|
Chirp Transmitter
An ionosonde, or chirpsounder, is a special radar for the examination of the ionosphere. The basic ionosonde technology was invented in 1925 by Gregory Breit and Merle A. Tuve and further developed in the late 1920s by a number of prominent physicists, including Edward Victor Appleton. The term ''ionosphere'' and hence, the etymology of its derivatives, was proposed by Robert Watson-Watt. Components An ionosonde consists of: * A high frequency (HF) radio transmitter, automatically tunable over a wide range. Typically the frequency coverage is 0.5–23 MHz or 1–40 MHz, though normally sweeps are confined to approximately 1.6–12 MHz. * A tracking HF receiver which can automatically track the frequency of the transmitter. * An antenna with a suitable radiation pattern, which transmits well vertically upwards and is efficient over the whole frequency range used. * Digital control and data analysis circuits. The transmitter sweeps all or part of the HF frequency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Frequency
High frequency (HF) is the ITU designation for the range of radio frequency electromagnetic waves (radio waves) between 3 and 30 megahertz (MHz). It is also known as the decameter band or decameter wave as its wavelengths range from one to ten decameters (ten to one hundred meters). Frequencies immediately below HF are denoted medium frequency (MF), while the next band of higher frequencies is known as the very high frequency (VHF) band. The HF band is a major part of the shortwave band of frequencies, so communication at these frequencies is often called shortwave radio. Because radio waves in this band can be reflected back to Earth by the ionosphere layer in the atmosphere – a method known as "skip" or " skywave" propagation – these frequencies are suitable for long-distance communication across intercontinental distances and for mountainous terrains which prevent line-of-sight communications. The band is used by international shortwave broadcasting stations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance (''ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. A radar system consists of a transmitter producing electromagnetic waves in the radio or microwaves domain, a transmitting antenna, a receiving antenna (often the same antenna is used for transmitting and receiving) and a receiver and processor to determine properties of the objects. Radio waves (pulsed or continuous) from the transmitter reflect off the objects and return to the receiver, giving information about the objects' locations and speeds. Radar was developed secretly for military use by several countries in the period before and during World War II. A key development was the cavity magnetron in the United Kingdom, which allowed the creation of relatively small systems with sub-meter resolution. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trevor Wadley
Trevor Lloyd Wadley, (1920 – 21 May 1981) was a South African electrical engineer, best known for his development of the Wadley Loop circuit for greater stability in communications receivers and the Tellurometer, a land surveying device. Life and career Wadley was born in 1920 in Durban, South Africa. His father was the Mayor of Durban and Trevor was one of 12 children. He attended Durban High School where he excelled in mathematics and science but was uninterested in any sport. The exception was one year when he entered the annual cross-country athletics event and predicted that he would win in record time and his record would stand for 15 years. He went on to do exactly as he had predicted. His training method involved calculating the time he needed to run each section of the course and then training himself to run at the required pace for each section. He then went to Howard College (now the University of KwaZulu-Natal), where he studied under Hugh Clark and Eric Phillip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Total Electron Content
Total electron content (TEC) is an important descriptive quantity for the ionosphere of the Earth. TEC is the total number of electrons integrated between two points, along a tube of one meter squared cross section, i.e., the electron columnar number density. It is often reported in multiples of the so-called ''TEC unit'', defined as TECU1016el/m2. TEC is significant in determining the scintillation and group and phase delays of a radio wave through a medium. Ionospheric TEC is characterized by observing carrier phase delays of received radio signals transmitted from satellites located above the ionosphere, often using Global Positioning System satellites. TEC is strongly affected by solar activity. Formulation The TEC is path-dependent. By definition, it can be calculated by integrating along the path ''ds'' through the ionosphere with the location-dependent electron density ''ne(s)'': : TEC = \int n_e(s)\,ds The ''vertical'' TEC (''VTEC'') is determined by integration of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Propagation Beacon
An amateur radio propagation beacon is a radio beacon, whose purpose is the investigation of the propagation of radio signals. Most radio propagation beacons use amateur radio frequencies. They can be found on LF, MF, HF, VHF, UHF, and microwave frequencies. Microwave beacons are also used as signal sources to test and calibrate antennas and receivers. The International Amateur Radio Union (IARU) and its member societies coordinate beacons established by radio amateurs. Transmission characteristics Most beacons operate in continuous wave (A1A) and transmit their identification ( call sign and location). Some of them send long dashes to facilitate signal strength measurement. A small number of beacons transmit Morse code by frequency-shift keying (F1A). A few beacons transmit signals in digital modulation modes, like radioteletype (F1B) and PSK31 (G1B). Legality In the US, unattended beacons on frequencies lower than the 10-meter band are not legal. 2200-meter beacons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionosonde Juliusruh
The Ionosonde Juliusruh is a facility of the institute for atmospheric physics near Juliusruh in northeastern Germany for sounding the ionosphere with radar systems in the short wave range (frequencies between 1 MHz and 30 MHz). The landmark of the station is a 70 metre high grounded free standing steel framework tower, which was built in 1960/61 and which carries a cage aerial for the transmitter of the ionosonde. See also *List of towers Several extant building fulfill the engineering definition of a tower: "a tall human structure, always taller than it is wide, for public or regular operational access by humans, but not for living in or office work, and are ''self-supporting' ... External links * http://www.ionosonde.iap-kborn.de/indexeng.htm * * http://www.skyscraperpage.com/diagrams/?b45849 {{authority control Research institutes in Germany Towers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duga Radar
''Duga'' (, ) was an over-the-horizon radar (OTH) system used in the Soviet Union as part of its early-warning radar network for missile defense. It operated from July 1976 to December 1989. Two operational ''duga'' radars were deployed, with one near Chernobyl and Chernihiv in the Ukrainian SSR (present-day Ukraine), and the other in eastern Siberia (present-day Russia). The ''duga'' system was extremely powerful, reaching over 10 MW, and broadcast in the shortwave radio bands. It was given the nickname Russian Woodpecker by shortwave listeners for its emissions randomly appearing and sounding like sharp, repetitive tapping noises at a frequency of 10 Hz. The random frequency hops often disrupted legitimate broadcasts, amateur radio operations, oceanic commercial aviation communications, and utility transmissions, resulting in thousands of complaints by many countries worldwide. The signal became such a nuisance that some communications receivers began including "Woodpecker ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software-defined Radio
Software-defined radio (SDR) is a radio communication system where components that have been traditionally implemented in analog hardware (e.g. mixers, filters, amplifiers, modulators/demodulators, detectors, etc.) are instead implemented by means of software on a personal computer or embedded system. While the concept of SDR is not new, the rapidly evolving capabilities of digital electronics render practical many processes which were once only theoretically possible. A basic SDR system may consist of a personal computer equipped with a sound card, or other analog-to-digital converter, preceded by some form of RF front end. Significant amounts of signal processing are handed over to the general-purpose processor, rather than being done in special-purpose hardware (electronic circuits). Such a design produces a radio which can receive and transmit widely different radio protocols (sometimes referred to as waveforms) based solely on the software used. Software radios have signif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Over-the-horizon Radar
Over-the-horizon radar (OTH), sometimes called beyond the horizon radar (BTH), is a type of radar system with the ability to detect targets at very long ranges, typically hundreds to thousands of kilometres, beyond the radar horizon, which is the distance limit for ordinary radar. Several OTH radar systems were deployed starting in the 1950s and 1960s as part of early warning radar systems, but these have generally been replaced by airborne early warning systems. OTH radars have recently been making a comeback, as the need for accurate long-range tracking becomes less important with the ending of the Cold War, and less-expensive ground-based radars are once again being considered for roles such as maritime reconnaissance and drug enforcement. Technology The frequency of radio waves used by most radars, in the form of microwaves, travel in straight lines. This generally limits the detection range of radar systems to objects on their horizon (generally referred to as "line of sig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
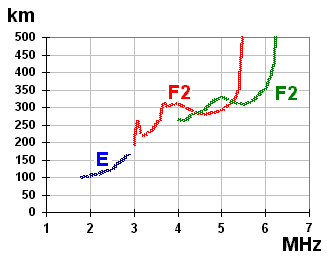
Ionosphere
The ionosphere () is the ionized part of the upper atmosphere of Earth, from about to above sea level, a region that includes the thermosphere and parts of the mesosphere and exosphere. The ionosphere is ionized by solar radiation. It plays an important role in atmospheric electricity and forms the inner edge of the magnetosphere. It has practical importance because, among other functions, it influences radio propagation to distant places on Earth. History of discovery As early as 1839, the German mathematician and physicist Carl Friedrich Gauss postulated that an electrically conducting region of the atmosphere could account for observed variations of Earth's magnetic field. Sixty years later, Guglielmo Marconi received the first trans-Atlantic radio signal on December 12, 1901, in St. John's, Newfoundland (now in Canada) using a kite-supported antenna for reception. The transmitting station in Poldhu, Cornwall, used a spark-gap transmitter to produce a signal with a freq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single-sideband Modulation
In radio communications, single-sideband modulation (SSB) or single-sideband suppressed-carrier modulation (SSB-SC) is a type of modulation used to transmit information, such as an audio signal, by radio waves. A refinement of amplitude modulation, it uses transmitter power and bandwidth more efficiently. Amplitude modulation produces an output signal the bandwidth of which is twice the maximum frequency of the original baseband signal. Single-sideband modulation avoids this bandwidth increase, and the power wasted on a carrier, at the cost of increased device complexity and more difficult tuning at the receiver. Basic concept Radio transmitters work by mixing a radio frequency (RF) signal of a specific frequency, the carrier wave, with the audio signal to be broadcast. In AM transmitters this mixing usually takes place in the final RF amplifier (high level modulation). It is less common and much less efficient to do the mixing at low power and then amplify it in a linear ampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |