|
Charitable Trusts In English Law
Charitable trusts in English law are a form of express trust dedicated to charitable goals. There are a variety of advantages to charitable trust status, including exception from most forms of tax and freedom for the trustees not found in other types of English trust. To be a valid charitable trust, the organisation must demonstrate both a charitable purpose and a public benefit. Applicable charitable purposes are normally divided into categories for public benefit including the relief of poverty, the promotion of education, the advancement of health and saving of lives, promotion of religion and all other types of trust recognised by the law. There is also a requirement that the trust's purposes benefit the public (or some section of the public), and not simply a group of private individuals. Such trusts will be invalid in several circumstances; charitable trusts are not allowed to be run for profit, nor can they have purposes that are not charitable (unless these are ancillar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Courts Of Justice
The Royal Courts of Justice, commonly called the Law Courts, is a court building in Westminster which houses the High Court and Court of Appeal of England and Wales. The High Court also sits on circuit and in other major cities. Designed by George Edmund Street, who died before it was completed, it is a large grey stone edifice in the Victorian Gothic Revival style built in the 1870s and opened by Queen Victoria in 1882. It is one of the largest courts in Europe. It is a Grade I listed building. It is located on Strand within the City of Westminster, near the border with the City of London ( Temple Bar). It is surrounded by the four Inns of Court, St Clement Danes church, The Australian High Commission, King's College London and the London School of Economics. The nearest London Underground stations are Chancery Lane and Temple. The Central Criminal Court, widely known as the Old Bailey after its street, is about to the east—a Crown Court centre with no direct connection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inter Vivos
Inter vivos (Latin, ''between the living'') is a legal term referring to a transfer or gift made during one's lifetime, as opposed to a testamentary transfer that takes effect on the death of the giver. The term is often used to describe a trust established during one's lifetime, i.e., an inter vivos trust as opposed to a testamentary trust that is established on one's death, usually as part of a will. An inter vivos trust, by definition, includes both revocable and irrevocable trusts. Other meaning The term ''inter vivos'' is also used to describe living organ donation Organ donation is the process when a person allows an organ of their own to be removed and transplanted to another person, legally, either by consent while the donor is alive or dead with the assent of the next of kin. Donation may be for re ..., in which one patient donates an organ to another while both are alive. Generally, the organs transplanted are either non-vital organs such as corneas or redunda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charitable Uses Act 1601
The Charitable Uses Act of 1601 (known as the ''Statute of Elizabeth'') is an Act of Parliament, Act (43 Eliz I, c.4) of the Parliament of England. It was repealed by section 13(1) of the Mortmain and Charitable Uses Act 1888 (c.42) (but see section 13(2) of that Act). The preamble to the act contained a list of purposes or activities that was, in effect, a list of purposes or activities that the State believed were of general benefit to society, and to which the State wanted to encourage private contributions. The list has formed the foundation of the modern definition of charitable purposes, which has developed through case law. This has come about because the courts, in considering whether or not a particular purpose was charitable in law, have tended to look for an analogy between the purpose under consideration and the list, and to recognise the purpose as charitable if an analogy with the 1601 list could be found. The list contained in the 1601 Preamble is: # "The relief ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macnaghten E Vanity Fair 1895-10-31
Macnaghten may refer to: *Clan Macnaghten *Daniel M'Naghten, namesake of the M'Naghten rules *Edward Macnaghten *Elliot Macnaghten *Half Hung MacNaghten *Macnaghten Baronets *Melville Macnaghten *William Hay Macnaghten (1793-1841), killed in the First Anglo-Afghan War See also * Macnaughtan * McNaughton {{Disambiguation, surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charities Act 2006
The Charities Act 2006 (c 50) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom intended to alter the regulatory framework in which charities operate, partly by amending the Charities Act 1993. The Act was mostly superseded by the Charities Act 2011, which consolidates charity law in the UK. Provisions The Act contains three main provisions: definition of the requirements to qualify as a charity, the establishment of a Charity Tribunal to hear appeals from decisions of the Charity Commission, and alterations to the requirements for registering charities. Charitable status The Act imposes conditions on bodies wishing to attain or maintain charitable status. For the purposes of the law, a charitable organisation must demonstrate that it serves the public interest, and that its purpose lies entirely in the promotion of one or more of the following causes: * the prevention or relief of poverty; * the advancement of education; * the advancement of religion; * the advancement of h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charities Act 1993
The Charities Act 2011c 25 is a UK Act of Parliament. It consolidated the bulk of the Charities Act 2006, outstanding provisions of the Charities Act 1993, and various other enactments. Repeals Legislation repealed in its entirety by the 2011 Act include the Recreational Charities Act 1958, Charities Act 1993, Charities (Amendment) Act 1995, Charities Act 1993 (Substitution of Sums) Order 1995, Charities Act 2006 (Charitable Companies Audit and Group Accounts Provisions) Order 2008, and Charities (Pre-consolidation Amendments) Order 2011. Amendments were made to other legislation. It replaces most of the Charities Act 1992 and Charities Act 2006. See also *English trust law English trust law concerns the protection of assets, usually when they are held by one party for another's benefit. Trusts were a creation of the English law of property and obligations, and share a subsequent history with countries across the ... * Charitable trusts in English law Notes References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HM Revenue & Customs
HM Revenue and Customs (His Majesty's Revenue and Customs, or HMRC) is a non-ministerial government department, non-ministerial Departments of the United Kingdom Government, department of the His Majesty's Government, UK Government responsible for the tax collection, collection of Taxation in the United Kingdom, taxes, the payment of some forms of Welfare state in the United Kingdom, state support, the administration of other regulatory Regime#Politics, regimes including the national minimum wage and the issuance of national insurance numbers. HMRC was formed by the merger of the Inland Revenue and HM Customs and Excise, which took effect on 18 April 2005. The department's logo is the St Edward's Crown enclosed within a circle. Prior to the Elizabeth II, Queen's death on 8 September 2022, the department was known as ''Her'' Majesty's Revenue and Customs and has since been amended to reflect the change of monarch. Departmental responsibilities The department is responsible for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gift Aid
Gift Aid is a UK tax incentive that enables tax-effective giving by individuals to charities in the United Kingdom. Gift Aid was introduced in the Finance Act 1990 for donations given after 1 October 1990, but was originally limited to cash gifts of £600 or more. This threshold was successively reduced in April 2000 when the policy was substantially revised and the minimum donation limit removed entirely. A similar policy applies to charitable donations by companies that are subject to the UK corporation tax. Gift Aid was originally intended for cash donations only. However, since 2006, HMRC compliant systems have been introduced to allow tax on the income earned by charity shops, acting as an agent for a donor, to be reclaimed. In order for the charity to operate effectively they will need HMRC-approved systems to be able to record and track the progress of each item from receipt to sale and confirm with the donor that the donation should still go ahead. In the financial year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
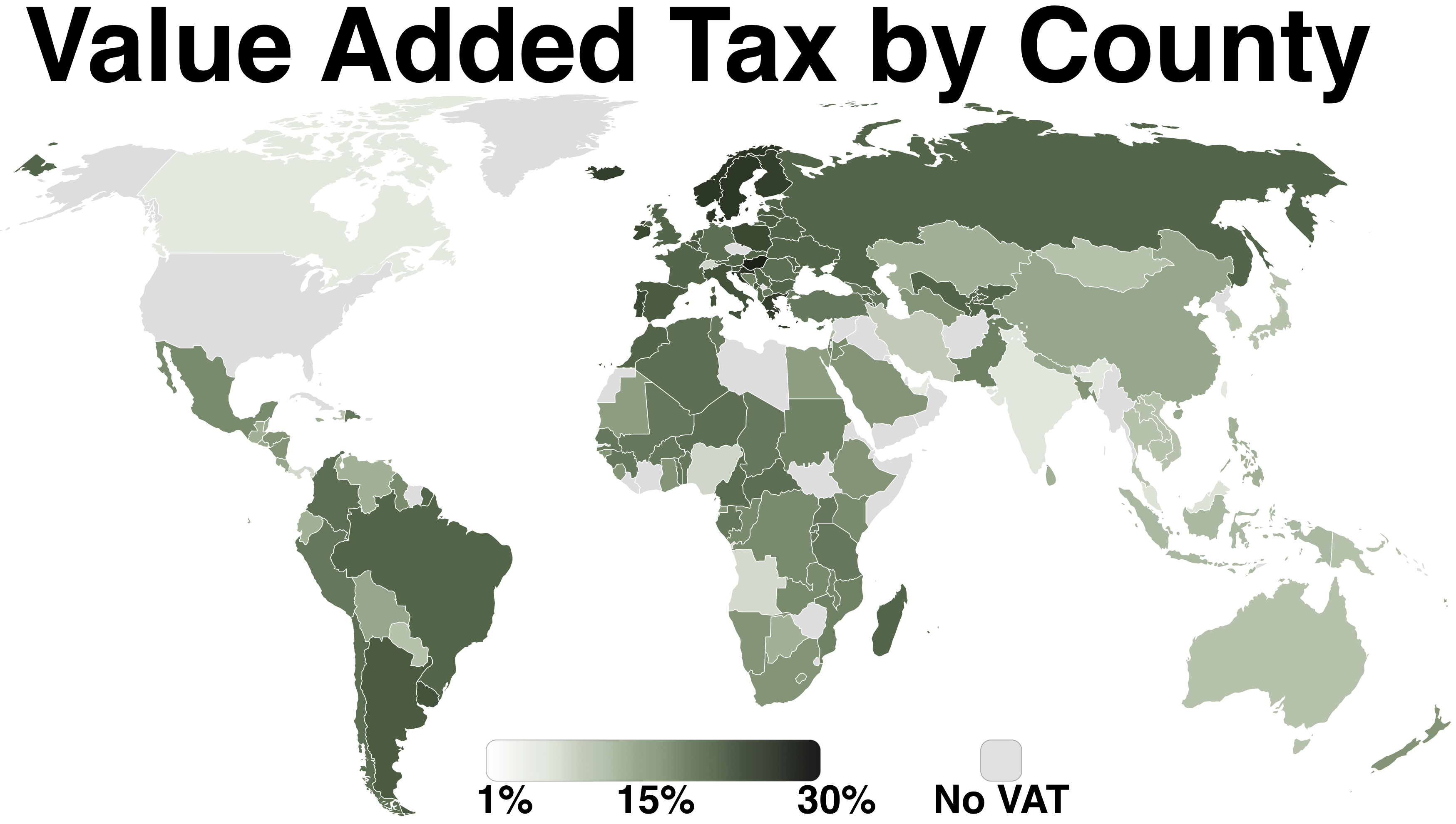
Value Added Tax
A value-added tax (VAT), known in some countries as a goods and services tax (GST), is a type of tax that is assessed incrementally. It is levied on the price of a product or service at each stage of production, distribution, or sale to the end consumer. If the ultimate consumer is a business that collects and pays to the government VAT on its products or services, it can reclaim the tax paid. It is similar to, and is often compared with, a sales tax. VAT is an indirect tax because the person who ultimately bears the burden of the tax is not necessarily the same person as the one who pays the tax to the tax authorities. Not all localities require VAT to be charged, and exports are often exempt. VAT is usually implemented as a destination-based tax, where the tax rate is based on the location of the consumer and applied to the sales price. The terms VAT, GST, and the more general consumption tax are sometimes used interchangeably. VAT raises about a fifth of total tax revenues bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Tax
Council Tax is a local taxation system used in England, Scotland and Wales. It is a tax on domestic property, which was introduced in 1993 by the Local Government Finance Act 1992, replacing the short-lived Community Charge The Community Charge, commonly known as the poll tax, was a system of taxation introduced by Margaret Thatcher's government in replacement of domestic rates in Scotland from 1989, prior to its introduction in England and Wales from 1990. It pr ..., which in turn replaced the domestic rates. Each property is assigned one of eight bands in England and Scotland (A to H), or nine bands in Wales (A to I), based on property value, and the tax is set as a fixed amount for each band. The more valuable the property, the higher the tax, except for properties valued above £320,000 (in 1991 prices). Some property is exempt from the tax, and some people are exempt from the tax, while some get a discount. In 2011, the average annual levy on a property in England was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital Gains Tax
A capital gains tax (CGT) is the tax on profits realized on the sale of a non-inventory asset. The most common capital gains are realized from the sale of stocks, Bond (finance), bonds, precious metals, real estate, and property. Not all countries impose a capital gains tax and most have different rates of taxation for individuals versus corporations. Countries that do not impose a capital gains tax include Bahrain, Barbados, Belize, Cayman Islands, Isle of Man, Jamaica, New Zealand, Sri Lanka, Singapore, and others. In some countries, such as New Zealand and Singapore, professional traders and those who trade frequently are taxed on such profits as a business income. In Sweden, the Investment Savings Account (ISK – ''Investeringssparkonto'') was introduced in 2012 in response to a decision by Parliament to stimulate saving in funds and equities. There is no tax on capital gains in ISKs; instead, the saver pays an annual standard low rate of tax. Fund savers nowadays mainly ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
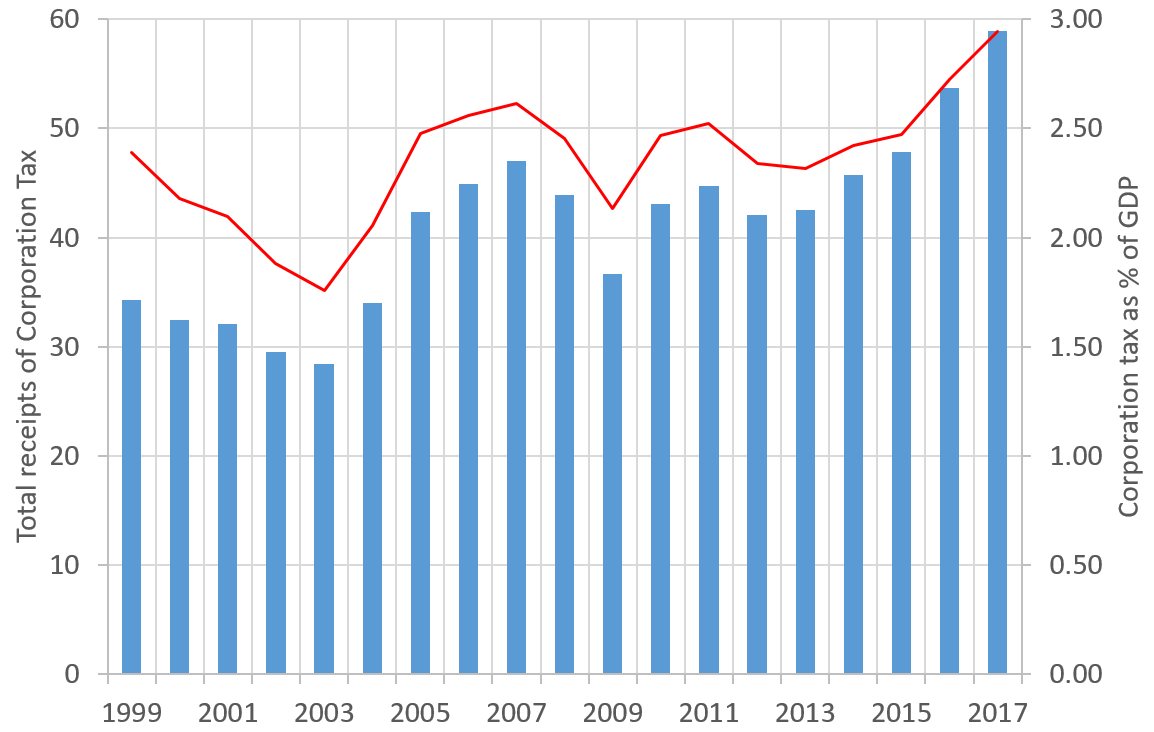
Corporation Tax In The United Kingdom
: ''Throughout this article, the term "pound" and the £ symbol refer to the Pound sterling.'' Corporation tax in the United Kingdom is a corporate tax levied in on the profits made by UK-resident companies and on the profits of entities registered overseas with permanent establishments in the UK. Until 1 April 1965, companies were taxed at the same income tax rates as individual taxpayers, with an additional profits tax levied on companies. Finance Act 1965 replaced this structure for companies and associations with a single corporate tax, which took its basic structure and rules from the income tax system. Since 1997, the UK's Tax Law Rewrite ProjectTax Law Rewrite , |

.jpg)