|
Chapbooks
A chapbook is a small publication of up to about 40 pages, sometimes bound with a saddle stitch. In early modern Europe a chapbook was a type of printed street literature. Produced cheaply, chapbooks were commonly small, paper-covered booklets, usually printed on a single sheet folded into books of 8, 12, 16 and 24 pages. They were often illustrated with crude woodcuts, which sometimes bore no relation to the text (much like today's stock photos), and were often read aloud to an audience. When illustrations were included in chapbooks, they were considered popular prints. The tradition of chapbooks arose in the 16th century, as soon as printed books became affordable, and rose to its height during the 17th and 18th centuries. Many different kinds of ephemera and popular or folk literature were published as chapbooks, such as almanacs, children's literature, folk tales, ballads, nursery rhymes, pamphlets, poetry, and political and religious tracts. The term "chapbook" for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cordel Literature
Cordel literature (from the Portuguese term, ''literatura de cordel'', literally “string literature”, ) are popular and inexpensively printed booklets or pamphlets containing folk novels, poems and songs. They are produced and sold in street markets and by street vendors in Brazil, mainly in the Northeast. They are so named because they are hung from strings to display them to potential customers, and the word for rope in Portuguese is ''corda'', from which the term ''cordel'' is derived. History Cordel literature forms one of the least altered continuations of the Western traditions of popular literature, such as chapbooks, and popular prints. Its history dates back to the 16th century, when the printing of oral reports became popularized in the Renaissance. This genre derives from the '' papel volante'' tradition of Portugal, a literary genre also found in Spain during the 18th and 19th centuries, and offered readers a wide array of topics, from basic instruction to poli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chapmen
A chapman (plural ''chapmen'') was an itinerant dealer or hawker in early modern Britain. Etymology Old English ''céapmann'' was the regular term for "dealer, seller", cognate with the Dutch ''koopman'' with the same meaning. Old English ''céap'' meant "deal, barter, business". The modern adjective ''cheap'' is a comparatively recent development from the phrase ''a good cheap'', literally "a good deal" (cf. modern Dutch ''goedkoop'' = cheap). The word also appears in names such as Cheapside, Eastcheap, Chepstow and the prefix Chipping: all markets or dealing places. The name of the Danish capital Copenhagen has a similar origin, being derived from ''Køpmannæhafn'', meaning "merchants' harbour" or "buyer's haven". By 1600, the word ''chapman'' had come to be applied to an itinerant dealer in particular, but it remained in use for "customer, buyer" as well as "merchant" in the 17th and 18th centuries. The slang term for man, "chap" arose from the use of the abbreviated word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
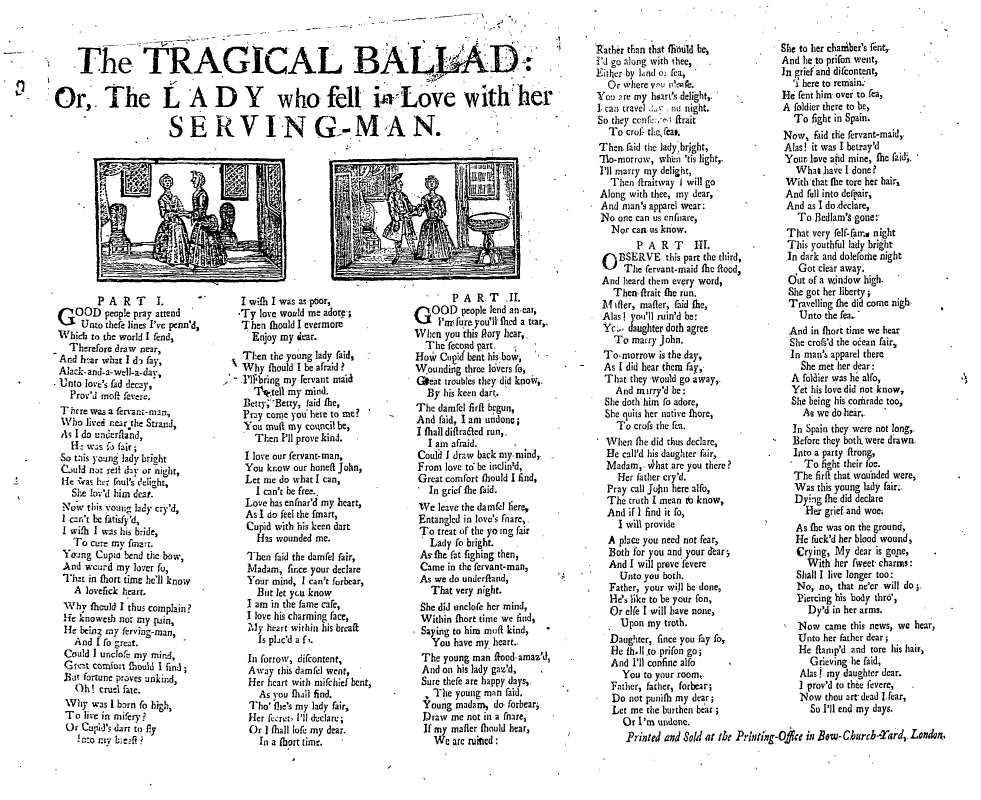
Broadside Ballads
A broadside (also known as a broadsheet) is a single sheet of inexpensive paper printed on one side, often with a ballad, rhyme, news and sometimes with woodcut illustrations. They were one of the most common forms of printed material between the sixteenth and nineteenth centuries, particularly in Britain, Ireland and North America because they are easy to produce and are often associated with one of the most important forms of traditional music from these countries, the ballad. Development of broadsides Ballads developed out of minstrelsy from the fourteenth and fifteenth century. These were narrative poems that had combined with French courtly romances and Germanic legends that were popular at the King’s court, as well as in the halls of lords of the realm. By the seventeenth century, minstrelsy had evolved into ballads whose authors wrote on a variety of topics. The authors could then have their ballads printed and distributed. Printers used a single piece of paper known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Street Literature
Street literature is any of several different types of publication sold on the streets, at fairs and other public gatherings, by travelling hawkers, pedlars or chapmen, from the fifteenth to the nineteenth centuries. Robert Collison's account of the subject describes street literature as the "forerunner of the popular press". Leslie Shepard's "History of Street Literature" identifies a range of different publications as indicated by his subtitle: "The Story of Broadside Ballads, Chapbooks, Proclamations, News-Sheets, Election Bills, Tracts, Pamphlets, Cocks, Catchpennies, and Other Ephemera". Street literature therefore includes several different printed formats and publication types. The main formats are: Broadside ballad Broadside ballads are traditional ballads printed on one side of a full sheet or half sheet of paper, often in landscape orientation. Intended to be pasted on to walls for public consultation. Chapbook Chapbooks were small, paper-covered booklets, usually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ephemera
Ephemera are transitory creations which are not meant to be retained or preserved. Its etymological origins extends to Ancient Greece, with the common definition of the word being: "the minor transient documents of everyday life". Ambiguous in nature, various interpretations of ephemera and related items have been contended, including menus, newspapers, postcards, posters, sheet music, stickers and valentines. Since the printing revolution, ephemera has been a long-standing element of everyday life. Some ephemera are ornate in their design, acquiring prestige, whereas others are minimal and notably utilitarian. Virtually all conceptions of ephemera make note of the matter's disposability. Ephemera has long been collected by the likes of families, hobbyists and curators, with certain instances of ephemera intended to be collected. Literature by collectors and societies has contributed to a greater willingness to preserve ephemera, which is now ubiquitous in archives and librar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Children's Literature
Children's literature or juvenile literature includes stories, books, magazines, and poems that are created for children. Modern children's literature is classified in two different ways: genre or the intended age of the reader. Children's literature can be traced to traditional stories like fairy tales, that have only been identified as children's literature in the eighteenth century, and songs, part of a wider oral tradition, that adults shared with children before publishing existed. The development of early children's literature, before printing was invented, is difficult to trace. Even after printing became widespread, many classic "children's" tales were originally created for adults and later adapted for a younger audience. Since the fifteenth century much literature has been aimed specifically at children, often with a moral or religious message. Children's literature has been shaped by religious sources, like Puritan traditions, or by more philosophical and scientif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peddler
A peddler, in British English pedlar, also known as a chapman, packman, cheapjack, hawker, higler, huckster, (coster)monger, colporteur or solicitor, is a door-to-door and/or travelling vendor of goods. In England, the term was mostly used for travellers hawking goods in the countryside to small towns and villages. In London, more specific terms were used, such as costermonger. From antiquity, peddlers filled the gaps in the formal market economy by providing consumers with the convenience of door-to-door service. They operated alongside town markets and fairs where they often purchased surplus stocks which were subsequently resold to consumers. Peddlers were able to distribute goods to the more geographically-isolated communities such as those who lived in mountainous regions of Europe. They also called on consumers who, for whatever reason, found it difficult to attend town markets. Thus, peddlers played an important role in linking these consumers and regions to wider tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballads
A ballad is a form of verse, often a narrative set to music. Ballads derive from the medieval French ''chanson balladée'' or '' ballade'', which were originally "dance songs". Ballads were particularly characteristic of the popular poetry and song of Britain and Ireland from the Late Middle Ages until the 19th century. They were widely used across Europe, and later in Australia, North Africa, North America and South America. Ballads are often 13 lines with an ABABBCBC form, consisting of couplets (two lines) of rhymed verse, each of 14 syllables. Another common form is ABAB or ABCB repeated, in alternating eight and six syllable lines. Many ballads were written and sold as single sheet broadsides. The form was often used by poets and composers from the 18th century onwards to produce lyrical ballads. In the later 19th century, the term took on the meaning of a slow form of popular love song and is often used for any love song, particularly the sentimental ballad of pop or r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alehouse
A pub (short for public house) is a kind of drinking establishment which is licensed to serve alcoholic drinks for consumption on the premises. The term ''public house'' first appeared in the United Kingdom in late 17th century, and was used to differentiate private houses from those which were, quite literally, open to the public as "alehouses", " taverns" and "inns". By Georgian times, the term had become common parlance, although taverns, as a distinct establishment, had largely ceased to exist by the beginning of the 19th century. Today, there is no strict definition, but CAMRA states a pub has four characteristics:GLA Economics, Closing time: London's public houses, 2017 # is open to the public without membership or residency # serves draught beer or cider without requiring food be consumed # has at least one indoor area not laid out for meals # allows drinks to be bought at a bar (i.e., not only table service) The history of pubs can be traced to Roman taverns in B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridgeshire
Cambridgeshire (abbreviated Cambs.) is a Counties of England, county in the East of England, bordering Lincolnshire to the north, Norfolk to the north-east, Suffolk to the east, Essex and Hertfordshire to the south, and Bedfordshire and Northamptonshire to the west. The city of Cambridge is the county town. Following the Local Government Act 1972 restructuring, modern Cambridgeshire was formed in 1974 through the amalgamation of two administrative counties: Cambridgeshire and Isle of Ely, comprising the Historic counties of England, historic county of Cambridgeshire (including the Isle of Ely); and Huntingdon and Peterborough, comprising the historic county of Huntingdonshire and the Soke of Peterborough, historically part of Northamptonshire. Cambridgeshire contains most of the region known as Silicon Fen. The county is now divided between Cambridgeshire County Council and Peterborough City Council, which since 1998 has formed a separate Unitary authorities of England, unita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halfpenny (British Pre-decimal Coin)
The British pre-decimal halfpenny, (pronounced ), historically also known as the obol and once abbreviated ''ob.'' (from the Latin 'obulus'), was a denomination of sterling coinage worth of one pound, of one shilling, or of one penny. Originally the halfpenny was minted in copper, but after 1860 it was minted in bronze. In the run-up to decimalisation it ceased to be legal tender from 31 July 1969. The halfpenny featured two different designs on its reverse during its years in circulation. From 1672 until 1936 the image of Britannia appeared on the reverse, and from 1937 onwards the image of the Golden Hind appeared. Like all British coinage, it bore the portrait of the monarch on the obverse. "Halfpenny" was colloquially written ''ha’penny'', and "''d''" was spoken as "a penny ha’penny" or ''three ha’pence'' . "Halfpenny" is a rare example of a word in the English language that has a silent ' f'. Before Decimal Day in 1971, sterling used the Carolingian mon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penny
A penny is a coin ( pennies) or a unit of currency (pl. pence) in various countries. Borrowed from the Carolingian denarius (hence its former abbreviation d.), it is usually the smallest denomination within a currency system. Presently, it is the formal name of the British penny ( p) and the ''de facto'' name of the American one-cent coin (abbr. ¢) as well as the informal Irish designation of the 1 cent euro coin (abbr. c). It is the informal name of the cent unit of account in Canada, although one-cent coins are no longer minted there. The name is used in reference to various historical currencies, also derived from the Carolingian system, such as the French denier and the German pfennig. It may also be informally used to refer to any similar smallest-denomination coin, such as the euro cent or Chinese fen. The Carolingian penny was originally a 0.940-fine silver coin, weighing pound. It was adopted by Offa of Mercia and other English kings and rem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)




.jpg)