|
Chemi-ionization
Chemi-ionization is the formation of an ion through the reaction of a gas phase atom or molecule with an atom or molecule in an excited state while also creating new bonds. C01044 This process is helpful in mass spectrometry because it creates unique bands that can be used to identify molecules. This process is extremely common in nature as it is considered the primary initial reaction in flames. History The term chemi-ionization was coined by Hartwell F. Calcote in 1948 in the Third Symposium on Combustion and Flame, and Explosion Phenomena. The Symposium performed much of the early investigation into this phenomenon in the 1950s. The majority of the research on this topic was performed in the 1960s and '70s. It is currently seen in many different ionization techniques used for mass spectrometry. Reactions Chemi-ionization can be represented by :G^\ast + M -> M^ + e^- + G where G is the excited state species (indicated by the super-scripted asterisk), and M is the species th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemi-ionization
Chemi-ionization is the formation of an ion through the reaction of a gas phase atom or molecule with an atom or molecule in an excited state while also creating new bonds. C01044 This process is helpful in mass spectrometry because it creates unique bands that can be used to identify molecules. This process is extremely common in nature as it is considered the primary initial reaction in flames. History The term chemi-ionization was coined by Hartwell F. Calcote in 1948 in the Third Symposium on Combustion and Flame, and Explosion Phenomena. The Symposium performed much of the early investigation into this phenomenon in the 1950s. The majority of the research on this topic was performed in the 1960s and '70s. It is currently seen in many different ionization techniques used for mass spectrometry. Reactions Chemi-ionization can be represented by :G^\ast + M -> M^ + e^- + G where G is the excited state species (indicated by the super-scripted asterisk), and M is the species th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
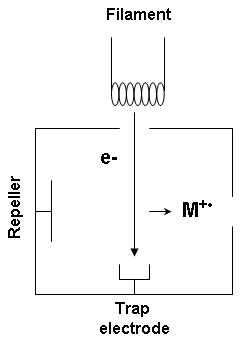
Associative Ionization
An ion source is a device that creates atomic and molecular ions. Ion sources are used to form ions for mass spectrometers, optical emission spectrometers, particle accelerators, ion implanters and ion engines. Electron ionization Electron ionization is widely used in mass spectrometry, particularly for organic molecules. The gas phase reaction producing electron ionization is :M + e^- -> M^ + 2e^- where M is the atom or molecule being ionized, e^- is the electron, and M^ is the resulting ion. The electrons may be created by an arc discharge between a cathode and an anode. An electron beam ion source (EBIS) is used in atomic physics to produce highly charged ions by bombarding atoms with a powerful electron beam. Its principle of operation is shared by the electron beam ion trap. Electron capture ionization Electron capture ionization (ECI) is the ionization of a gas phase atom or molecule by attachment of an electron to create an ion of the form A−•. The reaction i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charge-exchange Ionization
An ion source is a device that creates atomic and molecular ions. Ion sources are used to form ions for mass spectrometers, optical emission spectrometers, particle accelerators, ion implanters and ion engines. Electron ionization Electron ionization is widely used in mass spectrometry, particularly for organic molecules. The gas phase reaction producing electron ionization is :M + e^- -> M^ + 2e^- where M is the atom or molecule being ionized, e^- is the electron, and M^ is the resulting ion. The electrons may be created by an arc discharge between a cathode and an anode. An electron beam ion source (EBIS) is used in atomic physics to produce highly charged ions by bombarding atoms with a powerful electron beam. Its principle of operation is shared by the electron beam ion trap. Electron capture ionization Electron capture ionization (ECI) is the ionization of a gas phase atom or molecule by attachment of an electron to create an ion of the form A−•. The reaction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penning Ionization
Penning ionization is a form of chemi-ionization, an ionization process involving reactions between neutral atoms or molecules. The Penning effect is put to practical use in applications such as gas-discharge neon lamps and fluorescent lamps, where the lamp is filled with a Penning mixture to improve the electrical characteristics of the lamps. History The process is named after the Dutch physicist Frans Michel Penning who first reported it in 1927. Penning started to work at the Philips Natuurkundig Laboratorium at Eindhoven to continue the investigation of electric discharge on rare gases. Later, he started measurements on the liberation of electrons from metal surfaces by positive ions and metastable atoms, and especially on the effects related to ionization by metastable atoms. Reaction Penning ionization refers to the interaction between an electronically excited gas-phase atom G* and a target molecule M. The collision results in the ionization of the molecule yielding a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atom
Every atom is composed of a nucleus and one or more electrons bound to the nucleus. The nucleus is made of one or more protons and a number of neutrons. Only the most common variety of hydrogen has no neutrons. Every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics, as if they were tennis balls for example, is not possible due to quantum effects. More than 99.94% of an atom's mass is in the nucleus. The protons have a positive electric charge, the electrons have a negative electric charge, and the neutrons have no electric charge. If the number of protons and electrons are equal, then the atom is electrically neutral. If an atom has more or fewer electrons than protons, then it has an overall negative or positive charge, respectively – such atoms are called ions. The electrons of an atom are a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and biochemistry, the distinction from ions is dropped and ''molecule'' is often used when referring to polyatomic ions. A molecule may be homonuclear, that is, it consists of atoms of one chemical element, e.g. two atoms in the oxygen molecule (O2); or it may be heteronuclear, a chemical compound composed of more than one element, e.g. water (two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom; H2O). In the kinetic theory of gases, the term ''molecule'' is often used for any gaseous particle regardless of its composition. This relaxes the requirement that a molecule contains two or more atoms, since the noble gases are individual atoms. Atoms and complexes connected by non-covalent interactions, such as hydrogen bonds or ionic bonds, are typically not consid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excited State
In quantum mechanics, an excited state of a system (such as an atom, molecule or nucleus) is any quantum state of the system that has a higher energy than the ground state (that is, more energy than the absolute minimum). Excitation refers to an increase in energy level above a chosen starting point, usually the ground state, but sometimes an already excited state. The temperature of a group of particles is indicative of the level of excitation (with the notable exception of systems that exhibit negative temperature). The lifetime of a system in an excited state is usually short: spontaneous or induced emission of a quantum of energy (such as a photon or a phonon) usually occurs shortly after the system is promoted to the excited state, returning the system to a state with lower energy (a less excited state or the ground state). This return to a lower energy level is often loosely described as decay and is the inverse of excitation. Long-lived excited states are often called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a ''mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is used in many different fields and is applied to pure samples as well as complex mixtures. A mass spectrum is a type of plot of the ion signal as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. These spectra are used to determine the elemental or isotopic signature of a sample, the masses of particles and of molecules, and to elucidate the chemical identity or structure of molecules and other chemical compounds. In a typical MS procedure, a sample, which may be solid, liquid, or gaseous, is ionized, for example by bombarding it with a beam of electrons. This may cause some of the sample's molecules to break up into positively charged fragments or simply become positively charged without fragmenting. These ions (fragments) are then separated accordin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family, and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have no known components or substructure. The electron's mass is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton. Quantum mechanical properties of the electron include an intrinsic angular momentum ( spin) of a half-integer value, expressed in units of the reduced Planck constant, . Being fermions, no two electrons can occupy the same quantum state, in accordance with the Pauli exclusion principle. Like all elementary particles, electrons exhibit properties of both particles and waves: They can collide with other particles and can be diffracted like light. The wave properties of electrons are easier to observe with experiments than those of other particles like neutrons and protons because electrons have a lower mass and hence a longer de Broglie wavele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radical (chemistry)
In chemistry, a radical, also known as a free radical, is an atom, molecule, or ion that has at least one unpaired valence electron. With some exceptions, these unpaired electrons make radicals highly chemically reactive. Many radicals spontaneously dimerize. Most organic radicals have short lifetimes. A notable example of a radical is the hydroxyl radical (HO·), a molecule that has one unpaired electron on the oxygen atom. Two other examples are triplet oxygen and triplet carbene (꞉) which have two unpaired electrons. Radicals may be generated in a number of ways, but typical methods involve redox reactions. Ionizing radiation, heat, electrical discharges, and electrolysis are known to produce radicals. Radicals are intermediates in many chemical reactions, more so than is apparent from the balanced equations. Radicals are important in combustion, atmospheric chemistry, polymerization, plasma chemistry, biochemistry, and many other chemical processes. A majority of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cation
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convention. The net charge of an ion is not zero because its total number of electrons is unequal to its total number of protons. A cation is a positively charged ion with fewer electrons than protons while an anion is a negatively charged ion with more electrons than protons. Opposite electric charges are pulled towards one another by electrostatic force, so cations and anions attract each other and readily form ionic compounds. Ions consisting of only a single atom are termed atomic or monatomic ions, while two or more atoms form molecular ions or polyatomic ions. In the case of physical ionization in a fluid (gas or liquid), "ion pairs" are created by spontaneous molecule collisions, where each generated pair consists of a free electron and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermodynamic Equilibrium
Thermodynamic equilibrium is an axiomatic concept of thermodynamics. It is an internal state of a single thermodynamic system, or a relation between several thermodynamic systems connected by more or less permeable or impermeable walls. In thermodynamic equilibrium, there are no net macroscopic flows of matter nor of energy within a system or between systems. In a system that is in its own state of internal thermodynamic equilibrium, no macroscopic change occurs. Systems in mutual thermodynamic equilibrium are simultaneously in mutual thermal, mechanical, chemical, and radiative equilibria. Systems can be in one kind of mutual equilibrium, while not in others. In thermodynamic equilibrium, all kinds of equilibrium hold at once and indefinitely, until disturbed by a thermodynamic operation. In a macroscopic equilibrium, perfectly or almost perfectly balanced microscopic exchanges occur; this is the physical explanation of the notion of macroscopic equilibrium. A thermodynamic sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)

