|
Cavaquinho
The cavaquinho (pronounced in Portuguese) is a small Portuguese string instrument in the European guitar family, with four wires or gut strings. More broadly, ''cavaquinho'' is the name of a four-stringed subdivision of the lute family of instruments. A cavaquinho player is called a ''cavaquista''. Forms There are several forms of cavaquinho used in different regions and for different styles of music. Separate varieties are named for Portugal, Braga (''braguinha''), Minho (''minhoto''), Lisbon, Madeira, Brazil, and Cape Verde; other forms are the ''braguinha'', ‘''cavacolele''’, cavaco, machete, and ukulele. Portuguese The Venezuelan concert cuatro is very nearly the same instrument, but somewhat larger. Cavaquinho Brasileiro, cavaco, and cuatro The Brazilian cavaquinho is slightly larger than the Portuguese cavaquinho, resembling a small classical guitar. Its neck is raised above the level of the sound box, and the sound hole is usually round, like cavaquinhos from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
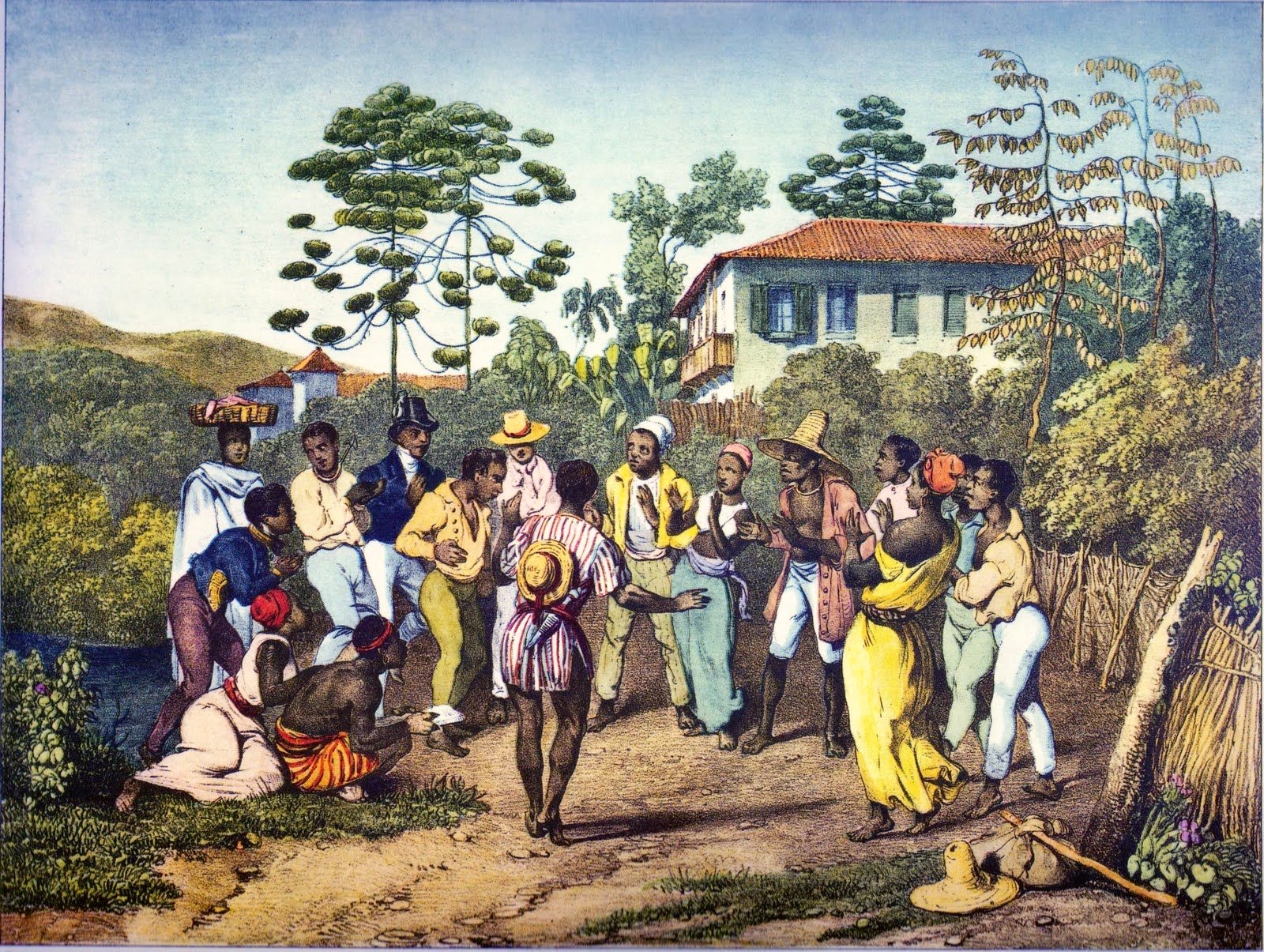
Samba
Samba (), also known as samba urbano carioca (''urban Carioca samba'') or simply samba carioca (''Carioca samba''), is a Brazilian music genre that originated in the Afro-Brazilian communities of Rio de Janeiro in the early 20th century. Having its roots in Brazilian folk traditions, especially those linked to the primitive rural samba of the colonial and imperial periods, it is considered one of the most important cultural phenomena in Brazil and one of the country's symbols. Present in the Portuguese language at least since the 19th century, the word "samba" was originally used to designate a "popular dance". Over time, its meaning has been extended to a "batuque-like circle dance", a dance style, and also to a "music genre". This process of establishing itself as a musical genre began in the 1910s and it had its inaugural landmark in the song " Pelo Telefone", launched in 1917. Despite being identified by its creators, the public, and the Brazilian music industry as "samba", ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samba Cavaco
Samba (), also known as samba urbano carioca (''urban Carioca samba'') or simply samba carioca (''Carioca samba''), is a Brazilian music genre that originated in the Afro-Brazilians, Afro-Brazilian communities of Rio de Janeiro in the early 20th century. Having its roots in Brazilian mythology, Brazilian folk traditions, especially those linked to the primitive rural samba of the Colonial Brazil, colonial and Empire of Brazil, imperial periods, it is considered one of the most important cultural phenomena in Brazil and one of the country's symbols. Present in the Portuguese language at least since the 19th century, the word "samba" was originally used to designate a "popular dance". Over time, its meaning has been extended to a "batuque-like circle dance", a Samba (Brazilian dance), dance style, and also to a "music genre". This process of establishing itself as a musical genre began in the 1910s and it had its inaugural landmark in the song ":pt:Pelo Telefone, Pelo Telefone", l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuatro (Venezuela)
The cuatro of Venezuela has four single nylon strings, tuned (ad'f#'b). It is similar in shape and tuning to the ukulele, but their character and playing technique are vastly different. It is tuned in a similar fashion to the traditional D tuning of the ukulele, but the A and B are an octave lower. Consequently, the same fingering can be used to shape the chords, but it produces a different inversion of each chord. A cuatro player is called a ''cuatrista''. History The predecessor of the Venezuelan cuatro is the four-string Spanish renaissance guitar which disappeared in the 16th century after a short period of surging popularity. In the 1950s, Fredy Reyna documented the evolution of the renaissance guitar into the current Venezuelan Cuatro, and reinvented the cuatro as a solo instrument, equally capable of rendering traditional Venezuelan music as well as Renaissance pieces. The popularity of the instrument in Venezuela and elsewhere may be due to its apparent simplicity, hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viola Braguesa
Viola braguesa is a stringed instrument from Braga, north-western Portugal. It has 10 strings in 5 courses. The strings are made of steel. It is tuned C4/C3–G4/G3–A4/A3–D4/D4–G4/G4. The scale length is about . Requinta Many , such as the Viola braguesa, have smaller requinto versions also, called 'requinta'. The viola braguesa requinta is tuned: A4/A3–C5/C4–F5/F4–C5/C5–E5/E5. This tuning is a fifth above the standard Viola braguesa. See also * Viola caipira * Cavaquinho * Bandolim * Guitarra portuguesa The Portuguese guitar or Portuguese guitarra ( pt, guitarra portuguesa, ) is a plucked string instrument with twelve steel strings, strung in six course (music), courses of two strings. It is one of the few musical instruments that still uses wat ... References External links The Stringed Instrument DatabaseATLAS of Plucked Instruments String instruments Portuguese musical instruments {{viola-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuatro (instrument)
The cuatro is a family of Latin American string instruments played in Puerto Rico, Venezuela and other Latin American countries. It is derived from the Spanish guitar. Although some have viola-like shapes, most cuatros resemble a small to mid-sized classical guitar. In Puerto Rico and Venezuela, the cuatro is an ensemble instrument for secular and religious music, and is played at parties and traditional gatherings. Cuatro means ''four'' in Spanish; the instrument's 15th century predecessors were the Spanish vihuela and the Portuguese cavaquinho, the latter having four strings like the cuatro. Modern cuatros come a variety of sizes and shapes, and number of strings. Cuatros can either have single-strings, like a guitar, or double- or triple-coursed strings like a mandolin, and vary in size from a large mandolin or small guitar, to the size of a full-size guitar. Depending on their particular stringing, cuatros are part of the guitar or mandolin subfamilies of the lute fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viola Braguesa
Viola braguesa is a stringed instrument from Braga, north-western Portugal. It has 10 strings in 5 courses. The strings are made of steel. It is tuned C4/C3–G4/G3–A4/A3–D4/D4–G4/G4. The scale length is about . Requinta Many , such as the Viola braguesa, have smaller requinto versions also, called 'requinta'. The viola braguesa requinta is tuned: A4/A3–C5/C4–F5/F4–C5/C5–E5/E5. This tuning is a fifth above the standard Viola braguesa. See also * Viola caipira * Cavaquinho * Bandolim * Guitarra portuguesa The Portuguese guitar or Portuguese guitarra ( pt, guitarra portuguesa, ) is a plucked string instrument with twelve steel strings, strung in six course (music), courses of two strings. It is one of the few musical instruments that still uses wat ... References External links The Stringed Instrument DatabaseATLAS of Plucked Instruments String instruments Portuguese musical instruments {{viola-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machete (musical Instrument)
file:Machette kos.pg.jpg, Older machete from Latin America file:Gerber Machete.jpg, Gerber Legendary Blades, Gerber machete/saw combo file:Agustín Cruz Tinoco working.jpg, Agustín Cruz Tinoco of San Agustín de las Juntas, Oaxaca uses a machete to carve wood. file:Mexican machete.JPG, Mexican machete, from Acapulco, 1970. Horn handle, hand forged blade (hammer marks visible). A machete (; ) is a broad blade used either as an agricultural implement similar to an axe, or in combat like a long-bladed knife. The blade is typically long and usually under thick. In the Spanish language, the word is possibly a diminutive form of the word ''macho'', which was used to refer to sledgehammers. Alternatively, its origin may be ''machaera'', the name given by the Romans to the falcata. It is the origin of the English language equivalent term ''matchet'', though it is less commonly used. In much of the English-speaking Caribbean, such as Jamaica, Barbados, Guyana, Grenada, and Trinidad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guitar
The guitar is a fretted musical instrument that typically has six strings. It is usually held flat against the player's body and played by strumming or plucking the strings with the dominant hand, while simultaneously pressing selected strings against frets with the fingers of the opposite hand. A plectrum or individual finger picks may also be used to strike the strings. The sound of the guitar is projected either acoustically, by means of a resonant chamber on the instrument, or amplified by an electronic pickup and an amplifier. The guitar is classified as a chordophone – meaning the sound is produced by a vibrating string stretched between two fixed points. Historically, a guitar was constructed from wood with its strings made of catgut. Steel guitar strings were introduced near the end of the nineteenth century in the United States; nylon strings came in the 1940s. The guitar's ancestors include the gittern, the vihuela, the four- course Renaissance guitar, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neck (music)
The neck is the part of certain string instruments that projects from the main body and is the base of the fingerboard, where the fingers are placed to stop the strings at different pitches. Guitars, banjos, ukuleles, lutes, the violin family, and the mandolin family are examples of instruments which have necks. Necks are also an integral part of certain woodwind instruments, like for instance the saxophone. The word for neck also sometimes appears in other languages in musical instructions. The terms include ''manche'' (French), ''manico'' (Italian), and ''Hals'' (German). Guitar The neck of a guitar includes the guitar's frets, fretboard, tuners, headstock, and truss rod. The wood used to make the fretboard will usually differ from the wood in the rest of the neck. The bending stress on the neck is considerable, particularly when heavier gauge strings are used (see Strings and tuning), and the ability of the neck to resist bending (see Truss rod) is important to the gu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
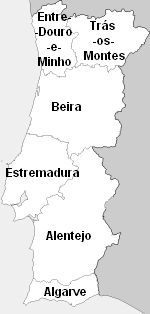
Entre-Douro-e-Minho Province
Entre Douro e Minho () is one of the historical provinces of Portugal which encompassed the country's northern Atlantic seaboard between the Douro and Minho rivers. Contemporaries often referred to the province as simply "Minho". It was one of six provinces Portugal was commonly divided into from the early modern period until 1936, although these provinces were not recognized as official units of government. Geography The coastline of Entre Minho e Douro is level and unbroken except by the estuaries of the main rivers; inland, the elevation gradually increases towards the north and east, where several mountain ranges mark the frontier. Of these, the most important are the Serra da Peneda (), between the rivers Minho and Lima; the Serra do Gerez (), on the Galician border; the Serra da Cabreira (), immediately to the south; and the Serra do Marão (), in the extreme south-east. As its name implies, the province is bounded by two rivers, the Douro on the south, and the Minho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machete
Older machete from Latin America Gerber machete/saw combo Agustín Cruz Tinoco of San Agustín de las Juntas, Oaxaca">San_Agustín_de_las_Juntas.html" ;"title="Agustín Cruz Tinoco of San Agustín de las Juntas">Agustín Cruz Tinoco of San Agustín de las Juntas, Oaxaca uses a machete to carve wood. file:Mexican machete.JPG, Mexican machete, from Acapulco, 1970. Horn handle, hand forged blade (hammer marks visible). A machete (; ) is a broad blade used either as an agricultural implement similar to an axe, or in combat like a long-bladed knife. The blade is typically long and usually under thick. In the Spanish language, the word is possibly a diminutive form of the word ''macho'', which was used to refer to sledgehammers. Alternatively, its origin may be ''machaera'', the name given by the Romans to the falcata. It is the origin of the English language equivalent term ''matchet'', though it is less commonly used. In much of the English-speaking Caribbean, such as Jamai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portuguese (language)
Portuguese ( or, in full, ) is a western Romance languages, Romance language of the Indo-European language family, originating in the Iberian Peninsula of Europe. It is an official language of Portugal, Brazil, Cape Verde, Angola, Mozambique, Guinea-Bissau and São Tomé and Príncipe, while having co-official language status in East Timor, Equatorial Guinea, and Macau. A Portuguese-speaking person or nation is referred to as "Lusophone" (). As the result of expansion during colonial times, a cultural presence of Portuguese speakers is also found around the world. Portuguese is part of the Iberian Romance languages, Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several dialects of Vulgar Latin in the medieval Kingdom of Galicia and the County of Portugal, and has kept some Gallaecian language, Celtic phonology in its lexicon. With approximately 250 million native speakers and 24 million L2 (second language) speakers, Portuguese has approximately 274 million total speakers. It is usual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |