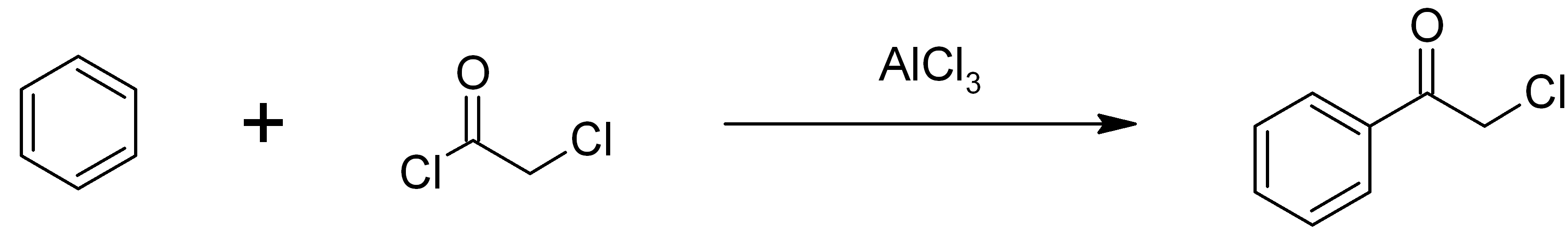|
Chloroacetophenone
Phenacyl chloride, also commonly known as chloroacetophenone, is a substituted acetophenone. It is a useful building block in organic chemistry. Apart from that, it has been historically used as a riot control agent, where it is designated CN. It should not be confused with cyanide, another agent used in chemical warfare, which has the chemical structure CN−. Preparation Phenacyl chloride is readily available and was first prepared by chlorination of acetophenone vapour. It may also be synthesized by the Friedel-Crafts acylation of benzene using chloroacetyl chloride, with an aluminium chloride catalyst: Riot control agent It was investigated, but not used, during the First and Second World Wars. Because of its significantly greater toxicity, it has largely been supplanted by CS gas. Even though CN is still supplied to paramilitary and police forces in a small pressurized aerosol known as “ Mace” or tear gas, its use is falling as pepper spray both works and disperses mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetophenone
Acetophenone is the organic compound with the formula C6H5C(O)CH3. It is the simplest aromatic ketone. This colorless, viscous liquid is a precursor to useful resins and fragrances. Production Acetophenone is formed as a byproduct of the cumene process, the industrial route for the synthesis of phenol and acetone. In the Hock rearrangement of isopropylbenzene hydroperoxide, migration of a methyl group rather than the phenyl group gives acetophenone and methanol as a result of an alternate rearrangement of the intermediate: :C6H5C(CH3)2O2H -> C6H5C(O)CH3 + CH3OH The cumene process is conducted on such a large scale that even the small amount of acetophenone by-product can be recovered in commercially useful quantities. Acetophenone is also generated from ethylbenzene hydroperoxide. Ethylbenzene hydroperoxide is primarily converted to 1-phenylethanol (α-methylbenzyl alcohol) in the process with a small amount of by-product acetophenone. Acetophenone is recovered or hydrogena ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synonymous
A synonym is a word, morpheme, or phrase that means exactly or nearly the same as another word, morpheme, or phrase in a given language. For example, in the English language, the words ''begin'', ''start'', ''commence'', and ''initiate'' are all synonyms of one another: they are ''synonymous''. The standard test for synonymy is substitution: one form can be replaced by another in a sentence without changing its meaning. Words are considered synonymous in only one particular sense: for example, ''long'' and ''extended'' in the context ''long time'' or ''extended time'' are synonymous, but ''long'' cannot be used in the phrase ''extended family''. Synonyms with exactly the same meaning share a seme or denotational sememe, whereas those with inexactly similar meanings share a broader denotational or connotational sememe and thus overlap within a semantic field. The former are sometimes called cognitive synonyms and the latter, near-synonyms, plesionyms or poecilonyms. Lexicograph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TRPA1
Transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily A, member 1, also known as transient receptor potential ankyrin 1, TRPA1, or The Wasabi Receptor, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TRPA1'' (and in mice and rats by the ''Trpa1'') gene. TRPA1 is an ion channel located on the plasma membrane of many human and animal cells. This ion channel is best known as a sensor for pain, cold and itch in humans and other mammals, as well as a sensor for environmental irritants giving rise to other protective responses (tears, airway resistance, and cough). Function TRPA1 is a member of the transient receptor potential channel family. TRPA1 contains 14 N-terminal ankyrin repeats and is believed to function as a mechanical and chemical stress sensor. One of the specific functions of this protein studies involves a role in the detection, integration and initiation of pain signals in the peripheral nervous system. It can be activated at sites of tissue injury or sites of infl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asphyxia
Asphyxia or asphyxiation is a condition of deficient supply of oxygen to the body which arises from abnormal breathing. Asphyxia causes generalized hypoxia, which affects primarily the tissues and organs. There are many circumstances that can induce asphyxia, all of which are characterized by the inability of a person to acquire sufficient oxygen through breathing for an extended period of time. Asphyxia can cause coma or death. In 2015, about 9.8 million cases of unintentional suffocation occurred which resulted in 35,600 deaths. The word asphyxia is from Ancient Greek "without" and , "squeeze" (throb of heart). Causes Situations that can cause asphyxia include but are not limited to: airway obstruction, the constriction or obstruction of airways, such as from asthma, laryngospasm, or simple blockage from the presence of foreign materials; from being in environments where oxygen is not readily accessible: such as underwater, in a low oxygen atmosphere, or in a vacuum; envir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulmonary Injury
A chest injury, also known as chest trauma, is any form of physical injury to the chest including the ribs, heart and lungs. Chest injuries account for 25% of all deaths from traumatic injury. Typically chest injuries are caused by blunt mechanisms such as direct, indirect, compression, contusion, deceleration, or blasts- caused by motor vehicle collisions or penetrating mechanisms such as stabbings. Classification Chest injuries can be classified as blunt or penetrating. Blunt and penetrating injuries have different pathophysiologies and clinical courses. Specific types of injuries include: * Injuries to the chest wall ** Chest wall contusions or hematomas. ** Rib fractures ** Flail chest ** Sternal fractures ** Fractures of the shoulder girdle * Pulmonary injury (injury to the lung) and injuries involving the pleural space ** Pulmonary contusion ** Pulmonary laceration ** Pneumothorax ** Hemothorax ** Hemopneumothorax * Injury to the airways ** Tracheobronchial tear * Car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemosis
Chemosis is the swelling (or edema) of the conjunctiva. The term derives from the Greek ''chem-'' meaning chemical and ''-osis'' meaning denoting action. A chemical reaction, or in this case, a chemical reaction of the conjunctiva which is due to the oozing of exudate from abnormally permeable capillaries. In general, chemosis is a nonspecific sign of eye irritation. The outer surface covering appears to have fluid in it. The conjunctiva becomes swollen and gelatinous in appearance. Often, the eye area swells so much that the eyes become difficult or impossible to close fully. Sometimes, it may also appear as if the eyeball has moved slightly backwards from the white part of the eye due to the fluid filled in the conjunctiva all over the eyes except the iris. The iris is not covered by this fluid and so it appears to be moved slightly inwards. Causes It is usually caused by allergies or viral infections, often inciting excessive eye rubbing. Chemosis is also included in the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corneal Epithelium
The corneal epithelium (epithelium corneæ anterior layer) is made up of epithelial tissue and covers the front of the cornea. It acts as a barrier to protect the cornea, resisting the free flow of fluids from the tears, and prevents bacteria from entering the epithelium and corneal stroma. Anatomy The corneal epithelium consists of several layers of cells. The cells of the deepest layer are columnar, known as basal cells which are attached by multiprotein complexes known as hemidesmosomes to an underlying basement membrane. Then follow two or three layers of polyhedral cells, commonly known as wing cells. The majority of these are prickle cells, similar to those found in the stratum mucosum of the cuticle. Lastly, there are three or four layers of squamous cells, with flattened nuclei. The layers of the epithelium are constantly undergoing mitosis. Basal and wing cells migrate to the anterior of the cornea, while squamous cells age and slough off into the tear film. Central ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermatitis
Dermatitis is inflammation of the skin, typically characterized by itchiness, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become thickened. The area of skin involved can vary from small to covering the entire body. Dermatitis is often called eczema, and the difference between those terms is not standardized. The exact cause of the condition is often unclear. Cases may involve a combination of allergy and poor venous return. The type of dermatitis is generally determined by the person's history and the location of the rash. For example, irritant dermatitis often occurs on the hands of those who frequently get them wet. Allergic contact dermatitis occurs upon exposure to an allergen, causing a hypersensitivity reaction in the skin. Prevention of atopic dermatitis is typically with essential fatty acids, and may be treated with moisturizers and steroid creams. The steroid creams should generally be of mid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fainting
Syncope, commonly known as fainting, or passing out, is a loss of consciousness and muscle strength characterized by a fast onset, short duration, and spontaneous recovery. It is caused by a decrease in blood flow to the brain, typically from low blood pressure. There are sometimes symptoms before the loss of consciousness such as lightheadedness, sweating, pale skin Pallor is a pale color of the skin that can be caused by illness, emotional shock or stress, stimulant use, or anemia, and is the result of a reduced amount of oxyhaemoglobin and may also be visible as pallor of the conjunctivae of the eyes o ..., blurred vision, nausea, vomiting, or feeling warm. Syncope may also be associated with a short episode of muscle twitching. Psychiatric causes can also be determined when a patient experiences fear, anxiety, or panic; particularly before a stressful event usually medical in nature. When consciousness and muscle strength are not completely lost, it is called presy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tracheobronchial
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of respiration in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respiratory mucosa. Air is breathed in through the nose to the nasal cavity, where a layer of nasal mucosa acts as a filter and traps pollutants and other harmful substances found in the air. Next, air moves into the pharynx, a passage that contains the intersection between the oesophagus and the larynx. The opening of the larynx has a special flap of cartilage, the epiglottis, that opens to allow air to pass through but closes to prevent food from moving into the airway. From the larynx, air moves into the trachea and down to the intersection known as the carina that branches to form the right and left primary (main) bronchi. Each of these bronchi branches into a secondary (lobar) bronchus that branches into tertiary (segmental) bronchi, that branch into smaller airways called bronchioles that ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conjunctiva
The conjunctiva is a thin mucous membrane that lines the inside of the eyelids and covers the sclera (the white of the eye). It is composed of non-keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium with goblet cells, stratified columnar epithelium and stratified cuboidal epithelium (depending on the zone). The conjunctiva is highly vascularised, with many microvessels easily accessible for imaging studies. Structure The conjunctiva is typically divided into three parts: Blood supply Blood to the bulbar conjunctiva is primarily derived from the ophthalmic artery. The blood supply to the palpebral conjunctiva (the eyelid) is derived from the external carotid artery. However, the circulations of the bulbar conjunctiva and palpebral conjunctiva are linked, so both bulbar conjunctival and palpebral conjunctival vessels are supplied by both the ophthalmic artery and the external carotid artery, to varying extents. Nerve supply Sensory innervation of the conjunctiva is divided into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucous Membrane
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is mostly of endodermal origin and is continuous with the skin at body openings such as the eyes, eyelids, ears, inside the nose, inside the mouth, lips, the genital areas, the urethral opening and the anus. Some mucous membranes secrete mucus, a thick protective fluid. The function of the membrane is to stop pathogens and dirt from entering the body and to prevent bodily tissues from becoming dehydrated. Structure The mucosa is composed of one or more layers of epithelial cells that secrete mucus, and an underlying lamina propria of loose connective tissue. The type of cells and type of mucus secreted vary from organ to organ and each can differ along a given tract. Mucous membranes line the digestive, respiratory and reproductive trac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |