|
Catena (geology)
A crater chain is a line of craters along the surface of an astronomical body. The descriptor term for crater chains is catena , plural catenae (Latin for "chain"), as specified by the International Astronomical Union's rules on planetary nomenclature. Many examples of such chains are thought to have been formed by the impact of a body that was broken up by tidal forces into a string of smaller objects following roughly the same orbit. An example of such a tidally disrupted body that was observed prior to its impact on Jupiter is Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9. During the Voyager observations of the Jupiter system, planetary scientists identified 13 crater chains on Callisto and three on Ganymede (except those formed by secondary craters). Later some of these chains turned out to be secondary or tectonic features, but some other chains were discovered. As of 1996, 8 primary chains on Callisto and 3 on Ganymede were confirmed. Other cases, such as many of those on Mars, represent chai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawaii Volcanoes National Park
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only state geographically located within the tropics. Hawaii comprises nearly the entire Hawaiian archipelago, 137 volcanic islands spanning that are physiographically and ethnologically part of the Polynesian subregion of Oceania. The state's ocean coastline is consequently the fourth-longest in the U.S., at about . The eight main islands, from northwest to southeast, are Niihau, Kauai, Oahu, Molokai, Lānai, Kahoolawe, Maui, and Hawaii—the last of these, after which the state is named, is often called the "Big Island" or "Hawaii Island" to avoid confusion with the state or archipelago. The uninhabited Northwestern Hawaiian Islands make up most of the Papahānaumokuākea Marine National Monument, the United States' largest protected area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of Australia). The Moon is a planetary-mass object with a differentiated rocky body, making it a satellite planet under the geophysical definitions of the term and larger than all known dwarf planets of the Solar System. It lacks any significant atmosphere, hydrosphere, or magnetic field. Its surface gravity is about one-sixth of Earth's at , with Jupiter's moon Io being the only satellite in the Solar System known to have a higher surface gravity and density. The Moon orbits Earth at an average distance of , or about 30 times Earth's diameter. Its gravitational influence is the main driver of Earth's tides and very slowly lengthens Earth's day. The Moon's orbit around Earth has a sidereal period of 27.3 days. During each synodic period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neptune
Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun and the farthest known planet in the Solar System. It is the fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 times the mass of Earth, and slightly more massive than its near-twin Uranus. Neptune is denser and physically smaller than Uranus because its greater mass causes more gravitational compression of its atmosphere. It is referred to as one of the solar system's two ice giant planets (the other one being Uranus). Being composed primarily of gases and liquids, it has no well-defined "solid surface". The planet orbits the Sun once every 164.8 julian year (astronomy), years at an average distance of . It is named after the Neptune (mythology), Roman god of the sea and has the astronomical symbol , representing Neptune's trident. Neptune is not visible to the unaided eye and is the only planet in the Solar System found by mathematical prediction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Geological Features On Dione
This is a list of named geological features on Dione, a moon of Saturn. Dionean geological features are named after people and places in Roman mythology. Catenae Catenae are crater chains. They are named after rivers in Roman mythology. Chasmata Dionean chasms or canyons are called chasmata . They are named after important locations in Roman mythology and history. Dorsa Dionean ridges are called dorsa. They are named after Roman hills. Fossae Dionean fossae (long narrow depressions) are named after cities, streets and rivers in Roman mythology. Lineae Originally, three geological features were labelled lineae (bright wispy markings). However, later evidence from the '' Cassini'' probe revealed them to be icy chasms, and they were all renamed as such (see above). Craters Dionean craters are named after figures from Greek and Roman mythology, especially Virgil's '' The Aeneid''. See also *List of quadrangles on Dione External links USGS: Dione nome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Geological Features On Rhea
This is a list of named geological features on Rhea, the second largest moon of Saturn. Planetary features are approved by the International Astronomical Union's (IAU) Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature (WGPSN). Catenae A ''catena'' is a crater chain. Chasmata Rhean chasms are called chasmata. They are named after sacred places in world mythologies. Craters Rhean craters are named after figures from the mythologies of mostly non-European cultures. As of 2017, there are 128 named craters. back to top Fossae A fossa is a long, narrow depression. Lineae A linea is a long marking on a planet or moon's surface. See also * List of craters in the Solar System * List of quadrangles on Rhea References External links USGS: Rhea nomenclature {{DEFAULTSORT:List Of Geological Features On Rhea Rhea (moon) Rhea (moon) Rhea () is the second-largest moon of Saturn and the ninth-largest moon in the Solar System. It is the smalles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; however, with its larger volume, Saturn is over 95 times more massive. Saturn's interior is most likely composed of a core of iron–nickel and rock (silicon and oxygen compounds). Its core is surrounded by a deep layer of metallic hydrogen, an intermediate layer of liquid hydrogen and liquid helium, and finally, a gaseous outer layer. Saturn has a pale yellow hue due to ammonia crystals in its upper atmosphere. An electrical current within the metallic hydrogen layer is thought to give rise to Saturn's planetary magnetic field, which is weaker than Earth's, but which has a magnetic moment 580 times that of Earth due to Saturn's larger size. Saturn's magnetic field strength is around one-twentieth of Jupiter's. The outer atmosphere is g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Geological Features On Io
This is a list of named geological features on Io, a moon of Jupiter. See also the list of mountains on Io and the list of paterae on Io. Eruptive Centers Eruptive centers on Io, locations typically where major volcanic activity was observed and characterized before the volcanic landform was, are named after the gods of volcanoes and/or blacksmiths in various mythologies. Catenae On Io, catenae (crater chains, sg. ''catena'') are named after sun gods in various mythologies. In 2006, the use of the term ''catena'' was discontinued in favor of the '' patera'' (plural ''paterae'' ). Below is a list of features that previously used the descriptor term ''catena''. Fluctūs Ionian fluctus (areas of lava flow)Latin sg. ''fluctus'' and pl. ''fluctūs'' are spelled and pronounced the same in English are named after fire and thunder gods in various mythologies, or after locations in Greek mythology associated with Io. Mensae Ionian mensae (mesas, sg. ''mensa'') are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Geological Features On Ganymede
This is a list of named geological features, except craters, on Ganymede, a moon of Jupiter. The list is complete as of August 2022. Catenae (crater chains) Faculae Fossae (ditches) Paterae Regiones Sulci See also * List of quadrangles on Ganymede * List of craters on Ganymede ReferencesList of named surface features on Ganymede {{Surface features of space objects * Ganymede Ganymede (moon) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Geological Features On Callisto
This is a list of named geological features on Callisto, a moon of Jupiter. This list is complete as of August 2022. Catenae Callistoan catenae ( crater chains) are named after rivers, valleys, and ravines in myths and folktales of cultures of the Far North (all current names come from Norse mythology Norse, Nordic, or Scandinavian mythology is the body of myths belonging to the North Germanic peoples, stemming from Old Norse religion and continuing after the Christianization of Scandinavia, and into the Nordic folklore of the modern period ...). Craters Faculae Faculae (bright spots) on Callisto are named after characters related to frost, snow, cold, and sleet from myths and folktales of people of the Far North. Large ring features The enormous impact-related ring features on Callisto are named after places (other than rivers, valleys and ravines) from myths and folktales of the Far North. References External links USGS, IAU: Callisto nomenclature {{Sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
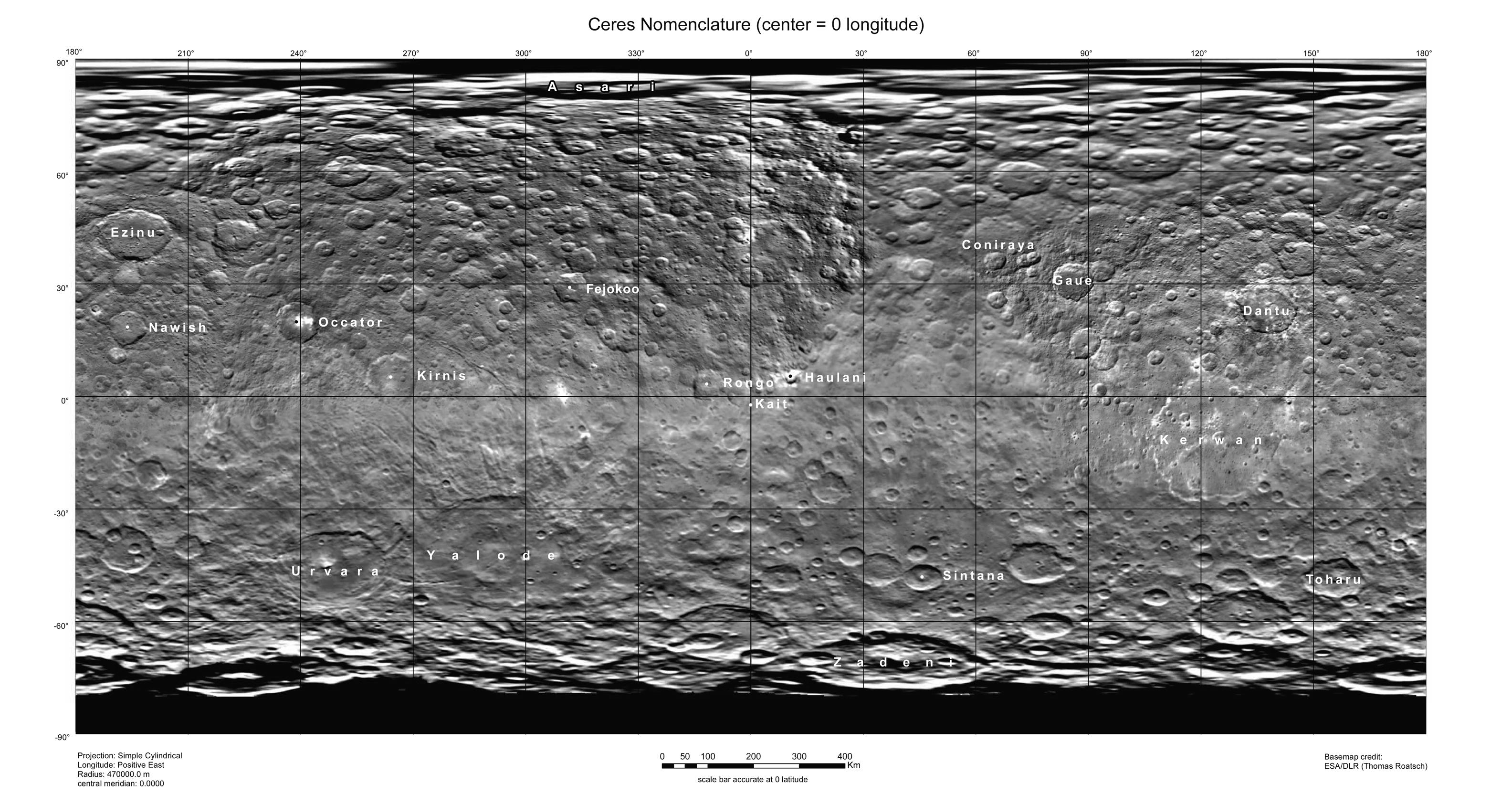
List Of Geological Features On Ceres
Ceres is a dwarf planet in the asteroid belt that lies between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. The IAU has adopted two themes for naming surface features on Ceres: agricultural deities for craters and agricultural festivals for everything else. As of 2020, the IAU has approved names for 151 geological features on Ceres: craters, montes, catenae, rupēs, plana, tholi, planitiae, fossae and sulci. In July 2018, NASA released a comparison of physical features found on Ceres with similar ones present on Earth. ''Piazzi'', named after Giuseppe Piazzi, the discoverer of Ceres, is a dark region southwest of Dantu crater Dantu is a large crater on Ceres, located within the Vendimia Planitia. It is rimmed by a number of minor faculae, which together form Bright Spot 2. Etymology The crater is named after ''Dantu'', the timekeeper and first god of planting (mil ... in ground-based images that was named before '' Dawn'' arrived at Ceres. Overview of features Catenae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceres (dwarf Planet)
Ceres (; minor-planet designation: 1 Ceres) is a dwarf planet in the asteroid belt between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. It was the first asteroid discovered, on 1 January 1801, by Giuseppe Piazzi at Palermo Astronomical Observatory in Sicily and announced as a new planet. Ceres was later classified as an asteroid and then a dwarf planetthe only one always inside Neptune's orbit. Ceres's small size means that even at its brightest, it is too dim to be seen by the naked eye, except under extremely dark skies. Its apparent magnitude ranges from 6.7 to 9.3, peaking at opposition (when it is closest to Earth) once every 15- to 16-month synodic period. As a result, its surface features are barely visible even with the most powerful telescopes, and little was known about it until the robotic NASA spacecraft ''Dawn'' approached Ceres for its orbital mission in 2015. ''Dawn'' found Ceres's surface to be a mixture of water ice, and hydrated minerals such as carbonates and clay. Gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Catenae On Mars
This is a list of named catenae on Mars. In planetary geology, a catena is a chain of similarly sized craters. On Mars, they are named after nearby classical albedo features as prescribed by the International Astronomical Union's rules for planetary nomenclature. While catenae on most bodies of the Solar System consist of mainly of impact craters, those on Mars consist primarily of collapse pits. References *This article was adapted from thGazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature See also *List of craters on Mars __NOTOC__ This is a list of craters on Mars. Impact craters on Mars larger than exist by the hundreds of thousands, but only about one thousand of them have names. Names are assigned by the International Astronomical Union after petitioning by ... {{Portal bar, Solar System * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |