the genetic mutation. Mechanism Exon skipping is used to restore the reading frame within a gene. Genes are the genetic instructions for creating a protein, and are composed of introns and exons. Exons are the sections of DNA that contain the instruction set for generating a protein; they are interspersed with non-coding regions called introns. The introns are later removed before the protein is made, leaving only the coding exon regions. Splicing naturally occurs in pre-mRNA when introns are being removed to form mature-mRNA that consists solely of exons. Starting in the late 1990s, scientists realized they could take advantage of this naturally occurring cellular splicing to downplay genetic mutations into less harmful ones. The mechanism behind exon skipping is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal Structure
In crystallography, crystal structure is a description of the ordered arrangement of atoms, ions or molecules in a crystal, crystalline material. Ordered structures occur from the intrinsic nature of the constituent particles to form symmetric patterns that repeat along the principal directions of Three-dimensional space (mathematics), three-dimensional space in matter. The smallest group of particles in the material that constitutes this repeating pattern is the unit cell of the structure. The unit cell completely reflects the symmetry and structure of the entire crystal, which is built up by repetitive Translation (geometry), translation of the unit cell along its principal axes. The translation vectors define the nodes of the Bravais lattice. The lengths of the principal axes, or edges, of the unit cell and the angles between them are the lattice constants, also called ''lattice parameters'' or ''cell parameters''. The symmetry properties of the crystal are described by the con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histidine
Histidine (symbol His or H) is an essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated –NH3+ form under biological conditions), a carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated –COO− form under biological conditions), and an imidazole side chain (which is partially protonated), classifying it as a positively charged amino acid at physiological pH. Initially thought essential only for infants, it has now been shown in longer-term studies to be essential for adults also. It is encoded by the codons CAU and CAC. Histidine was first isolated by Albrecht Kossel and Sven Gustaf Hedin in 1896. It is also a precursor to histamine, a vital inflammatory agent in immune responses. The acyl radical is histidyl. Properties of the imidazole side chain The conjugate acid (protonated form) of the imidazole side chain in histidine has a p''K''a of approximately 6.0. Thus, below a pH of 6, the imidazole ring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroxyl
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy groups. Both the negatively charged anion , called hydroxide, and the neutral radical , known as the hydroxyl radical, consist of an unbonded hydroxy group. According to IUPAC definitions, the term ''hydroxyl'' refers to the hydroxyl radical () only, while the functional group is called a ''hydroxy group''. Properties Water, alcohols, carboxylic acids, and many other hydroxy-containing compounds can be readily deprotonated due to a large difference between the electronegativity of oxygen (3.5) and that of hydrogen (2.1). Hydroxy-containing compounds engage in intermolecular hydrogen bonding increasing the electrostatic attraction between molecules and thus to higher boiling and melting points than found for compounds that lack this f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Bond
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (or H-bond) is a primarily electrostatic force of attraction between a hydrogen (H) atom which is covalently bound to a more electronegative "donor" atom or group (Dn), and another electronegative atom bearing a lone pair of electrons—the hydrogen bond acceptor (Ac). Such an interacting system is generally denoted , where the solid line denotes a polar covalent bond, and the dotted or dashed line indicates the hydrogen bond. The most frequent donor and acceptor atoms are the second-row elements nitrogen (N), oxygen (O), and fluorine (F). Hydrogen bonds can be intermolecular (occurring between separate molecules) or intramolecular (occurring among parts of the same molecule). The energy of a hydrogen bond depends on the geometry, the environment, and the nature of the specific donor and acceptor atoms and can vary between 1 and 40 kcal/mol. This makes them somewhat stronger than a van der Waals interaction, and weaker than fully covalent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coenzyme A
Coenzyme A (CoA, SHCoA, CoASH) is a coenzyme, notable for its role in the synthesis and oxidation of fatty acids, and the oxidation of pyruvate in the citric acid cycle. All genomes sequenced to date encode enzymes that use coenzyme A as a substrate, and around 4% of cellular enzymes use it (or a thioester) as a substrate. In humans, CoA biosynthesis requires cysteine, pantothenic acid, pantothenate (vitamin B5), and adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In acetyl-CoA, its acetyl form, coenzyme A is a highly versatile molecule, serving metabolic functions in both the Anabolism, anabolic and Catabolism, catabolic pathways. Acetyl-CoA is utilised in the post-translational regulation and allosteric regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase and carboxylase to maintain and support the partition of Pyruvic acid, pyruvate synthesis and degradation. Discovery of structure Coenzyme A was identified by Fritz Lipmann in 1946, who also later gave it its name. Its structure was determined during the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine Triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of life, ATP is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. When consumed in metabolic processes, it converts either to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or to adenosine monophosphate (AMP). Other processes regenerate ATP. The human body recycles its own body weight equivalent in ATP each day. It is also a precursor to DNA and RNA, and is used as a coenzyme. From the perspective of biochemistry, ATP is classified as a nucleoside triphosphate, which indicates that it consists of three components: a nitrogenous base (adenine), the sugar ribose, and the Polyphosphate, triphosphate. Structure ATP consists of an adenine attached by the 9-nitrogen atom to the 1′ carbon atom of a sugar (ribose), which i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine Triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of life, ATP is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. When consumed in metabolic processes, it converts either to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or to adenosine monophosphate (AMP). Other processes regenerate ATP. The human body recycles its own body weight equivalent in ATP each day. It is also a precursor to DNA and RNA, and is used as a coenzyme. From the perspective of biochemistry, ATP is classified as a nucleoside triphosphate, which indicates that it consists of three components: a nitrogenous base (adenine), the sugar ribose, and the Polyphosphate, triphosphate. Structure ATP consists of an adenine attached by the 9-nitrogen atom to the 1′ carbon atom of a sugar (ribose), which i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |