|
Cholesterol Absorption Inhibitor
Cholesterol absorption inhibitors are a class of compounds that prevent the uptake of cholesterol from the small intestine into the circulatory system. Most of these molecules are monobactams but show no antibiotic activity. An example is ezetimibe (SCH 58235) Another example is Sch-48461. The "Sch" is for Schering-Plough, where these compounds were developed. Phytosterols are also cholesterol absorption inhibitors. Physiology There are two sources of cholesterol in the upper intestine: dietary (from food) and biliary (from bile). Dietary cholesterol, in the form of lipid emulsions, combines with bile salts, to form bile salt micelles from which cholesterol can then be absorbed by the intestinal enterocyte. Once absorbed by the enterocyte, cholesterol is reassembled into intestinal lipoproteins called chylomicrons. These chylomicrons are then secreted into the lymphatics and circulated to the liver. These cholesterol particles are then secreted by the liver into the blood as VLD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholesterol
Cholesterol is any of a class of certain organic molecules called lipids. It is a sterol (or modified steroid), a type of lipid. Cholesterol is biosynthesized by all animal cells and is an essential structural component of animal cell membranes. When chemically isolated, it is a yellowish crystalline solid. Cholesterol also serves as a precursor for the biosynthesis of steroid hormones, bile acid and vitamin D. Cholesterol is the principal sterol synthesized by all animals. In vertebrates, hepatic cells typically produce the greatest amounts. It is absent among prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), although there are some exceptions, such as '' Mycoplasma'', which require cholesterol for growth. François Poulletier de la Salle first identified cholesterol in solid form in gallstones in 1769. However, it was not until 1815 that chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul named the compound "cholesterine". Etymology The word "cholesterol" comes from the Ancient Greek ''chole-'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterocyte
Enterocytes, or intestinal absorptive cells, are simple columnar epithelial cells which line the inner surface of the small and large intestines. A glycocalyx surface coat contains digestive enzymes. Microvilli on the apical surface increase its surface area. This facilitates transport of numerous small molecules into the enterocyte from the intestinal lumen. These include broken down proteins, fats, and sugars, as well as water, electrolytes, vitamins, and bile salts. Enterocytes also have an endocrine role, secreting hormones such as leptin. Function The major functions of enterocytes include: *Ion uptake, including sodium, calcium, magnesium, iron, zinc, and copper. This typically occurs through active transport. *Water uptake. This follows the osmotic gradient established by Na+/K+ ATPase on the basolateral surface. This can occur transcellularly or paracellularly. *Sugar uptake. Polysaccharides and disaccharidases in the glycocalyx break down large sugar molecules, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statins
Statins, also known as HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, are a class of lipid-lowering medications that reduce illness and mortality in those who are at high risk of cardiovascular disease. They are the most common cholesterol-lowering drugs. Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) carriers of cholesterol play a key role in the development of atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease via the mechanisms described by the lipid hypothesis. Statins are effective in lowering LDL cholesterol and so are widely used for primary prevention in people at high risk of cardiovascular disease, as well as in secondary prevention for those who have developed cardiovascular disease. Side effects of statins include muscle pain, increased risk of diabetes mellitus, and abnormal blood levels of liver enzymes. Additionally, they have rare but severe adverse effects, particularly muscle damage. They inhibit the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase which plays a central role in the production of cholesterol. High cholester ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antihyperlipidemics
Lipid-lowering agents, also sometimes referred to as hypolipidemic agents, cholesterol-lowering drugs, or antihyperlipidemic agents are a diverse group of pharmaceuticals that are used to lower the level of lipids and lipoproteins such as cholesterol, in the blood (hyperlipidemia). The American Heart Association recommends the descriptor 'lipid lowering agent' be used for this class of drugs rather than the term 'hypolipidemic'. Classes The several classes of lipid lowering drugs may differ in both their impact on the cholesterol profile and adverse effects. For example, some may lower low density lipoprotein (LDL) levels more so than others, while others may preferentially increase high density lipoprotein (HDL). Clinically, the choice of an agent depends on the patient's cholesterol profilecardiovascular risk and the liver and kidney functions of the patient, evaluated against the balancing of risks and benefits of the medications. In the United States, this is guided by the ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypercholesterolemia
Hypercholesterolemia, also called high cholesterol, is the presence of high levels of cholesterol in the blood. It is a form of hyperlipidemia (high levels of lipids in the blood), hyperlipoproteinemia (high levels of lipoproteins in the blood), and dyslipidemia (any abnormalities of lipid and lipoprotein levels in the blood). Elevated levels of non-HDL cholesterol and LDL in the blood may be a consequence of diet, obesity, inherited (genetic) diseases (such as LDL receptor mutations in familial hypercholesterolemia), or the presence of other diseases such as type 2 diabetes and an underactive thyroid. Cholesterol is one of three major classes of lipids produced and used by all animal cells to form membranes. Plant cells manufacture phytosterols (similar to cholesterol), but in rather small quantities. Cholesterol is the precursor of the steroid hormones and bile acids. Since cholesterol is insoluble in water, it is transported in the blood plasma within protein particles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VLDL
Very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), density relative to extracellular water, is a type of lipoprotein made by the liver. VLDL is one of the five major groups of lipoproteins (chylomicrons, VLDL, intermediate-density lipoprotein, low-density lipoprotein, high-density lipoprotein) that enable fats and cholesterol to move within the water-based solution of the bloodstream. VLDL is assembled in the liver from triglycerides, cholesterol, and apolipoproteins. VLDL is converted in the bloodstream to low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and intermediate-density lipoprotein (IDL). VLDL particles have a diameter of 30–80 nm. VLDL transports endogenous products, whereas chylomicrons transport exogenous (dietary) products. In the early 2010s both the lipid composition and protein composition of this lipoprotein were characterised in great detail. Function Very-low-density lipoproteins transport endogenous triglycerides, phospholipids, cholesterol, and cholesteryl esters. It functions a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphatics
The lymphatic vessels (or lymph vessels or lymphatics) are thin-walled vessels (tubes), structured like blood vessels, that carry lymph. As part of the lymphatic system, lymph vessels are complementary to the cardiovascular system. Lymph vessels are lined by endothelial cells, and have a thin layer of smooth muscle, and adventitia that binds the lymph vessels to the surrounding tissue. Lymph vessels are devoted to the propulsion of the lymph from the lymph capillaries, which are mainly concerned with the absorption of interstitial fluid from the tissues. Lymph capillaries are slightly bigger than their counterpart capillaries of the vascular system. Lymph vessels that carry lymph to a lymph node are called afferent lymph vessels, and those that carry it from a lymph node are called efferent lymph vessels, from where the lymph may travel to another lymph node, may be returned to a vein, or may travel to a larger lymph duct. Lymph ducts drain the lymph into one of the subclavian ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chylomicron
Chylomicrons (from the Greek χυλός, chylos, meaning ''juice'' (of plants or animals), and micron, meaning ''small particle''), also known as ultra low-density lipoproteins (ULDL), are lipoprotein particles that consist of triglycerides (85–92%), phospholipids (6–12%), cholesterol (1–3%), and proteins (1–2%). They transport dietary lipids from the intestines to other locations in the body. ULDLs are one of the five major groups of lipoproteins (sorted by density) that enable fats and cholesterol to move within the water-based solution of the bloodstream. A protein specific to chylomicrons is ApoB48. There is an inverse relationship in the density and size of lipoprotein particles: fats have a lower density than water or smaller protein molecules, and the larger particles have a higher ratio of internal fat molecules with respect to the outer emulsifying protein molecules in the shell. ULDLs, if in the region of 1,000 nm or more, are the only lipoprotein partic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chylomicrons
Chylomicrons (from the Greek χυλός, chylos, meaning ''juice'' (of plants or animals), and micron, meaning ''small particle''), also known as ultra low-density lipoproteins (ULDL), are lipoprotein particles that consist of triglycerides (85–92%), phospholipids (6–12%), cholesterol (1–3%), and proteins (1–2%). They transport dietary lipids from the intestines to other locations in the body. ULDLs are one of the five major groups of lipoproteins (sorted by density) that enable fats and cholesterol to move within the water-based solution of the bloodstream. A protein specific to chylomicrons is ApoB48. There is an inverse relationship in the density and size of lipoprotein particles: fats have a lower density than water or smaller protein molecules, and the larger particles have a higher ratio of internal fat molecules with respect to the outer emulsifying protein molecules in the shell. ULDLs, if in the region of 1,000 nm or more, are the only lipoprotein parti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
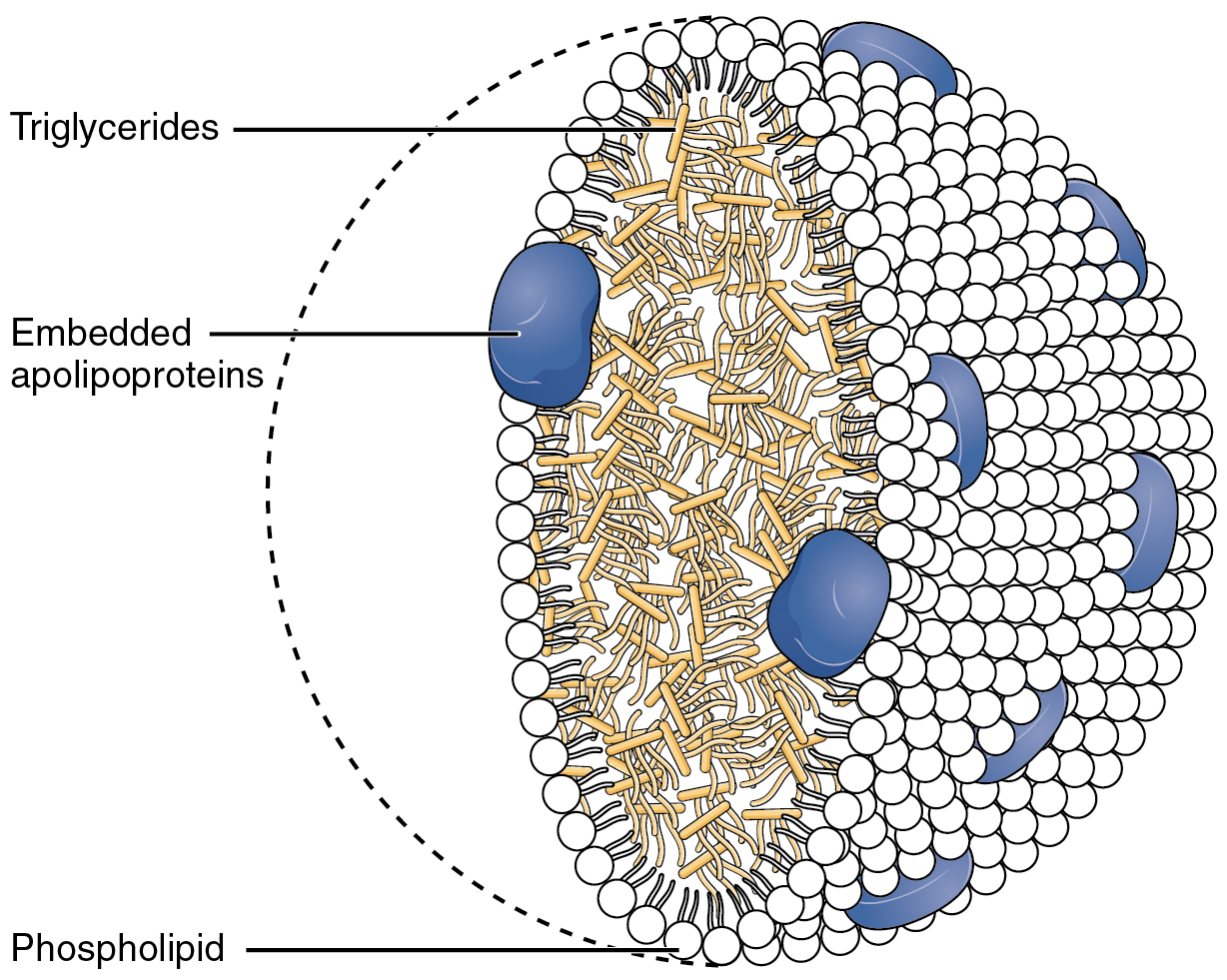
Lipoproteins
A lipoprotein is a biochemical assembly whose primary function is to transport hydrophobic lipid (also known as fat) molecules in water, as in blood plasma or other extracellular fluids. They consist of a triglyceride and cholesterol center, surrounded by a phospholipid outer shell, with the hydrophilic portions oriented outward toward the surrounding water and lipophilic portions oriented inward toward the lipid center. A special kind of protein, called apolipoprotein, is embedded in the outer shell, both stabilising the complex and giving it a functional identity that determines its role. Many enzymes, transporters, structural proteins, antigens, adhesins, and toxins are lipoproteins. Examples include plasma lipoprotein particles ( HDL, LDL, IDL, VLDL and chylomicrons). Subgroups of these plasma particles are primary drivers or modulators of atherosclerosis. Scope Transmembrane lipoproteins Some transmembrane proteolipids, especially those found in bacteria, are referred t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micelles
A micelle () or micella () (plural micelles or micellae, respectively) is an aggregate (or supramolecular assembly) of surfactant amphipathic lipid molecules dispersed in a liquid, forming a colloid, colloidal suspension (also known as associated colloidal system). A typical micelle in aqueous solution, water forms an aggregate with the hydrophilic "head" regions in contact with surrounding solvent, sequestering the hydrophobic single-tail regions in the micelle centre. This phase is caused by the Lipid bilayer phase behavior, packing behavior of single-tail lipids in a lipid bilayer, bilayer. The difficulty filling all the volume of the interior of a bilayer, while accommodating the area per head group forced on the molecule by the hydration of the lipid head group, leads to the formation of the micelle. This type of micelle is known as a normal-phase micelle (oil-in-water micelle). Inverse micelles have the head groups at the centre with the tails extending out (water-in-oil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monobactams
Monobactams are monocyclic and bacterially-produced β-lactam antibiotics. The β-lactam ring is not fused to another ring, in contrast to most other β-lactams. Monobactams are effective only against aerobic Gram-negative bacteria (e.g., ''Neisseria'', ''Pseudomonas''). Siderophore-conjugated monobactams show promise for the treatment of multi drug-resistant pathogens. Aztreonam is a commercially available monobactam antibiotic. Other examples of monobactams are tigemonam, nocardicin A, and tabtoxin. Adverse effects to monobactams can include skin rash and occasional abnormal liver functions. Monobactam antibiotics exhibit no IgE cross-reactivity reactions with penicillin but have shown some cross reactivity with cephalosporins, most notably ceftazidime Ceftazidime, sold under the brand name Fortaz among others, is a third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. Specifically it is used for joint infections, meni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |